Introduction
In my first three articles on CodeProject, I explained the fundamentals of Windows Communication Foundation (WCF), including:
Starting last month, I have started to write a few articles to explain LINQ, LINQ to SQL, Entity Framework, and LINQ to Entities. Followings are the articles I wrote or plan to write for LINQ, LINQ to SQL, and LINQ to Entities:
After finishing these five articles, I will come back to write some more articles on WCF from my real work experience, which will be definitely helpful to your real world work if you are using WCF right now.
Overview
In the previous article, we learned a few new features of C# 3.0 for LINQ. In this article and the next, we will see how to use LINQ to interact with a SQL Server database, or in other words, how to use LINQ to SQL in C#.
In this article, we will cover the basic concepts and features of LINQ to SQL, which include:
- What is ORM
- What is LINQ to SQL
- What is LINQ to Entities
- Comparing LINQ to SQL with LINQ to Objects and LINQ to Entities
- Modeling the Northwind database in LINQ to SQL
- Querying and updating a database with a table
- Deferred execution
- Lazy loading and eager loading
- Joining two tables
- Querying with a view
In the next article, we will cover the advanced concepts and features of LINQ to SQL, such as Stored Procedure support, inheritance, simultaneous updating, and transaction processing.
ORM—Object-Relational Mapping
LINQ to SQL is considered to be one of Microsoft's new ORM products. So before we start explaining LINQ to SQL, let us first understand what ORM is.
ORM stands for Object-Relational Mapping. Sometimes it is called O/RM, or O/R mapping. It is a programming technique that contains a set of classes that map relational database entities to objects in a specific programming language.
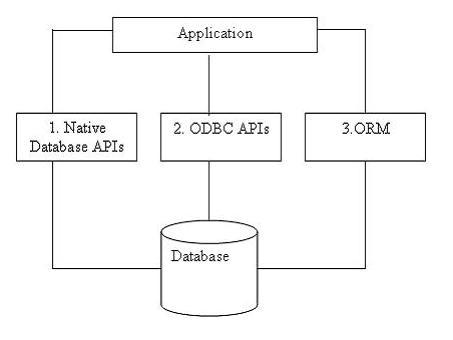
Initially, applications could call specified native database APIs to communicate with a database. For example, Oracle Pro*C is a set of APIs supplied by Oracle to query, insert, update, or delete records in an Oracle database from C applications. The Pro*C pre-compiler translates embedded SQL into calls to the Oracle runtime library (SQLLIB).
Then, ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) was developed to unify all of the communication protocols for various RDBMSs. ODBC was designed to be independent of programming languages, database systems, and Operating Systems. So with ODBC, an application could communicate with different RDBMSs by using the same code, simply by replacing the underlying ODBC drivers.
No matter which method is used to connect to a database, the data returned from a database has to be presented in some format in the application. For example, if an Order record is returned from the database, there has to be a variable to hold the Order number, and a set of variables to hold the Order details. Alternatively, the application may create a class for Orders and another class for Order details. When another application is developed, the same set of classes may have to be created again, or if it is designed well, they can be put into a library and re-used by various applications.
This is exactly where ORM fits in. With ORM, each database is represented by an ORM context object in the specific programming language, and database entities such as tables are represented by classes, with relationships between these classes. For example, the ORM may create an Order class to represent the Order table, and an OrderDetail class to represent the Order Details table. The Order class will contain a collection member to hold all of its details. The ORM is responsible for the mappings and the connections between these classes and the database. So, to the application, the database is now fully-represented by these classes. The application only needs to deal with these classes, instead of with the physical database. The application does not need to worry about how to connect to the database, how to construct the SQL statements, how to use the proper locking mechanism to ensure concurrency, or how to handle distributed transactions. These databases-related activities are handled by the ORM.
The following diagram shows the three different ways of accessing a database from an application. There are some other mechanisms to access a database from an application, such as JDBC and ADO.NET. However, to keep the diagram simple, they have not been shown here.
LINQ to SQL
LINQ to SQL is a component of the .NET Framework version 3.5 that provides a run-time infrastructure for managing relational data as objects.
In LINQ to SQL, the data model of a relational database is mapped to an object model expressed in the programming language of the developer. When the application runs, LINQ to SQL translates the language-integrated queries in the object model into SQL and sends them to the database for execution. When the database returns the results, LINQ to SQL translates them back to objects that you can work with in your own programming language.
LINQ to SQL fully supports transactions, views, Stored Procedures, and user-defined functions. It also provides an easy way to integrate data validation and business logic rules into your data model, and supports single table inheritance in the object model.
LINQ to SQL is one of Microsoft's new ORM products to compete with many existing ORM products for the .NET platform on the market, like the Open Source products NHibernate, NPersist, and commercial products LLBLGen and WilsonORMapper. LINQ to SQL has many overlaps with other ORM products, but because it is designed and built specifically for .NET and SQL Server, it has many advantages over other ORM products. For example, it takes the advantages of all the LINQ features and it fully supports SQL Server Stored Procedures. You get all the relationships (foreign keys) for all tables, and the fields of each table just become properties of its corresponding object. You have even the intellisense popup when you type in an entity (table) name, which will list all of its fields in the database. Also, all of the fields and the query results are strongly typed, which means you will get a compiling error instead of a runtime error if you miss spell the query statement or cast the query result to a wrong type. In addition, because it is part of the .NET Framework, you don’t need to install and maintain any third party ORM product in your production and development environments.
Under the hood of LINQ to SQL, ADO.NET SqlClient adapters are used to communicate with real SQL Server databases. We will see how to capture the generated SQL statements at runtime later in this article.
Below is a diagram showing the usage of LINQ to SQL in a .NET application:

