Preface
Recently, I started a project on the integration of SAP Web Services in Microsoft's .NET environment. The goal of this project was to write a test program where a user could call SAP Web Services dynamically and to provide the architecture to consume Web Services in environments like Microsoft Office. I documented my experiences in a series of three blogs in the SAP Developer Network. Still, I want to summarize my experiences once more in a more coherent way and want to make the information available not only in the SAP developer community (which is mostly ABAP oriented I assume) but also in the .NET/C# community.
Introduction
The invention of the Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) offers the user the possibility to call Web Services and integrate these into new applications. SAP Developer Network offers a special section for SOA, which can be accessed here.
When I started a prototype project of integrating Web Services into a .NET environment, one of the main challenges was to determine the WSDL and endpoint information of a given Web Service and to make the Web Service independent of the actual backend system - in other words, how to determine the WSDL dynamically at runtime.
Searching for information material for my prototype, I came across numerous articles telling how to determine the WSDL manually if you know a Services Registry system. Examples:
However, all of these examples rely on the knowledge of a well defined backend at design time. My goal was to find an implementation which enables the end user to choose a Services Registry backend at runtime.
For everything that I write below, I assume that a running Services Registry is available. I will not elaborate how to install and set-up a Services Registry. My blog is based on the publicly available Services Registry: http://sr.esworkplace.sap.com.
Services Registry
What is the Services Registry?
The Services Registry is a central server instance in a SOA landscape. In the case of an SAP setup, this will most likely be as well a physical server. In my words, the Services Registry is a kind of a "telephone book" where on the one hand service providers can publish information on a Web Service like:
- Name of the service
- Endpoint addresses
- System information
- etc.
On the other hand, service consumers can search in the Services Registry for the required information to be able to use the service. Thirdly, the Services Registry provides an API (ServicesRegistrySiPort) which can be used by developers to connect to the Services Registry and to exchange data between their application and the SR.
One more official definition provided by SAP looks like this: "SAP Services Registry (SR) is a part of SAP NetWeaver Composition Environment 7.1 (CE), a UDDI-compliant registry of service definitions available in the repository. It provides API for search and discovery of services, as well as for publishing custom services in the registry, and supports the Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) standard." (see: Anne Tarnoruder: "Introducing SAP Enterprise Services Explorer for Microsoft .NET").
Standard Services Registry in the ES Workplace
As mentioned in the introduction, SAP provides a publicly available Services Registry at the URL http://sr.esworkplace.sap.com. This SR is part of the "ES Workplace" (link: http://esworkplace.sap.com) and gives access to officially published SAP Web Services so a developer can test his/her program with these. To be able to use the services in the ES Workplace SR, you have to have a registered user in the ES Workplace. This user can be requested via an online form. Only after having registered, will you be able to use services from SAP backends with the following SAP functionality (status of March 2011):
- SAP ERP 6.0 (Ehp4)
- SAP CRM 7.0
- SAP SRM 7.0
- SAP PI 7.1
- SAP SCM
For more details on the Services Registry in the ES Workplace, please see the SDN article "Services Registry for ESWorkplace" by Harish Mehta, Joerg Dehmel, and Nikolay Kanchev. The Services Registry of ES Workplace and the Services Registry API can be used with a generic test user:
username: sruser
password: eswork123
General Architecture
In principle, it is enough to determine Web Service properties (Web Service URLs) via the SR and to use these endpoints for your service references directly in your program. As I want to go a more dynamic approach, the general architecture is based on determining all Web Service information via the Services Registry. As you can see in the graphic below, all information on the Web Services are retrieved from the Services Registry.
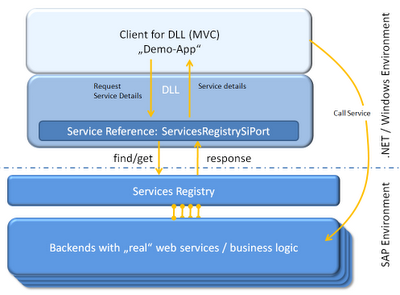
The consuming end-user application was built using the Model-View-Controller pattern, which I based on my blog "Model View Control (MVC) Pattern using C# - A real life example". As I was dealing with a demo application, I did not implement any logic for the actual backend service call. Still, I hope that the information herein is instructive and shows the principles of using the Services Registry API.
