Introduction
This is my first article on internet and I have tried my best to explain the things, shared my knowledge and want your comments to make the things much better.
This article is for beginner level. If you have already a good knowledge of Object-Oriented (OO) concepts then its make your knowledge in same stage. Here I have tried to explain about what is problem in Procedure Oriented (PO) Language how it overcome by OO Language and Brief Introduction and examples of Fundamental concepts of OO.I have not targeted any specific language so it is for all kind of OO learner.
Procedure-Oriented (PO) Language:
PO Language is fully concentrates on Procedures/functions/methods. It normally works as a sequence of actions as seen in flowchart or in any algorithm. It follows top-down approach. It totally focuses on methods and not the data which is utilized by methods.
In PO languages if data is used by many methods then its declared as global data but there is a problem if we do that, what is that, if we forgot or by mistake if we consume that data in some other method than it comes with problem. Mostly these scenarios happen in large systems.
Example: COBOL, PASCAL, C, FORTRAN etc.
Object-Oriented (OO) Language:
In PO programs the data is freely moving around the system and due to which there are chances of problem in system. So this problem is overcome by OO programs.OO concepts says it think about data and bind that data and methods those are manipulating that data into one entity known as object and then utilize that object into system.
Example: C++, Java, C#, VB.Net etc.
There are some fundamental concepts of OO Language which a language has to follow to be a truly OO language.
• OBJECT
• CLASS
• ABSTRACTION
• ENCAPSULATION
• DATA HIDING / INFORMATION HIDING
• INHERITANCE
• POLYMORPHISM
Lets take a brief look into these concepts.
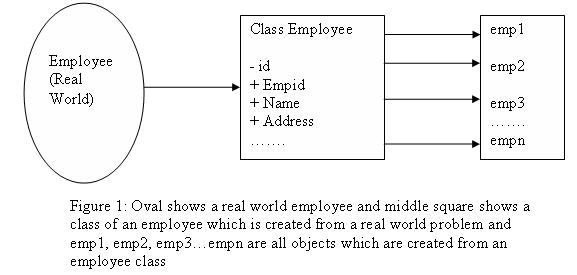
Objects: Object represent real world entity into a program. for example an employee which is real world entity we can make an object of it and then utilize it in a program with its behaviors and actions.
Some other common definitions
1. Object is an instance of a class.
2. Object is a variable of user defined type / abstract data type.
Class: Class represent template for an object. It actually contains data and there behavior / methods in it and for utilization of it we need to create an object of that particular class. we can create n number of object with one class.
Some other common definitions
1. A collection of data and code to handle that data.
2. Class is a user defined type / abstract data type.
3. Class defines basic layout and functionality of an object.
Abstraction: To implement real world entity into program. Class uses the concept of abstraction.
Some other common definitions
1. Abstraction is a process of mimicking a behavior.
2. Simplifying complex reality by modeling classes appropriate to problem.
3. Abstraction is a process that involves identifying the crucial behavior of an object and eliminating irrelevant and tedious details.
Encapsulation: Binding the data and code to access that data. Encapsulation only refers to a container which has a data and its related functions in it.
Some other common definitions
1. When an objects state and behavior are kept together they are encapsulated. The data and the methods that manipulated that data are stored together in cohesive unit.
Data Hiding / Information Hiding: As encapsulation bind data and methods together, data hiding restrict sensitive data accessing to the system. It is also achieved by using access modifiers i.e. Private, Protected and Public.
In Figure 1 you can see in class Employee that there are notations minus(-) and Plus(+) they represents access modifier, minus sign restrict access outside the class and plus sign gives access outside the class.
Some other common definitions
1. Insulation of data from direct access by the program.
Inheritance: Defining new classes from the existing one. The new class will get all the methods and properties of the existing class.
The new class known as sub class / child class / derived class.
The existing class known as super class / parent class / base class.
Inheritance is implied by “is-a” or “kind-of” relationship.
Inheritance is basically used for reuse the code and focus to make generic kind of thing rather than specific one.
Some other common definitions
1. An object can acquire the properties of another object.

Polymorphism: Ability to acquire different forms. There are basically two types of polymorphism. Compile Time (also knows as Early binding) and Run Time (also knows as Late binding) Polymorphism.
In Compile Time Polymorphism Object knows about itself at compile time. Overloading is a compile time polymorphism. In Overloading method should have same name with different arguments. Simple example of overloading is if you have scenario in which you want do Sum of two or three number what ever user will pass. So you can create two methods with same name “sum” and assign 2 and 3 arguments into it.
In Run Time Polymorphism, Object does not know about itself at compile time it assigns all the properties and methods at runtime. Overriding or inheritance-based polymorphism are kind of polymorphism. Simple and very common example I am talking about is if you have a class shape which is inherited to Triangle, Square and Circle classes. Shape class has a method name as “Draw” which will definitely inherited to all inherited class. Now, if you declare a variable of shape class and initialize it with any of the inherited class it will call the method of inherited class.
Some other common definitions
1. One name many forms.
2. One interface multiple methods / ways.
