Problem Definition
The objective is to monitor "run" registry keys, for example, HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce. Whenever a new application is added to one of the registry keys or an existing application is changed, etc., the change should be immediately displayed to the user. There are several different ways to implement this; feel free to implement whichever way is preferable to you.
Requirements
Coding Language
GUI
- Start/stop button
- A list of registry keys being monitored
- Log displaying applications that were added to the "run" keys
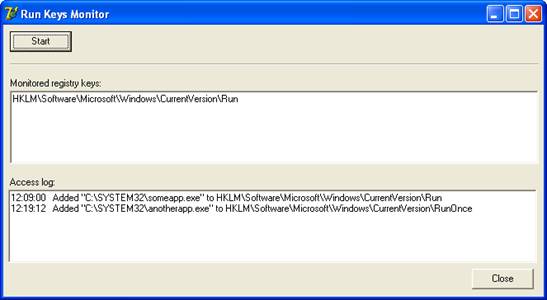
Figure 1: The GUI
Analysis and Approach
The registry is a directory which stores settings and options for the operating system; it is organised with keys and value pairs. An approach to this problem would be:
- Start preparing the GUI.
- Make a multi-threaded environment on button start and stop.
- In each thread, monitor the registry key.
- Report registry key changes to the GUI.
Preparing the GUI
It will be a dialog-based application with the following controls:
- The GUI will have buttons derived from
CButton. - The MFC edit control displays the messages derived from
CEdit.
Program Explained
MyClass *c = new MyClass(this->m_hWnd,HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,
"Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\RunOnce");
pThread = AfxBeginThread(MyThreadFunc,c,THREAD_PRIORITY_NORMAL,0,0);
MyClass *c1 = new MyClass(this->m_hWnd,HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,
"Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run");
pThread = AfxBeginThread(MyThreadFunc,c1,THREAD_PRIORITY_NORMAL,0,0);
CString temp_str;
m_edit1.SetWindowText(
"STARED:\r\nHKLM\\Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\" +
"RunOnce\r\nHKLM\\Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run");
g_eventStart.SetEvent();
Code segment 1: OnStart()
To start observing the registry keys in the thread, we need to use the function called AfxBeginThread(). This takes a parameter of the type of a global function name. Here, the function is called MyThreadFunc. The My Thread function is supposed to take only one parameter, which is of type LPVOID. So, if we need to pass more parameters, we just collect them up in a structure or a class and pass that as a parameter.
Here in the above program, we choose MyClass to pass as one of the parameters. MyClass has members like HKEY, the full path of the key and the handle to the window. We need the handle to the window because we want to invoke user-defined messages. Threads are started with normal priority.
Thread Function
The tread function has the following main calls:
RegNotifyChangeKeyValue(hKey, TRUE, dwFilter, hEvent, TRUE);
Code segment 2: Event capture key
This notifies the caller about changes to the attributes or contents of a specified registry key [1]. Once a change in the key is noticed, hEvent is signaled. So, we need to capture hEvent. To capture hEvent, we have a function called as:
WaitForSingleObject(hEvent, INFINITE)
Code segment 3: Waiting for event to occur
Now the thread will wait for infinite time until the event is triggered. Once the event is triggered, we need to collect all the data. To collect data from that registry key, we have a function called as:
retCode = RegQueryInfoKey(
hKey, achClass, &cchClassName, NULL, &cSubKeys, &cbMaxSubKey, &cchMaxClass, &cValues, &cchMaxValue, &cbMaxValueData, &cbSecurityDescriptor, &ftLastWriteTime);
Code segment 4: Getting registry information
With the above query info, we will also get the last modified time of the key. This is required in order to display it in logs. However, the time is in the file format. So, we convert the time into GMT time and thereafter to the local time setting on the computer.
FileTimeToSystemTime(&ftLastWriteTime, &stUTC);
SystemTimeToTzSpecificLocalTime(NULL, &stUTC, &stLocal);
Code segment 5: Find time and date
Now from above [2], if CValues is more than zero then we have some value element in the key. To read value elements in the key, we call a function:
retCode = RegEnumValue(hKey, i,
achValue,
&cchValue,
NULL,
&type,
data,
&dataSize);
Code segment 6: Read data from the key
The value is in achValue and the data is in the data key. The size of the data is in the datasize key while the type of the data is stored in the type key. We assume all the data to be string (REG_SZ).
Now we iterate through the enumeration to read all the data. Once the data is read and we assume it is of type string, then we store it in the form of a map (STL). Why choose a map? A map is a container with a name value pair. So, we can store all the registry key values in a map. To find a registry key, we will just search the map on the name. Once we have the map ready, we will try to compare the latest values after change notification. We have categorized changes as:
Once these changes are identified, we notify the GUI of the changes. We post a message to the GUI:
PostMessage(hWnd,WM_USER_THREAD_UPDATE_PROGRESS,i,100);
Code segment 7: To notify the GUI about changes
This is a user-created message which is defined in a message loop:
ON_MESSAGE(WM_USER_THREAD_FINISHED, OnThreadFinished)
ON_MESSAGE(WM_USER_THREAD_UPDATE_PROGRESS, OnThreadUpdateProgress)
Then I write my own definition in the functions for OnThreadFinished and OnThreadUpdateProgress. Once we receive the message WM_USER_THREAD_UPDATE_PROGRESS, we will process the message and display it to the user.
Events
During the start of the application, we have an event called as:
g_eventStart.SetEvent();
So, it should start the event. We also have a call in the thread:
WaitForSingleObject(g_eventStart, INFINITE);
For a stop, we have a similar pair:
g_eventKill.SetEvent();
WaitForSingleObject(g_eventKill, 0) == WAIT_OBJECT_0
When we are reading and writing the data, we use the critical section locks so the global string variable is protected between threads.
Improvements
- Make an INI file and get the keys to be monitored.
- Change the
OnStart function to read it from the INI file and then iterate through it to initialize the thread. Due to the scope of this assignment, threads are restricted to watch only two keys. - Instead of using
MyThreadFunc, we can also use a wrapper class around CWinThread and functionality can be defined as we require. This is only required in large applications. - Change the global variable to a vector and store the strings in it so that we maintain the history of the changes. This can be later dumped into a file or into XML format.
- The registry keys can be outputted in XML format for easy storage and comparison. This can be an alternate way when we are monitoring a registry tree node and not a key.
Test Results
GUI

Figure 2: Test Results 1
References
[1] MSDN
[2] Code segment 4
History
- 22 October, 2007 -- Original version posted