For reuse purposes, I decided to encapsulate the Services Registry API logic in a DLL, which abstracts the direct calls to a level, which is convenient for a developer.
Encapsulating the Services Registry API in DLL
Referencing the Services Registry API
To create a DLL, you have to create a new Application Library project in Visual Studio - I assume that you are familiar with this. To incorporate the Services Registry API, create a new Service Reference in your project (click on menu item "Project" -> "Add Service Reference") and a popup will open where you enter the service details:
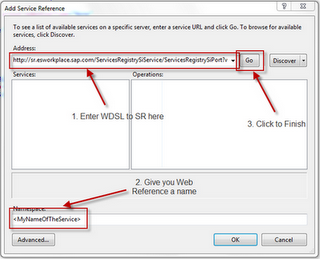
The Services Registry API has the following connection details:
After clicking "Go", Visual Studio will generate code so the service can be used in your program. Of special interest are the entries in the application configuration file app.config which typically look like this:
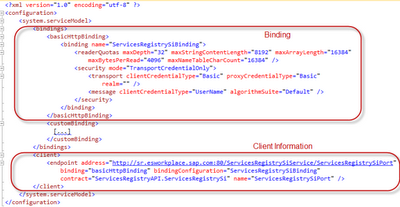
It will be our goal to get rid of these entries so we can define the links to the Services Registry at runtime.
app.config Stripping
The most simple way to call the services defined in app.config is by introducing statements like:
ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient theApiClient =
new ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient(<app.config-endpointconfigname>);
But then, the URL to the Services Registry API would be hard coded via app.config. Thus, we need to define the binding information programmatically by using statements like:
BasicHttpBinding servicesRegistryBinding =
new BasicHttpBinding("ServicesRegistrySiBinding");
servicesRegistryBinding.Security.Mode = BasicHttpSecurityMode.TransportCredentialOnly;
servicesRegistryBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
EndpointAddress servicesRegistryEndpointAddress =
new EndpointAddress(<servRegEndpointAddress>);
ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient theApiClient =
new ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient(servicesRegistryBinding,
servicesRegistryEndpointAddress);
Please note that the security settings depend on the configuration of the binding which depends on the actual settings on the server side. The code above works for my demo project but please consider that it is mostly intended for instruction purposes. If the binding of the Services Registry is coded like in my example, we can get rid of the app.config file completely.
DLL Coding
I implemented the main class of the DLL as a singleton following the article "Implementing the Singleton Pattern in C#". The singleton implementation was mostly chosen because I wanted to get/set the attribute _serivceToTest independent of an instance.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Channels;
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
namespace SoaConnect
{
public sealed class CSoaConnector : ISoaConnector
{
private static CSoaConnector _theSoaConnectorInstance = null;
static readonly object padlock = new object();
private ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient
theServicesRegistrySiClient;
private string _serviceToTest;
public string serviceToTest
{
get { return _serviceToTest; }
set { _serviceToTest = value; }
}
public static CSoaConnector Instance
{
get
{
lock (padlock)
{
if (_theSoaConnectorInstance == null)
{
_theSoaConnectorInstance = new CSoaConnector();
}
return _theSoaConnectorInstance;
}
}
}
public CSoaConnector() { }
public ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient
getServicesRegistryClient(string servRegEndpointAddress,
string userName, string password)
{
BasicHttpBinding servicesRegistryBinding =
new BasicHttpBinding("ServicesRegistrySiBinding");
servicesRegistryBinding.Security.Mode =
BasicHttpSecurityMode.TransportCredentialOnly;
servicesRegistryBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
EndpointAddress servicesRegistryEndpointAddress =
new EndpointAddress(servRegEndpointAddress);
theServicesRegistrySiClient = new
ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient(
servicesRegistryBinding, servicesRegistryEndpointAddress);
theServicesRegistrySiClient.ClientCredentials.
