Contents
Introduction
In this Vista Goodies article, I will cover the new TaskDialogIndirect() API, which you can use
to create complex dialogs without needing to build your own dialog resource and write code to handle a lot of controls.
While TaskDialogIndirect() is very complex, the results can be quite impressive, and you'll know that
the dialogs will look right in all Vista themes, and will continue to work in future versions of Windows.
Covering all the features of TaskDialogIndirect() would make this article far too big, so in this
article, I will talk about dialogs that get input from the user when he needs to make a decision. The sample code
presented here is set in the same situation as the previous article on TaskDialog(): our app needs
to know if the user wants to download an update.
This article is written for the RTM version of Vista, using Visual Studio 2005, WTL
7.5, and the
Windows SDK. See the introduction in the first Vista Goodies
article for more information on where you can download those components.
Basic Example of How To Use TaskDialogIndirect
All the task dialog features are controlled by a TASKDIALOGCONFIG struct. Because this is a huge
structure, I will introduce new parts of it over the course of the article as I talk about various features of
the task dialog.
The prototype of TaskDialogIndirect() is:
HRESULT TaskDialogIndirect (
const TASKDIALOGCONFIG* pTaskConfig, int* pnButton,
int* pnRadioButton, BOOL *pfVerificationFlagChecked );
The parameters are:
pTaskConfig- Pointer to a
TASKDIALOGCONFIG struct that you fill in before calling the function. This struct
controls much of the appearance and behavior of the dialog.
pnButton- Pointer to an
int that is set to indicate which button the user clicked to close the dialog. If
the user clicks a built-in button, the value can be one of: IDOK, IDYES, IDNO,
IDCANCEL, IDRETRY, IDCLOSE. If the user clicks a custom button, this value
is set to that button's ID. If the function fails, the value will be set to 0. You can pass NULL for
this parameter if you don't need to know which button was clicked.
pnRadioButton- Pointer to an int that is set to indicate which radio button was selected when the dialog was closed. If the
dialog does not have radio buttons, you can pass
NULL for this parameter.
pfVerificationFlagChecked- Pointer to a
BOOL that indicates the state of the check box when the dialog was closed. If the
dialog does not have a check box, you can pass NULL for this parameter.
The return value is an HRESULT that indicates whether the function succeeds. It can fail if it
is unable to load a resource, or in low-memory conditions.
Let's start by making a task dialog that looks like the one from the previous article:
void CTheApp::OnUpdateAvailable()
{
HRESULT hr;
TASKDIALOGCONFIG tdc = { sizeof(TASKDIALOGCONFIG) };
int nClickedBtn;
LPCWSTR szTitle = L"Mike's AntiFluff Scanner",
szHeader = L"An update for Mike's AntiFluff Scanner is available",
szBodyText = L"Version 2007.1 of Mike's AntiFluff Scanner has been released. " \
L"Do you want to download the update now?";
tdc.hwndParent = m_hWnd;
tdc.dwCommonButtons = TDCBF_YES_BUTTON|TDCBF_NO_BUTTON;
tdc.pszWindowTitle = szTitle;
tdc.pszMainIcon = TD_INFORMATION_ICON;
tdc.pszMainInstruction = szHeader;
tdc.pszContent = szBodyText;
hr = TaskDialogIndirect ( &tdc, &nClickedBtn, NULL, NULL );
if ( SUCCEEDED(hr) && IDYES == nClickedBtn )
{
}
}
As you can see, we indicate the text to show in the dialog by setting members in the TASKDIALOGCONFIG
struct. Not surprisingly, this produces a dialog identical to the one that TaskDialog() shows:
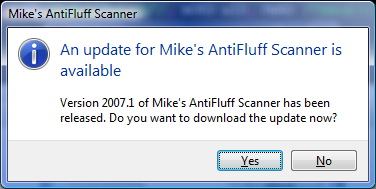
Capabilities of TaskDialogIndirect
In this section, we'll take a quick tour through some of the features you can have in your task dialogs. (Remember
that this article won't cover everything that task dialogs can do.)
I didn't consciously plan it this way, but as I was adding features to the sample task dialog and writing about
