Introduction
This article demonstrates how easy it is to handle exceptions in Microsoft BizTalk Server 2009 view them using ESB Toolkit 2.0 (ESB Portal).
Use Case: Purchase Order Processing
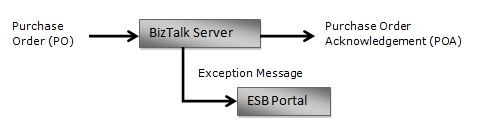
Consider a simple scenario where a Purchase Order (PO) needs to be processed and PO acknowledgement needs to be generated. An exception needs to be raised in the case where the PO amount (POAmt) is less than or equal to zero.
How Does BizTalk ESB Toolkit Help Us?
It provides a building block for handling exceptions and viewing failed message(s) through the use of the ESB Portal.
How Do I Code An Orchestration to Send Fault Messages to ESB Portal?
Add the following references to your orchestration:
Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.Schemas.Faults
Step 1: Determine the Scenarios where Exception Needs to be Handled
In order to effectively handle exceptions, brainstorm all the scenarios where exceptions are required to be handled.
Place a "Scope" shape around the points where exceptions need to be handled.
Step 2: Handle the Exception and Send the Fault Message
Create a fault message of type "Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.Schemas.Faults.FaultMessage", in the example I have used a multipart message for brevity.
Set the Fault message properties in a thoughtful manner.
FaultMsg = Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.ExceptionMgmt.CreateFaultMessage();
FaultMsg.ESBFault.FailureCategory = "POFaults";
FaultMsg.ESBFault.Scope = "local";
FaultMsg.ESBFault.FaultCode = "InvalidPO";
FaultMsg.ESBFault.FaultDescription =
"This PO is invalid. See the error for more details.";
FaultMsg.ESBFault.FaultSeverity =
Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.FaultSeverity.Severe;
Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.ExceptionMgmt.AddMessage(FaultMsg, POMsg);
Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.ExceptionMgmt.AddMessage(FaultMsg, POAMsg);
Notice that each message, in this case PO and POA messages are added to the Fault message, this will help to view the incoming and outgoing messages using the ESB Portal.

Finally, a direct bound send port is used to write this fault message to the message box.
ESB Portal
The screen shots illustrate the various views of ESB Portal:


What Else Can Be Done Using the ESB Exception Handling Framework?
Step 1: Develop a custom exception handler orchestration with a filter on the activatable receive shape set as:
(Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.Schemas.Property.FaultCode == "InvalidPO")
This will enable all the Fault messages to be routed to the custom orchestration from the message box and an appropriate action can be taken.
Step 2: Retrieve all the messages in a fault message using the code below.
Declare a variable of type "Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.MessageCollection" and assign the variable to the code shown below:
Microsoft.Practices.ESB.ExceptionHandling.ExceptionMgmt.GetMessages(FaultMsg);
What Can You Do with the Built-in Exception Handling Web Service in the ESB Toolkit?
Any .NET application which is not a part of BizTalk can be used to submit "Fault" messages to the Exception Handling Web Service.
Find this web service installed at "http://localhost/ESB.ExceptionHandlingServices/ExceptionHandling.asmx". Note that a WCF flavor of this web service is also provided by the default installation.
The final task would be to generate a Fault message by referencing the web service in your .NET application and submitting this Fault message using the web method "SubmitFault".
Downloadable Sample Code
BizTalk Server 2009, Visual Studio 2008 and ESB Toolkit 2.0 has been used for this sample.
References