HttpDigest.AllowedImpersonationLevel =
System.Security.Principal.TokenImpersonationLevel.Impersonation;
theServicesRegistrySiClient.ClientCredentials.
HttpDigest.ClientCredential.UserName = userName;
theServicesRegistrySiClient.ClientCredentials.
HttpDigest.ClientCredential.Password = password;
theServicesRegistrySiClient.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = userName;
theServicesRegistrySiClient.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = password;
return theServicesRegistrySiClient;
}
public ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
getFindServiceDefinition(string serviceName, string remoteSystemID)
{
ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionSearchAttributes
theSearchAttributes =
new ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionSearchAttributes();
theSearchAttributes.name = serviceName;
if (remoteSystemID != "")
{
string[] systemIDs = new string[1];
systemIDs[0] = remoteSystemID;
theSearchAttributes.physicalSystemSldIDs = systemIDs;
}
ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitions findServiceDefinitions =
new ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitions();
findServiceDefinitions.serviceDefinitionSearchAttributes = theSearchAttributes;
ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
theServiceDefinitionResponse =
theServicesRegistrySiClient.findServiceDefinitions(findServiceDefinitions);
return theServiceDefinitionResponse;
}
public ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
getServiceDefinitions(string searchParameter)
{
ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitions theFindServiceDefinition =
new ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitions();
theFindServiceDefinition.serviceDefinitionSearchAttributes =
new ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionSearchAttributes();
theFindServiceDefinition.serviceDefinitionSearchAttributes.name = searchParameter;
ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
theServiceDefinitionResponse =
new ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse();
theServiceDefinitionResponse =
theServicesRegistrySiClient.findServiceDefinitions(theFindServiceDefinition);
theFindServiceDefinition.serviceDefinitionSearchAttributes.maxRows =
theServiceDefinitionResponse.@return.listDescription.actualCount;
theServiceDefinitionResponse =
theServicesRegistrySiClient.findServiceDefinitions(theFindServiceDefinition);
return theServiceDefinitionResponse;
}
}
}
error CS0030: Cannot convert type
When making the call to determine the Web Service configuration, the code consists of just one line:
ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse theServiceDefinitionResponse =
theServicesRegistrySiClient.findServiceDefinitions(findServiceDefinitions);
This line causes a system error "CS0030: Cannot convert type for ...classificationPair[] ...classificationPair". The solution to this error is documented in David Klein's Blog, which recommends to replace the entries like "classificationPair[][]" with "classificationPair[]" in the file references.cs in the .NET software project.
Services Registry API Added Statically
Please note the variables starting with the namespace "ServicesRegistryAPI". These references belong to a static services reference to the Services Registry API which has to be added to your project at design time.