them, this section turned into sort of a solo iterative design session. I hope you enjoy this glimpse into what
us UI guys go through when trying to design something that users will actually be able to read and use. :)
The first TASKDIALOGCONFIG member to look at is dwFlags. While many task dialog features
are enabled simply by storing a valid value in a TASKDIALOGCONFIG member, there are some flags that
control the behavior of the dialog or a particular feature. Some flags that you can always set, and that affect
the dialog itself, are:
TDF_ALLOW_DIALOG_CANCELLATION: If this flag is set, the user can close the dialog with Esc and
Alt+F4, even if the dialog does not have a button whose ID is IDCANCEL.
TDF_POSITION_RELATIVE_TO_WINDOW: When this flag is set, the task dialog is centered relative to
the window in hwndParent. Without this flag, the dialog is centered on the monitor that hwndParent
is on.
TDF_CAN_BE_MINIMIZED: If this flag is set, the task dialog can be minimized by right-clicking
the title bar and picking Minimize on the menu. You must also set the TDF_ALLOW_DIALOG_CANCELLATION
flag, or have a button with ID IDCANCEL, for this flag to have an effect. Since a task dialog is always
modal, this flag isn't very useful for prompts that require input.
Flags that control individual features will be mentioned below along with the corresponding features.
Features Also In TaskDialog
These members of TASKDIALOGCONFIG control features that are comparable to the corresponding TaskDialog()
parameters:
hwndParent: The window to use as the task dialog's parent.
hInstance: The HINSTANCE that the API should load resources from.
dwCommonButtons: Which built-in buttons should be shown in the dialog.
pszWindowTitle: The string (or string resource ID) to show in the dialog's title bar.
pszMainIcon: The icon resource ID (or the ID of a built-in icon) to show in the dialog.
pszMainInstruction: The string (or resource ID) to show at the top of the dialog.
pszContent: The string (or resource ID) to show in the body of the dialog.
As with TaskDialog(), any of the strings can be NULL, and you must use the MAKEINTRESOURCE
macro on resource IDs. Also, pszMainInstruction and pszContent can contain '\n'
to create a line break. No flags need to be set for these members to be used.
Buttons with Custom Text
With TaskDialogIndirect(), we're not limited to six pre-defined buttons. We can create any number
of buttons, with any text we like, and even mix them with the pre-defined buttons. Two TASKDIALOGCONFIG
members control these buttons:
pButtons: Pointer to an array of TASKDIALOG_BUTTON structs, one for each button.
cButtons: UINT indicating how many structs are in that array.
TASKDIALOG_BUTTON is a simple struct:
struct TASKDIALOG_BUTTON {
int nButtonID;
PCWSTR pszButtonText;
};
nButtonID is the button's ID, and can be any ID that isn't already assigned to the pre-defined
buttons. pszButtonText is either a zero-terminated Unicode string, or a string resource ID. This string
is used for the button's text, and can contain an ampersand to indicate the mnemonic key.
Here is a new version of the task dialog, using two new strings in place of Yes and No (new code
is shown in bold):
void CTheApp::OnUpdateAvailable()
{
HRESULT hr;
TASKDIALOGCONFIG tdc = { sizeof(TASKDIALOGCONFIG) };
int nClickedBtn;
LPCWSTR szTitle = L"Mike's AntiFluff Scanner",
szHeader = L"An update for Mike's AntiFluff Scanner is available",
szBodyText = L"Version 2007.1 of Mike's AntiFluff Scanner has been released. " \
L"Do you want to download the update now?";
TASKDIALOG_BUTTON aCustomButtons[] = {
{ 1000, L"Heck &Yeah!" },
{ 1001, L"N&o Way Dude" }
};
tdc.hwndParent = m_hWnd;
tdc.dwCommonButtons = TDCBF_YES_BUTTON|TDCBF_NO_BUTTON;
tdc.pButtons = aCustomButtons;
tdc.cButtons = _countof(aCustomButtons);
tdc.pszWindowTitle = szTitle;
tdc.pszMainIcon = TD_INFORMATION_ICON;
tdc.pszMainInstruction = szHeader;
tdc.pszContent = szBodyText;
hr = TaskDialogIndirect ( &tdc, &nClickedBtn, NULL, NULL );
if ( SUCCEEDED(hr) && 1000 == nClickedBtn )
{
}
}