We will explore LINQ to SQL features in detail in this article and the following article.
Comparing LINQ to SQL with LINQ to Objects
In the previous article, we used LINQ to query in-memory objects. Before we dive further to the world of LINQ to SQL, we will first look at the relationships between LINQ to SQL and LINQ to Objects.
Followings are some key differences between LINQ to SQL and LINQ to Objects:
- LINQ to SQL needs a Data Context object. The Data Context object is the bridge between LINQ and the database. LINQ to Objects doesn’t need any intermediate LINQ provider or API.
- LINQ to SQL returns data of type
IQueryable<T> while LINQ to Objects returns data of type IEnumerable<T>. - LINQ to SQL is translated to SQL by way of Expression Trees, which allow them to be evaluated as a single unit and translated to the appropriate and optimal SQL statements. LINQ to Objects does not need to be translated.
- LINQ to SQL is translated to SQL calls and executed on the specified database while LINQ to Objects is executed in the local machine memory.
The similarities shared between all aspects of LINQ are the syntax. They all use the same SQL like syntax and share the same groups of standard query operators. From a language syntax point, working with a database is the same as working with in-memory objects.
LINQ to Entities
For LINQ to SQL, another product that you will want to compare with is the .NET Entity Framework. Before comparing LINQ to SQL with the Entity Framework, let’s first see what Entity Framework is.
ADO.NET Entity Framework (EF) was first released with Visual Studio 2008 and .NET Framework 3.5 Service Pack 1. So far, many people view EF as just another ORM product from Microsoft, though by design it is supposed to be much more powerful than just an ORM tool.
With Entity Framework, developers work with a conceptual data model, an Entity Data Model, or EDM, instead of the underlying databases. The conceptual data model schema is expressed in the Conceptual Schema Definition Language (CSDL), the actual storage model is expressed in the Storage Schema Definition Language (SSDL), and the mapping in between is expressed in the Mapping Schema Language (MSL). A new data-access provider, EntityClient, is created for this new framework but under the hood, the ADO.NET data providers are still being used to communicate with the databases. The diagram below, which has been taken from the July 2008 issue of the MSDN Magazine, shows the architectures of the Entity Framework.