ISoaConnector - Interface to CSoaConnector
The interface to CSoaConnector is quite narrow:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace SoaConnect
{
public interface ISoaConnector
{
string serviceToTest { get; set; }
ServicesRegistryAPI.ServicesRegistrySiClient getServicesRegistryClient(
string servRegEndpointAddress, string userName, string password);
ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
getFindServiceDefinition(string serviceName, string remoteSystemID);
ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
getServiceDefinitions(string searchParameter);
}
}
DLL Consumer - The Demo Application
The demo program enables a user to enter the URL to a Services Registry API, user name, and password settings. By clicking on "Connect", the program connects to the Services Registry - here is where you need the singleton... After having connected to the SR, the user can enter a string as a search criterion ("Service Name to Search For") and by hitting "Search for Services", the system returns the services matching the search criteria. These services are listed in the dropdown box "Services Available in Services Registry", where the user can choose one. Below, the program displays some basic information on the service chosen by the user. The UI is fairly simple:
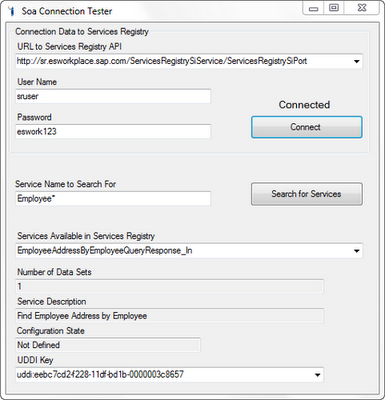
MVC - View
I based my Model View Controller on another article of mine in c-sharpcorner.com, which is an addendum to Matthew Cochran's blog: "Introduction to Model View Control (MVC) Pattern using C". The view behind the scenes is straightforward:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Linq;
namespace SOA_Test
{
public partial class FormMainWindow : Form, IMainWindow_View
{
private CSettingsFile theSettingsFileHandler;
public FormMainWindow()
{
theSettingsFileHandler = new CSettingsFile();
this.initialize(theMainWindowController, theMainWindowModel);
InitializeComponent();
string[] systemURLs = theSettingsFileHandler.getSystemURLs();
this.comboBox_SystemUrl.DataSource = systemURLs;
}
#region MVC related stuff
private IMainWindow_Controller theMainWindowController =
new CMainWindow_Controller();
private IMainWindow_Model theMainWindowModel = new CMainWindow_Model();
public void initialize(IMainWindow_Controller inMainWindowController,
IMainWindow_Model inMainWindowModel)
{
if (theMainWindowModel != null) {}
theMainWindowModel = inMainWindowModel;
theMainWindowController = inMainWindowController;
theMainWindowController.setModel(theMainWindowModel);
theMainWindowController.setView(this);
theMainWindowModel.addObserverView(this);
}
public void addObserver(IMainWindow_Controller inMainWindowController)
{
this.theMainWindowController = inMainWindowController;
}
public void updateUserInterface(IMainWindow_Model
inMainWindowModel, object sender)
{
}
#endregion
private void buttonConnect_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ComponentResourceManager theResourceManager =
new ComponentResourceManager(typeof(FormMainWindow));
CConstants.userSettings theUserSettings;
theUserSettings.systemURL = this.comboBox_SystemUrl.Text;
theUserSettings.userName = this.textBoxUserName.Text;
theUserSettings.password = this.textBoxPassword.Text;
theMainWindowController.buttonConnect_Click(theUserSettings);
this.label_Status.Text = "Connected";
this.pictureBox_Status.Image =
(Bitmap)theResourceManager.GetObject("Sphere_SAP_Warm_Green_Opaque.png");
this.button_SearchForService.Enabled = true;
}
private void FormMainWindow_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void comboBox_SystemUrl_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
CConstants.userSettings theUserSettings =
theMainWindowController.comboBox_SystemUrl_TextChanged(
this.comboBox_SystemUrl.Text);
this.textBoxUserName.Text = theUserSettings.userName;
this.textBoxPassword.Text = theUserSettings.password;
}
private void button_TestService_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
while ( this.comboBox_UddiKeys.Items.Count != 0)
{
this.comboBox_UddiKeys.Items.RemoveAt(0);
}
SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo[]