There are our two custom buttons! Notice that we now compare nClickedBtn with 1000 instead of IDYES,
since 1000 is the ID we assigned to the Heck Yeah! button.
Setting the Default Button
We can set the nDefaultButton member of TASKDIALOGCONFIG to make a specific button
the default button. This button will have the focus when the dialog is first shown. If we wanted to make the No
Way Dude button the default, we would add this line:
tdc.nDefaultButton = 1001;
To make a pre-defined button the default, set nDefaultButton to its pre-defined ID: IDOK,
IDRETRY, etc.
Using Command Links
In Vista, the button control has a new style, BS_COMMANDLINK, that turns it into a command link,
which is a larger button that can have an icon and optionally a second line of text. By setting the TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS
flag in dwFlags, all of our custom buttons become command links. If we add this line:
tdc.dwFlags = TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS;
the dialog will have two command links instead of two plain buttons:

Only custom buttons can be changed to command links. If we also put the pre-defined Close button in the
dialog, it would still appear at the bottom:

The goal of command links is to provide more helpful and meaningful labels, so let's change that text to be
a bit more user-friendly:
void CTheApp::OnUpdateAvailable()
{
HRESULT hr;
TASKDIALOGCONFIG tdc = { sizeof(TASKDIALOGCONFIG) };
int nClickedBtn;
LPCWSTR szTitle = L"Mike's AntiFluff Scanner",
szHeader = L"An update for Mike's AntiFluff Scanner is available",
szBodyText = L"Version 2007.1 of Mike's AntiFluff Scanner has been released." \
L"Do you want to download this update?";
TASKDIALOG_BUTTON aCustomButtons[] = {
{ 1000, L"&Download and install the update now" },
{ 1001, L"Do ¬ download the update" }
};
tdc.hwndParent = m_hWnd;
tdc.dwFlags = TDF_ALLOW_DIALOG_CANCELLATION|TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS;
tdc.pButtons = aCustomButtons;
tdc.cButtons = _countof(aCustomButtons);
tdc.pszWindowTitle = szTitle;
tdc.pszMainIcon = TD_INFORMATION_ICON;
tdc.pszMainInstruction = szHeader;
tdc.pszContent = szBodyText;
hr = TaskDialogIndirect ( &tdc, &nClickedBtn, NULL, NULL );
if ( SUCCEEDED(hr) && 1000 == nClickedBtn )
{
}
}
And here is the dialog with the updated text:

UI designers will tell you that rule #1 of UI is Users don't read the UI. (See this
article from Joel Spolsky for a good description of how more text
can be worse.) I think this version is preferable because the most important information is on the command links,
which are the controls that the user will have to read when making the decision. The header text is prominent
and the user's eye will likely be drawn there first, so it has a good chance at being read as well. Those three
elements tell the user everything he needs to know about the situation: What's happening (an update is available),
and what he can do (either download it, or not).
The body text is, honestly, not too important now that we've changed the buttons to command links. It's also
in between two larger UI elements, and I'd bet that many people would just skip over it entirely. Let's remove
that text and expand the text on the command links.
Command links can show a second line of text to provide more details about what the button will do. The two
lines are separated by a newline character. Here's the next version of our dialog:
void CTheApp::OnUpdateAvailable()
{
HRESULT hr;
TASKDIALOGCONFIG tdc = { sizeof(TASKDIALOGCONFIG) };
int nClickedBtn;
LPCWSTR szTitle = L"Mike's AntiFluff Scanner",
szHeader = L"An update for Mike's AntiFluff Scanner is available";
szBodyText = L"Version 2007.1 of Mike's AntiFluff Scanner has been released." \
L"Do you want to download this update?";
TASKDIALOG_BUTTON aCustomButtons[] = {
{ 1000, L"&Download and install the update now\n"
L"Update the program to version 2007.1" },
{ 1001, L"Do ¬ download the update\n"
L"You will be reminded to install the update in one week" }
};
tdc.hwndParent = m_hWnd;
tdc.dwFlags = TDF_ALLOW_DIALOG_CANCELLATION|TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS;
tdc.pButtons = aCustomButtons;
tdc.cButtons = _countof(aCustomButtons);
tdc.pszWindowTitle = szTitle;
tdc.pszMainIcon = TD_INFORMATION_ICON;
tdc.pszMainInstruction = szHeader;
tdc.pszContent = szBodyText;
hr = TaskDialogIndirect ( &tdc, &nClickedBtn, NULL, NULL );
if ( SUCCEEDED(hr) && 1000 == nClickedBtn )
{
}
}

