Introduction
Often need arises to migrate data between different environments for testing or audit purposes. For example, production data can be moved to test environment and this data can be used by testers. This gives a clear idea of how programs behave on actual data volumes. Using this utility, data can be migrated with ease of use. I used SqlBulkCopy of ADO.NET 2.0 for bulk copying data. This managed class provides similar functionality as the BCP utiltity. This program has been used successfully on large volumes of data. It took me approximately 1 hour for loading 8GB of data. More precisely, for loading 1.1 million records, it took 4 minutes and 30 seconds. It supports both SQL 2005 and SQL 2000 Servers. The available features are:
- Specific tables can be selected for migrating data
- Deletes existing data in selected tables<o:p>
- Reports progress as it loads data<o:p>
- Logs results of load or delete operations for every table<o:p>
- Can be cancelled in the middle of a process; the application stops loading data after finishing the current table.
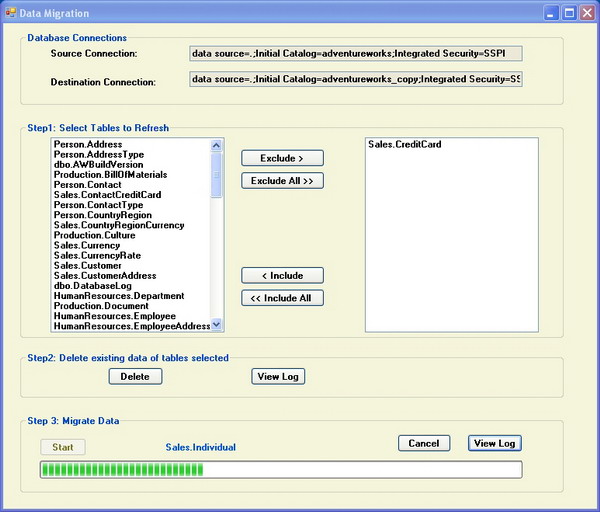
Solution walkthrough
This solution contains a C# Windows Forms project. This is a very simple project. A Windows Form does all the work. It uses the BackgroundWorker component to report progress. The source and destination connections are defined in the application configuration file. If any exception happens while deleting or loading data in a table, the application logs the exception and continues to process the next table.
The two main functions in this application are DeleteData and LoadData.
DeleteData
The following tasks are involved in this function:
- Disable constraints on all tables.
- Disable triggers on all tables.
- Delete data from a table (
DELETE or TRUNCATE statement used depending on the foreign key constraints on a table).
- Log results.
- Enable constraints on all tables.
- Enable triggers on all tables.
private void DeleteData()
{
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(strDestConn))
{
conn.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = conn.CreateCommand();
cmd.CommandTimeout = 0;
if (ds != null && ds.Tables[0].Rows.Count > 0)
{
foreach (DataRow dr in ds.Tables[0].Rows)
{
cmd.CommandText = "ALTER TABLE [" +
dr["TABLE_SCHEMA"].ToString() + "].[" +
dr["TABLE_NAME"].ToString() +
"] NOCHECK CONSTRAINT ALL";
cmd.CommandText += " ALTER TABLE [" +
dr["TABLE_SCHEMA"].ToString() + "].[" +
dr["TABLE_NAME"].ToString() +
"] DISABLE TRIGGER ALL";
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
string strLogFile = "DeleteLog" +
DateTime.Now.ToString("MMddyyyyHHmm") + ".txt";
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(strLogFile, false))
{
sw.AutoFlush = true;
foreach (object dr in lstInclude.Items)
{
try
{
cmd.CommandText =
"SELECT OBJECTPROPERTY ( object_id('" +
dr.ToString() + "'),'TableHasForeignRef')";
int intref = Convert.ToInt32(cmd.ExecuteScalar());
if (intref == 1)
cmd.CommandText = "DELETE FROM " + dr.ToString();
else
cmd.CommandText = "TRUNCATE TABLE " +
dr.ToString();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
sw.WriteLine("Data deleted successfully from " +
dr.ToString() + " at " +
DateTime.Now.ToString());
sw.WriteLine();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
sw.WriteLine("Error while deleting data" +
" in table " + dr.ToString() +
".Error is " + ex.Message);
sw.WriteLine();
}
}
}
foreach (DataRow dr in ds.Tables[0].Rows)
{
cmd.CommandText = "ALTER TABLE [" +
dr["TABLE_SCHEMA"].ToString() + "].[" +
dr["TABLE_NAME"].ToString() +
"] CHECK CONSTRAINT ALL";
cmd.CommandText += " ALTER TABLE [" +
dr["TABLE_SCHEMA"].ToString() + "].[" +
dr["TABLE_NAME"].ToString() +
"] ENABLE TRIGGER ALL";
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
}
LoadData
The following tasks are involved in this function:
- Load data from the source table using a SQL data reader.
- Create SqlBulkCopy with
KeepIdentity and TableLock options. A lock on the table makes the loading process quicker. By default, SqlBulkCopy disables constraints and triggers on a table while loading data.
- Map source and table columns. This is necessary if the column ordinal positions are different between the two environments.
- Eliminate computed columns while mapping columns.
- Bulk insert data in a table by passing the datareader to SqlBulkCopy.
private void LoadData(string pSourceConn,string pDestConn,string pTable)
{
using (SqlConnection srcConn = new SqlConnection(pSourceConn))
{
string[] strTable = pTable.Split('.');
srcConn.Open();
SqlCommand srcCommand = new SqlCommand("SELECT * FROM " +
pTable, srcConn);
srcCommand.CommandTimeout = 0;
SqlDataReader sqldr = srcCommand.ExecuteReader();
SqlBulkCopy sqlbcp = new SqlBulkCopy(pDestConn,
SqlBulkCopyOptions.KeepIdentity |
SqlBulkCopyOptions.TableLock);
SqlConnection destConn = new SqlConnection(pDestConn);
destConn.Open();
SqlCommand cmd1 = new SqlCommand("SELECT COLUMN_NAME," +
"COLUMNPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID('" +
strTable[0] +"." +strTable[1]+
"'),COLUMN_NAME,'IsComputed')AS 'IsComputed' " +
"FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS " +
"WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = '" +
strTable[0] + "' AND TABLE_NAME = '" +
strTable[1] + "'", destConn);
SqlDataReader drcolumns = cmd1.ExecuteReader();
while (drcolumns.Read())
{
if(drcolumns.GetInt32(1) != 1)
sqlbcp.ColumnMappings.Add(drcolumns.GetString(0),
drcolumns.GetString(0));
}
drcolumns.Close();
sqlbcp.BulkCopyTimeout = 0;
sqlbcp.DestinationTableName = pTable;
sqlbcp.WriteToServer(sqldr);
sqldr.Close();
}
}
Conclusion
That's all there is to it. I hope this application helps for migrating your data. This can be customized easily if you want to load data from different data sources (e.g.: XML files, flat files...). Thanks for reading. Please provide me feedback about issues or ways to improve.