serviceDefinitionInfos = theMainWindowController.testService(
this.comboBox_ServiceNames.Text);
this.textBox_NumberOfHits.Text = serviceDefinitionInfos.Count().ToString();
string[] uddiKeyList = new string[0];
int arrayCounter = uddiKeyList.Count();
foreach (SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo
serviceDefinitionInfo in serviceDefinitionInfos)
{
arrayCounter++;
Array.Resize(ref uddiKeyList, arrayCounter);
uddiKeyList[arrayCounter - 1] = serviceDefinitionInfo.key;
}
this.comboBox_UddiKeys.Items.AddRange(uddiKeyList);
this.comboBox_UddiKeys.SelectedIndex = 0;
if (serviceDefinitionInfos[0].configState != null)
{
this.textBox_ConfigState.Text = serviceDefinitionInfos[0].configState;
}
else { this.textBox_ConfigState.Text = "Not Defined"; }
this.textBox_ServiceDesc.Text = serviceDefinitionInfos[0].description[0].text;
}
private void button_SearchForService_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string searchParameter;
if (this.textBox_SearchString.Text != "")
{
searchParameter = this.textBox_SearchString.Text;
}
else { searchParameter = "*"; }
while (this.comboBox_ServiceNames.Items.Count != 0)
{
this.comboBox_ServiceNames.Items.RemoveAt(0);
}
this.comboBox_ServiceNames.Items.AddRange(
theMainWindowController.getServiceDefinitions(searchParameter));
this.comboBox_ServiceNames.SelectedIndex = 0;
this.comboBox_ServiceNames.Enabled = true;
this.comboBox_UddiKeys.Enabled = true;
}
private void comboBox_ServiceNames_SelectedValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
while ( this.comboBox_UddiKeys.Items.Count != 0)
{
this.comboBox_UddiKeys.Items.RemoveAt(0);
}
SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo[] serviceDefinitionInfos =
theMainWindowController.testService(this.comboBox_ServiceNames.Text);
this.textBox_NumberOfHits.Text = serviceDefinitionInfos.Count().ToString();
string[] uddiKeyList = new string[0];
int arrayCounter = uddiKeyList.Count();
foreach (SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo
serviceDefinitionInfo in serviceDefinitionInfos)
{
arrayCounter++;
Array.Resize(ref uddiKeyList, arrayCounter);
uddiKeyList[arrayCounter - 1] = serviceDefinitionInfo.key;
}
this.comboBox_UddiKeys.Items.AddRange(uddiKeyList);
this.comboBox_UddiKeys.SelectedIndex = 0;
if (serviceDefinitionInfos[0].configState != null)
{
this.textBox_ConfigState.Text = serviceDefinitionInfos[0].configState;
}
else { this.textBox_ConfigState.Text = "Not Defined"; }
this.textBox_ServiceDesc.Text = serviceDefinitionInfos[0].description[0].text;
}
}
}
MVC - Controller
As I only wanted to get my little app running, I did not implement any serious logic here. Basically, I only route user events from the View down to the Model:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace SOA_Test
{
class CMainWindow_Controller : IMainWindow_Controller
{
#region MVC related part
#region Attributes
IMainWindow_Model theMainWindowModel;
IMainWindow_View theMainWindowView;
#endregion
public CMainWindow_Controller(IMainWindow_Model inMainWindowModel,
IMainWindow_View inMainWindowView)
{
this.theMainWindowModel = inMainWindowModel;
this.theMainWindowView = inMainWindowView;
}
public CMainWindow_Controller()
{
}
public void setModel(IMainWindow_Model inMainWindowModel)
{
this.theMainWindowModel = inMainWindowModel;
}
public void setView(IMainWindow_View inMainWindowView)
{
this.theMainWindowView = inMainWindowView;
}
#endregion
public CConstants.userSettings comboBox_SystemUrl_TextChanged(string systemURL)
{
return theMainWindowModel.comboBox_SystemUrl_TextChanged(systemURL);
}
public void buttonConnect_Click(CConstants.userSettings inUserSettings)
{
theMainWindowModel.buttonConnect_Click(inUserSettings);
}
public string[] getServiceDefinitions(string searchParameter)
{
return theMainWindowModel.getServiceDefinitions(searchParameter);
}
public SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo[]
testService(string serviceName)
{
return theMainWindowModel.testService(serviceName);
}
}
}
MVC - Model
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using SoaConnect;
namespace SOA_Test
{
class CMainWindow_Model : IMainWindow_Model
{
#region MVC initialize