Now things are starting to shape up! The larger text on the command links still tells the user what each button
does, and the smaller second lines provide more details if the user cares to read them. Notice that, even if the
user reads only the first line on each button, he'll still be able to make a good decision.
Showing Additional Details
Another feature that is useful when you have more details available, but don't want to clutter the dialog with
a lot of text, is the expanded info text area. If we set the pszExpandedInformation member
of TASKDIALOGCONFIG, the dialog will have a button that the user can click to expand the dialog and
view the text in pszExpandedInformation. We can add this feature to our sample dialog with two changes:
LPCWSTR szExtraInfo =
L"This update was released on December 1, 2006 " \
L"and updates the Scanner to run properly on the Vista RTM build.";
tdc.pszExpandedInformation = szExtraInfo;
Now the dialog has a See details button at the bottom, which will show more detailed info about our update:

Clicking the button reveals the additional info:

The dialog can also show the expanded info in the footer area, below the See details button. To move
the text there, add the TDF_EXPAND_FOOTER_AREA flag to dwFlags. The expanded state will
then look like this:

The text of the details button can be customized by setting the pszExpandedControlText and pszCollapsedControlText
members of TASKDIALOGCONFIG. You can set just one of those two members if you want to use the same
text for the button in both the expanded and collapsed states.
Advanced UI Features
Now that we've seen how to build a dialog using basic UI elements, let's take a look at some of the more advanced
features.
Adding a Check Box
A task dialog can also show a check box, which is often used for a "Don't show me this again" message.
We can add a check box to our dialog by setting the pszVerificationText member of TASKDIALOGCONFIG.
TaskDialogIndirect() returns the state of the check box through its 4th parameter, so we need to add
a BOOL variable and pass its address in that parameter:
void CTheApp::OnUpdateAvailable()
{
HRESULT hr;
TASKDIALOGCONFIG tdc = { sizeof(TASKDIALOGCONFIG) };
int nClickedBtn;
BOOL bCheckboxChecked;
LPCWSTR szTitle = L"...", szHeader = L"...", szExtraInfo = L"...",
szCheckboxText = L"In&stall future updates automatically, without asking me";
TASKDIALOG_BUTTON aCustomButtons[] = { { 1000, L"..." }, { 1001, L"..." } };
tdc.hwndParent = m_hWnd;
tdc.dwFlags = TDF_ALLOW_DIALOG_CANCELLATION|TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS;
tdc.pButtons = aCustomButtons;
tdc.cButtons = _countof(aCustomButtons);
tdc.pszWindowTitle = szTitle;
tdc.pszMainIcon = TD_INFORMATION_ICON;
tdc.pszMainInstruction = szHeader;
tdc.pszExpandedInformation = szExtraInfo;
tdc.pszVerificationText = szCheckboxText;
hr = TaskDialogIndirect ( &tdc, &nClickedBtn, NULL, &bCheckboxChecked );
If the user clicks the button to download the update (the button with ID 1000), we also look at the check box
state. If it was checked, then our app would store a configuration setting telling it to automatically download
updates in the future:
if ( SUCCEEDED(hr) && 1000 == nClickedBtn )
{
if ( update_was_installed && bCheckboxChecked )
{
}
}
}
Here's how the dialog looks with the check box:

