Introduction
This article suggests an implementation of functors (i.e. function objects) in ATL for VBA/VB6 consumption.
VBA comes with very little support for pointers and no support for function pointers apart from the AddressOf operator. I have been working with Excel VBA for the past few years and I often feel that access to function pointers would make my life much easier when it comes to generic programming.
This implementation allows VBA code like the below to be written:
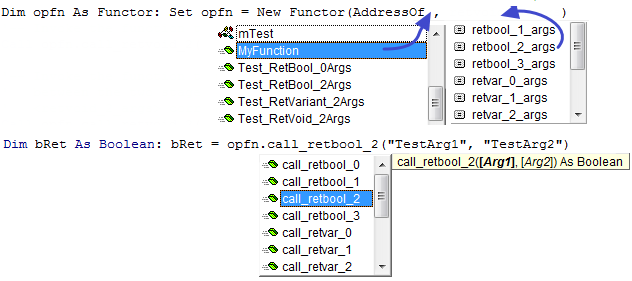
Dim opfn As Functor: Set opfn = New_Functor(AddressOf MyFunction, retvoid_2_args)
Call opfn.call_retvoid_2("This works", " fine!")
Background/ C++ Implementation
The project (written in C++ ATL - VS2010) compiles to a COM DLL. The exported Functor objects can be used in VBA code to:
- Store the address of a function (the function type is an input at this stage) and
- Later call it by using the method of the
Functor object that matches the function type
The IDL declarations of the HookFunction() method and a sample function calling method are:
interface IFunctor : IDispatch{
[id(1), helpstring("Hooks on a function")]
HRESULT HookFunction([in] LONG fnAddress, [in] enum FuncType functionType);
[id(8), helpstring("Calls Function that a)Retruns VARIANT b)Takes 2 arguments")]
HRESULT call_retvar_2([in,out,optional]VARIANT*
Arg1,[in,out,optional]VARIANT* Arg2,[out,retval]VARIANT*);
The hooked functions can be of one of the types that are typedef'd in Functor.h:
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvoid_0)(void);
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvoid_1)(VARIANT*);
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvoid_2)(VARIANT*, VARIANT*);
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvoid_3)(VARIANT*, VARIANT*, VARIANT*);
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvar_0)(VARIANT*);
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvar_1)(VARIANT*, VARIANT*);
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvar_2)(VARIANT*, VARIANT*, VARIANT*);
typedef HRESULT (__stdcall *pfn_retvar_3)(VARIANT*, VARIANT*, VARIANT*, VARIANT*);
typedef VARIANT_BOOL (__stdcall *pfn_retbool_0)(void);
typedef VARIANT_BOOL (__stdcall *pfn_retbool_1)(VARIANT*);
typedef VARIANT_BOOL (__stdcall *pfn_retbool_2)(VARIANT*, VARIANT*);
typedef VARIANT_BOOL (__stdcall *pfn_retbool_3)(VARIANT*, VARIANT*, VARIANT*);
These function types correspond to members of the enum FuncType (defined in VBA_Functors.idl) that is also exported from the DLL:
[
uuid(708D69A2-B470-4530-82B7-5D825EC9F8ED),
v1_enum
]
enum FuncType
{
retvoid_0_args,
retvoid_1_args,
retvoid_2_args,
retvoid_3_args,
retvar_0_args,
retvar_1_args,
retvar_2_args,
retvar_3_args,
retbool_0_args,
retbool_1_args,
retbool_2_args,
retbool_3_args
};
The DLL also exports an initializer class (used to simulate a constructor with arguments) that exposes functions that return newly initialized COM objects; here New_Functor()returns a newly initialized Functor (IFunctor) object. From ClassInitializer.cpp:
STDMETHODIMP CClassInitializer::New_Functor(LONG fnAddress,
FuncType functionType, IFunctor** ret)
{
HRESULT hr = CFunctor::CreateInstance(ret);
if (FAILED(hr)){
return hr;
}
return (*ret)->HookFunction(fnAddress, functionType);
}
The IDL declarations follow. Notice the appobject attribute of coclass ClassInitializer. This makes the object global (i.e. its methods can be invoked by VBA code that references the DLL without dimensioning a variable of the type).
[...]
interface IClassInitializer : IDispatch{
[id(1), helpstring("Returns a newly initialized Functor object")]
HRESULT New_Functor([in] LONG fnAddress, [in] enum FuncType functionType,
[out,retval] IFunctor**);
};
library VBA_FunctorsLib
{ ...