From the diagram, you can see that LINQ is one of the query languages that can be used to query against Entity Framework Entities. LINQ to Entities allows developers to create flexible, strongly typed queries against the Entity Data Model (EDM) by using LINQ expressions and the LINQ standard query operators. It is the same as what LINQ to SQL can do, though LINQ to Entities supports more features than LINQ to SQL, like multiple-table inheritance, and it supports many other mainstream RDBMS databases besides Microsoft SQL Server, like Oracle, DB2, and MySQL.
Comparing LINQ to SQL with LINQ to Entities
As described earlier, LINQ to Entities applications work against a conceptual data model (EDM). All mappings between the languages and the databases go through the new EntityClient mapping provider. The application no longer connects directly to a database or sees any database-specific construct; the entire application operates in terms of the higher-level EDM model.
This means that you can no longer use the native database query language; not only will the database not understand the EDM model, but also current database query languages do not have the constructs required to deal with the elements introduced by the EDM such as inheritance, relationships, complex-types, etc.
On the other hand, for developers that do not require mapping to a conceptual model, LINQ to SQL enables developers to experience the LINQ programming model directly over an existing database schema.
LINQ to SQL allows developers to generate .NET classes that represent data. Rather than mapping to a conceptual data model, these generated classes map directly to database tables, views, Stored Procedures, and user defined functions. Using LINQ to SQL, developers can write code directly against the storage schema using the same LINQ programming pattern as previously described for in-memory collections, Entities, or the DataSet, as well as other data sources such as XML.
Compared to LINQ to Entities, LINQ to SQL has some limitations, mainly because of its direct mapping against the physical relational storage schema. For example, you can’t map two different database entities into one single C# or VB object, and underlying database schema changes might require significant client application changes.
So in summary, if you want to work against a conceptual data model, use LINQ to Entities. If you want to have a direct mapping to the database from your programming languages, use LINQ to SQL.
The table below lists some supported features by these two data access methodologies:
Features
| LINQ to SQL
| LINQ to Entities
|
Conceptual Data Model
| No
| Yes
|
Storage Schema
| No
| Yes
|
Mapping Schema
| No
| Yes
|
New Data Access Provider
| No
| Yes
|
Non-SQL Server Database Support
| No
| Yes
|
Direct Database Connection
| Yes
| No
|
Language Extensions Support
| Yes
| Yes
|
Stored Procedures
| Yes
| Yes
|
Single-table Inheritance
| Yes
| Yes
|
Multiple-table Inheritance
| No
| Yes
|
Single Entity from Multiple Tables
| No
| Yes
|
Lazy Loading Support
| Yes
| Yes
|
We will use LINQ to SQL in this article, because we will use it in the data access layer, and the data access layer is only one of the three layers for a WCF service. LINQ to SQL is much less complex than LINQ to Entities, so we can still cover it in the same article with WCF. However, once you have learned how to develop WCF services with LINQ to SQL through this article, and you have learned how to use LINQ to Entities through some other means, you can easily migrate your data access layer to using LINQ to Entities.
Creating a LINQtoSQL Test Application
Now that we have learned some basic concepts of LINQ to SQL, next let’s start exploring LINQ to SQL with real examples.
First, we need to create a new project to test LINQ to SQL. We will reuse the solution we have created in the previous article (Introducing LINQ—Language Integrated Query). If you haven't read that article, you can just download the source file from that article, or create a new solution TestLINQ.
You will also need to have a SQL Server database with the sample database Northwind installed. You can just search "Northwind dample database download", then download and install the sample database. If you need detailed instructions as how to download/install the sample database, you can refer to the section "Preparing the Database" in one of my previous articles, Implementing a WCF Service with Entity Framework".
Now follow these steps to add a new application to the solution:
- Open (or create) the solution TestLINQ.
- From Solution Explorer, right click on the solution item and select Add | New Project … from the context menu.
- Select Visual C# | Windows as the project type, and Console Application as the project template, enter TestLINQToSQLApp as the (project) name, and D:\SOAwithWCFandLINQ\Projects\TestLINQ\TestLINQToSQLApp as the location.
- Click OK.
Modeling the Northwind Database
The next thing to do is to model the Northwind database. We will now drag and drop two tables and one view from the Northwind database to our project, so later on we can use them to demonstrate LINQ to SQL.
Adding a LINQ to SQL Item to the Project
To start with, let’s add a new item to our project TestLINQToSQLApp. The new item added should be of type LINQ to SQL Classes, and named Northwind, like in the Add New Item dialog window shown below.

After you click the button Add, the following three files will be added to the project: Northwind.dbml, Northwind.dbml.layout, and Northwind.designer.cs. The first file holds the design interface for the database model, while the second one is the XML format of the model. Only one of them can remain open inside the Visual Studio IDE. The third one is the code-behind for the model which defines the DataContext of the model.
At this point, the Visual Studio LINQ to SQL designer should be open and empty, like the following diagram:

Connecting to the Northwind Database
Now we need to connect to our Northwind sample database in order to drag and drop objects from the database.
- Open the Server Explorer window from the left most side of the IDE. You can hover your mouse over Server Explorer and wait for a second, or click on the Server Explorer to open it. If it is not visible in your IDE, select the menu View | Server Explorer, or press Ctrl+Alt+S to open it.
- From Server Explorer, right click on Data Connections and select Add Connection to bring the add connection window. In this window, specify your server name (including your instance name if it is not a default installation), logon information, and choose Northwind as the database. You can click the button Test Connection to make sure everything is set correctly.