Normally the check box starts out unchecked, but you can make it start checked by adding the TDF_VERIFICATION_FLAG_CHECKED
flag to dwFlags.
Adding Hyperlinks
The task dialog supports embedded hyperlinks in the pszContent and pszExpandedInformation
text elements (as well as pszFooter, a feature that we'll see later). For this example, we'll add
a link to our pszExpandedInformation text that will open a web page with more information about the
update. We need to do three things to add links:
- Add the
TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS flag to dwFlags.
- Indicate what part of the text in
pszExpandedInformation should be the link.
- Add a callback function so we are notified when the user clicks a link.
Creating the link in the text is simple, we just surround the text with an <a> tag, as in
HTML. In the <a> tag, we put an href attribute that contains the URL we want the
link to launch. You can see this tag in the szExtraInfo text below:
void CTheApp::OnUpdateAvailable()
{
HRESULT hr;
TASKDIALOGCONFIG tdc = { sizeof(TASKDIALOGCONFIG) };
int nClickedBtn;
BOOL bCheckboxChecked;
LPCWSTR szTitle = L"...", szHeader = L"...", szCheckboxText = L"...",
szExtraInfo =
L"This update was released on December 1, 2006 " \
L"and updates the Scanner to run properly on the Vista RTM build.\n" \
L"<a href=\"http://www.example.com/\">Full details about this update</a>";
TASKDIALOG_BUTTON aCustomButtons[] = { { 1000, L"..." }, { 1001, L"..." } };
tdc.hwndParent = m_hWnd;
tdc.dwFlags = TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS|TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS;
tdc.pButtons = aCustomButtons;
tdc.cButtons = _countof(aCustomButtons);
tdc.pszWindowTitle = szTitle;
tdc.pszMainIcon = TD_INFORMATION_ICON;
tdc.pszMainInstruction = szHeader;
tdc.pszExpandedInformation = szExtraInfo;
tdc.pszVerificationText = szCheckboxText;
tdc.pfCallback = TDCallback;
tdc.lpCallbackData = (LONG_PTR) this;
hr = TaskDialogIndirect ( &tdc, &nClickedBtn, NULL, &bCheckboxChecked );
}
The task dialog doesn't actually do anything when a link is clicked, it's the application's responsibility to
take the href and act on it. This is what we'll do in the TDCallback function. The callback
has this prototype:
HRESULT CALLBACK TaskDialogCallbackProc (
HWND hwnd, UINT uNotification, WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam, LONG_PTR dwRefData )
hwnd is the HWND of the task dialog; we can use it as the parent window for any UI
we show. uNotification is a constant indicating what event has occurred. wParam and lParam
are message-specific data. dwRefData is the same value that is stored in the lpCallbackData
member of TASKDIALOGCONFIG.
This callback is not completely documented yet, so for the time being, we'll have to inspect the parameters
and figure out what they contain. When the user clicks a link, uNotification is TDN_HYPERLINK_CLICKED,
and lParam is an LPCWSTR that contains the text from the href attribute.
Here's our TDCallback() that handles this notification:
HRESULT CALLBACK TDCallback (
HWND hwnd, UINT uNotification, WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam, LONG_PTR dwRefData )
{
switch ( uNotification )
{
case TDN_HYPERLINK_CLICKED:
ShellExecute ( hwnd, _T("open"), (LPCWSTR) lParam,
NULL, NULL, SW_SHOW );
break;
}
return S_OK;
}
Once we make these changes, the hyperlink will appear in the expanded into text:

Using the Footer Area
I think we've just about crammed all the useful info into this dialog that we can, so the last feature I'll
talk about is the footer area. Along with the button controls we've already seen and the expanded info text, a
task dialog can show an icon and some text that is always visible in the footer. The text can also contain hyperlinks.
For this last example, let's move the Full details hyperlink into the footer so it's always visible.
Here are the changes to make to the TASKDIALOGCONFIG struct, along with the new string:
LPCWSTR szFooter =
L"<a href=\"http://www.example.com/\">Full details about this update</a>";
tdc.pszFooter = szFooter;
tdc.pszFooterIcon = TD_INFORMATION_ICON;
And here's the result:

Conclusion
Task dialogs are definitely a welcome addition to Vista, and are a convenient way to build UI without having
to worry about the details of dialog templates and laying out of controls. Getting input is just one facet of what
task dialogs can do, be sure to check out the links in the Further Reading section to learn more about their other
features.
Further Reading
Windows
Vista for Developers - Part 2 - Task Dialogs in Depth. Kenny Kerr has a really long post talking about more
features of task dialogs, along with lots of sample code and an ATL wrapper class.
MSDN has some lengthy pages on the new
Vista UI guidelines. For task dialogs, the page to be familiar with is Text
and Tone.
Copyright and License
This article is copyrighted material, ©2006 by Michael Dunn. I realize this isn't going to stop people
from copying it all around the 'net, but I have to say it anyway. If you are interested in doing a translation
of this article, please email me to let me know. I don't foresee denying anyone permission to do a translation,
I would just like to be aware of the translation so I can post a link to it here.
The demo code that accompanies this article is released to the public domain. I release it this way so that
the code can benefit everyone. (I don't make the article itself public domain because having the article available
only on CodeProject helps both my own visibility and the CodeProject site.) If you use the demo code in your own
application, an email letting me know would be appreciated (just to satisfy my curiosity about whether folks are
benefitting from my code) but is not required. Attribution in your own source code is also appreciated but not
required.
Revision History
December 18, 2006: Article first published.
Series navigation: « Showing Friendly Messages with Task Dialogs