[
appobject,
uuid(C9CE3589-1E7F-4750-9E5F-4B48DB1883DB)
]
coclass ClassInitializer
{
[default] interface IClassInitializer;
};
}
Using the Code
The file [VBA_Functors_Test.xls] that is included with the source code contains a few (contrived) examples of using Functor objects from VBA.
- The VBA project contains a reference to the DLL (VBA_Functors.dll)
- The DLL is a COM DLL that needs to be registered (typically using regsvr32.exe, for some instructions, see this link)
In order to correctly initialize a Functor object from VBA, you need to:
- Dimension and initialize a
Functor variable - Hook to an existing VBA function. The function has to be of one of the pre-specified types and the correct function type needs to be passed-in through the second argument of
HookFunction() (as mentioned above, function types are encapsulated in the FuncType enum so VBA auto-complete conveniently kicks in)
Public Function SimpleFunction(ByRef vDisplay As Variant) As Variant
SimpleFunction = MsgBox(vDisplay, vbYesNo, "Did that display correctly?")
End Function
Public Sub UseFunctors()
Dim ofn As Functor: Set ofn = New Functor
Call ofn.HookFunction(AddressOf SimpleFunction, retvar_1_args)
End Sub
Using the function New_Functor() allows for more compact syntax:
Public Sub UseFunctors()
Dim ofn As Functor: Set ofn = New_Functor(AddressOf SimpleFunction, retvar_1_args)
End Sub
You can then use the Functor object to invoke the hooked function. Here is the UseFunctors() sub extended to include the function call:
Public Sub UseFunctors()
Dim ofn As Functor: Set ofn = New_Functor(AddressOf SimpleFunction, retvar_1_args)
Dim vbmRes As VbMsgBoxResult
vbmRes = ofn.call_retvar_1("Display this!")
End Sub
Using New_Functor() also enables inline initialization of functors when calling functions that take Functor arguments. Consider the following snippet taken from the MORE REALISTIC EXAMPLE section of the VBA code in the sample .xls file:
Public Function IsMultipleOfTwo(ByRef vNumber As Variant) As Boolean
IsMultipleOfTwo = (0 = vNumber Mod 2)
End Function
Public Function IsMultipleOfThree(ByRef vNumber As Variant) As Boolean
IsMultipleOfThree = (0 = vNumber Mod 3)
End Function
Public Function CountMultiplesOfNumber(ByRef lNumber() As Long, _
ByRef pfn As Functor) As Long
Dim vIter As Variant
For Each vIter In lNumber
If pfn.call_retbool_1(vIter) Then CountMultiplesOfNumber = _
CountMultiplesOfNumber + 1
Next vIter
End Function
Public Sub TestAbove()
Dim alNUms(0 To 100) As Long
MsgBox CountMultiplesOfNumber(alNUms, New_Functor_
(AddressOf IsMultipleOfThree, retbool_1_args))
End Sub
In my opinion, things become even more interesting when one considers exporting "stock" functors from a DLL (exported methods of a global object come to mind) that can be used selectively on the VBA side to drive the behaviour of algorithms exported by the DLL (mutating/non-mutating for_each on VBA SafeArrays for example?)
Points of Interest
Some points worth noting:
- Having worked in a corporate environment, I've come to realize that security policies can clash with the registration of COM components. The latter were traditionally registered under
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and the typical user doesn't have write access to the hive.
Registering components under HKEY_CURRENT_USER addresses this. In ATL AtlSetPerUserRegistration(true) can be used to that end. Here is the DllRegisterServer definition in VBA_Functors.cpp:
STDAPI DllRegisterServer(void)
{
ATL::AtlSetPerUserRegistration(true);
HRESULT hr = _AtlModule.DllRegisterServer();
return hr;
}
- The file com_definitions.h included in this project structures
HRESULTs commonly used as return values of COM methods in enums under COMErrorCodes namespace. This allows code like below to be written (without having to look up the codes in WinError.h):
STDMETHODIMP CFunctor::call_retvoid_0(void){
if (retvoid_0_args == m_ft){
...
}
else{
return Error(INCORRECT_FUNCTION_CALL_ERROR,
__uuidof(IFunctor), COMErrorCodes::E__INVALIDARG);
}
}
- Keen observers might have noticed in the
typedefs for functions that return Boolean, that the return values are not implemented as an extra [out,retval] parameter. True/False is instead returned directly through the function's return value (presumably for efficiency reasons):
typedef VARIANT_BOOL (__stdcall *pfn_retbool_0)(void);
History
- 03 June 2011: First revision