IMainWindow_View theMainWindowView;
public CMainWindow_Model()
{
}
public void addObserverView(IMainWindow_View inMainWindowView)
{
theMainWindowView = inMainWindowView;
}
public void notifyObserverView()
{
theMainWindowView.updateUserInterface(this, null);
}
#endregion
private CSettingsFile _theSettingsFileHandler;
public CSettingsFile theSettingsFileHandler
{
get {
if (_theSettingsFileHandler == null) {
_theSettingsFileHandler = new CSettingsFile();
}
return _theSettingsFileHandler;
}
set {
if (_theSettingsFileHandler == null)
{
_theSettingsFileHandler = new CSettingsFile();
}
_theSettingsFileHandler = value;
}
}
public void buttonConnect_Click(CConstants.userSettings inUserSettings)
{
theSettingsFileHandler.theUserSettings = inUserSettings;
theSettingsFileHandler.updateCurrentUserSettingsDoc();
theSettingsFileHandler.saveCurrentUsersettings();
SoaConnect.CSoaConnector.Instance.getServicesRegistryClient(
inUserSettings.systemURL, inUserSettings.userName,
inUserSettings.password);
}
public CConstants.userSettings comboBox_SystemUrl_TextChanged(string systemURL)
{
CConstants.userSettings theUserSettings = new CConstants.userSettings();
theUserSettings.userName =
theSettingsFileHandler.getUserSettingsForSystem(systemURL).userName;
theUserSettings.password =
theSettingsFileHandler.getUserSettingsForSystem(systemURL).password;
theUserSettings.systemURL = systemURL;
return theUserSettings;
}
public string[] getServiceDefinitions(string searchParameter)
{
string[] theServiceNames = new string[0];
int arraySize = theServiceNames.Count();
SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
theServiceDefinitions =
SoaConnect.CSoaConnector.Instance.getServiceDefinitions(searchParameter);
SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo[]
theServiceDefinitionInfoList =
theServiceDefinitions.@return.serviceDefinitionInfos;
foreach (SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo
serviceDefinitionInfo in theServiceDefinitionInfoList)
{
arraySize++;
Array.Resize(ref theServiceNames, arraySize);
theServiceNames[arraySize - 1] = serviceDefinitionInfo.name;
}
return theServiceNames;
}
public SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.serviceDefinitionInfo[]
testService(string serviceName)
{
SoaConnect.ServicesRegistryAPI.findServiceDefinitionsResponse
serviceDefinition =
SoaConnect.CSoaConnector.Instance.getFindServiceDefinition(
serviceName, "");
return serviceDefinition.@return.serviceDefinitionInfos;
}
}
}
Please note that I did not note down the interface definitions for the View, Controller, and Model.
CSettingsFile - Class to Read / Write User Settings
This class is used to write the connection data entered by the user in the UI to a configuration file. These data are read from the file and pre-fill the connection parameters at program start.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using System.Security.Principal;
namespace SOA_Test
{
class CSettingsFile
{
private XDocument userSettingsDocument;
private string appDirectory = Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath);
private string userSettingsPath = "";
private string currentUserName = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name;
private CConstants.userSettings _theUserSettings;
public CConstants.userSettings theUserSettings
{
get { return _theUserSettings; }
set { _theUserSettings = value; }
}
#region public methods
public CSettingsFile() {
userSettingsPath = appDirectory + "\\UserSettings.xml";
userSettingsDocument = new XDocument();
try { userSettingsDocument = XDocument.Load(userSettingsPath);
}
catch (FileNotFoundException) {
userSettingsDocument = createNewUserSettingsDocument();
}
}
public CConstants.userSettings getSettingsForSystem(string systemURL) {
XElement settingsForUser = null;
IEnumerable<XElement> settingsForUserList;
CConstants.userSettings theUserSettings;
theUserSettings.systemURL = systemURL;
try
{
settingsForUserList =
userSettingsDocument
.Descendants(CConstants.XElementName_UserSettings)
.Where(test => test.Element(
CConstants.XElementName_UserName).Value == currentUserName);
}
catch { settingsForUserList = null; }
