Introduction
I think this can go without saying, but I'll say it anyway: I realize there are encryption algorithms that are far superior to the one I am presenting here. That is not the purpose of this application. The purpose of this application is to demonstrate to potential encryption enthusiasts the possibilities of developing a very simple encryption application without resorting to extreme mathematical complexities.
How does it work?
The code is broken down into two major sections: a section for encryption and another for decryption. Each section is composed of a while loop that retrieves 4 bytes per cycle from a user-specified file to form a 32-bit unsigned integer block of data. This 32-bit unsigned integer block of data is then xored with a pseudo-random unsigned integer value that is seeded by one or more keys and then is rotated to the left or to the right in pseudo-random directions and magnitudes. This process is continued until the end of the file is reached. If a file is found to have a file size that is not divisible by 4, this application will use methods that perform calculations on 24-bit, 16-bit, or 8-bit unsigned integer blocks of data.
The following programmatically demonstrates the process of encrypting a block of 4 bytes:
while((a = fgetc(in)) != EOF && (b = fgetc(in)) !=
EOF && (c = fgetc(in)) != EOF && (d = fgetc(in)) != EOF)
{
polarity = rand()%2;
magnitude = rand()%32;
block = ((d<<24) | (c<<16) | (b<<8) | a);
block ^= ((rand()%256<<24) | (rand()%256<<16) |
(rand()%256<<8) | rand()%256);
if (polarity) block = ROTL32(block,magnitude);
else block = ROTR32(block,magnitude);
putc(block,out);
putc(block=block>>8,out);
putc(block=block>>8,out);
putc(block=block>>8,out);
}
The following visually demonstrates the behavior of the above code:

Using the program
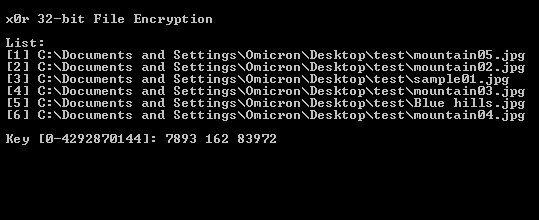
This program was originally designed to run on a Windows Operating System. To encrypt or decrypt a set of files, first select the intended files and drag them to the executable. The program will start and accept the files you just dragged and dropped as "command-line parameters". If this was done correctly, the files you selected will appear in a list. You can then specify a set of integer values that are within the range of 0 and 4292870144 as keys for seeding the pseudo-random number generator. Once you have indicated a set of keys, you will be asked if you want to encrypt or decrypt the selected files. Choose accordingly.
Note: To decrypt a file, you must specify the set of keys in reverse order.
History
- 16 June, 2007 -- Original version posted
- 25 June, 2007 -- Downloads updated