if (settingsForUserList.Count() == 1) {
settingsForUser = settingsForUserList.ElementAt(0);
}
else {
}
XElement userSettingsForSystem =
settingsForUser.Element(CConstants.XElementName_ServiceRegURLs);
theUserSettings.userName =
userSettingsForSystem.Element(CConstants.XElementName_UserName).Value;
theUserSettings.password =
userSettingsForSystem.Element(CConstants.XElementName_Password).Value;
return theUserSettings;
}
public string[] getSystemURLs() {
string[] systemURLArray = null;
int systemURLArraySize = 0;
IEnumerable<XElement> systemURLList =
userSettingsDocument
.Descendants(CConstants.XElementName_UserSettings)
.Elements(CConstants.XElementName_ServiceRegURLs);
foreach (XElement systemURL in systemURLList)
{
if (systemURL.Attribute(CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value != "")
{
systemURLArraySize++;
Array.Resize(ref systemURLArray, systemURLArraySize);
systemURLArray[systemURLArraySize - 1] =
systemURL.Attribute(CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value;
}
}
return systemURLArray;
}
public CConstants.userSettings getUserSettingsForSystem(string theSystemURL)
{
XElement userSettingsForSystem = null;
CConstants.userSettings localUserSettings;
localUserSettings.systemURL = "";
localUserSettings.userName = "";
localUserSettings.password = "";
XElement currentUserSettings =
userSettingsDocument
.Descendants(CConstants.XElementName_UserSettings)
.Where(test => test.Attribute(
CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value == currentUserName)
.ElementAt(0);
if (currentUserSettings != null)
{
try
{
userSettingsForSystem =
currentUserSettings
.Descendants(CConstants.XElementName_ServiceRegURLs)
.Where(test => test.Attribute(
CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value == theSystemURL)
.ElementAt(0);
}
catch { }
}
if (userSettingsForSystem != null)
{
localUserSettings.systemURL =
userSettingsForSystem.Attribute(
CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value;
localUserSettings.userName =
userSettingsForSystem.Element(
CConstants.XElementName_UserName).Attribute(
CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value;
localUserSettings.password = userSettingsForSystem.Element(
CConstants.XElementName_Password).Attribute(
CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value;
}
return localUserSettings;
}
public void updateCurrentUserSettingsDoc()
{
XElement currentUserElement =
new XElement(CConstants.XElementName_UserSettings);
XElement currentSystemElement =
new XElement(CConstants.XElementName_ServiceRegURLs);
&np; try
{
currentUserElement =
userSettingsDocument
.Descendants(CConstants.XElementName_UserSettings)
.Where(test => test.Attribute(
CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value ==
currentUserName).ElementAt(0);
}
catch { }
if (currentUserElement != null)
{
try {
currentSystemElement =
currentUserElement
.Elements(CConstants.XElementName_ServiceRegURLs)
.Where(test =>
test.Attribute(CConstants.XAttribute_Value).Value ==
theUserSettings.systemURL).ElementAt(0);
}
catch (ArgumentOutOfRangeException) {
currentUserElement.Add(new XElement(
CConstants.XElementName_ServiceRegURLs,
new XAttribute(CConstants.XAttribute_Value,
theUserSettings.systemURL),
new XElement(CConstants.XElementName_UserName,
new XAttribute(CConstants.XAttribute_Value,
theUserSettings.userName)),
new XElement(CConstants.XElementName_Password,
new XAttribute(CConstants.XAttribute_Value,
theUserSettings.password))));
}
}
}
public void saveCurrentUsersettings() {
userSettingsDocument.Save(userSettingsPath);
}
#endregion
#region private methods
private XElement createNewUserElement()
{
XElement theUserXElement =
new XElement(CConstants.XElementName_UserSettings,
new XAttribute(CConstants.XAttribute_Value, currentUserName));
return theUserXElement;
}
private XDocument createNewUserSettingsDocument() {
XDocument theUserSettings = new XDocument(
new XDeclaration("1.0", "UTF-8", "false"),
new XElement(CConstants.XElementName_UserSettingsRoot));
theUserSettings.Element(
CConstants.XElementName_UserSettingsRoot).Add(createNewUserElement());
return theUserSettings;
}
#endregion
}
}