- Click OK to add this connection. From now on, Visual Studio will use this database as the default database for your project. You can look at the new file Properties\Settings.Designer.cs for more information.
Adding Tables and Views to the Design Surface
The new connection Northwind.dbo should appear in the Server Explorer now. Next, we will drag and drop two tables and one view to the LINQ to SQL design surface.
- Expand the connection until all the tables are listed, and drag Products to the Northwind.dbml design surface. You should have a screen like in this diagram:

- Then drag the Categories table from Server Explorer to the Northwind.dbml design surface.
- We will also need to query data using a view, so drag the view Current Product List from Server Explorer to the Northwind.dbml design surface.
The Northwind.dbml design surface on your screen should look like this:

Generated LINQ to SQL Classes
If you open the file Northwind.Designer.cs, you will find following classes are generated for the project:
public partial class NorthwindDataContext : System.Data.Linq.DataContext
public partial class Product : INotifyPropertyChanging, INotifyPropertyChanged
public partial class Category : INotifyPropertyChanging, INotifyPropertyChanged
public partial class Current_Product_List
Among the above four classes, the DataContext class is the main conduit by which we'll query entities from the database as well as apply changes back to it. It contains various flavors of types and constructors, partial validation methods, and property members for all the included tables. It inherits from the System.Data.Linq.DataContext class which represents the main entry point for the LINQ to SQL framework.
The next two classes are for those two tables we are interested in. They all implement the INotifyPropertyChanging and INotifyPropertyChanged interfaces. These two interfaces define all the related property changing and property changed event methods, which we can extend to validate properties before and after the change.
The last class is for the view. It is a simple class with only two property members. Since we are not going to update the database through this view, it doesn’t define any property changing or changed event method.
Querying and Updating the Database with a Table
Now that we have the entity classes created, we will use them to interact with the database. We will first work with the products table to query, update records, as well as to insert and delete records.
Querying Records
First, we will query the database to get some products.
To query a database using LINQ to SQL, we first need to construct a DataContext object, like this:
NorthwindDataContext db = new NorthwindDataContext();
Then we can use this LINQ query syntax to retrieve records from the database:
IEnumerable<Product> beverages = from p in db.Products
where p.Category.CategoryName == "Beverages"
orderby p.ProductName
select p;
The preceding code will retrieve all products in the Beverages category sorted by product name.
Updating Records
We can update any of the products that we have just retrieved from the database, like this:
Product bev1 = beverages.ElementAtOrDefault(10);
if (bev1 != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("The price of {0} is {1}. Update to 20.0",
bev1.ProductName, bev1.UnitPrice);
bev1.UnitPrice = (decimal)20.00;
}
db.SubmitChanges();
We used ElementAtOrDefault, not the ElementAt method, just in case there is no product at element 10. Though, in the sample database, there are 12 beverage products, and the 11th (element 10 starting from index 0) is Steeleye Stout, whose unit price is 18.00. We change its price to 20.00, and called db.SubmitChanges() to update the record in the database. After you run the program, if you query the product with ProductID 35, you will find its price is now 20.00.
Inserting Records
We can also create a new product, then insert this new product into the database, like in the following code:
Product newProduct = new Product {ProductName="new test product" };
db.Products.InsertOnSubmit(newProduct);
db.SubmitChanges();
Deleting Records
To delete a product, we first need to retrieve it from the database, then just call the DeleteOnSubmit method, like in the following code:
Product delProduct = (from p in db.Products
where p.ProductName == "new test product"
select p).FirstOrDefault();
if(delProduct != null)
db.Products.DeleteOnSubmit(delProduct);
db.SubmitChanges();
Running the Program
The file Program.cs so far is followed. Note that we declared db as a class member, and added a method to contain all the test cases for the table operations. We will add more methods to test other LINQ to SQL functionalities.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data.Linq;
namespace TestLINQToSQLApp
{
class Program
{
static NorthwindDataContext db = new NorthwindDataContext();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestTables();
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void TestTables()
{
IEnumerable<Product> beverages = from p in db.Products
where p.Category.CategoryName == "Beverages"
orderby p.ProductName
select p;
Console.WriteLine("There are {0} Beverages", beverages.Count());
Product bev1 = beverages.ElementAtOrDefault(10);
if (bev1 != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("The price of {0} is {1}. Update to 20.0",
bev1.ProductName, bev1.UnitPrice);
bev1.UnitPrice = (decimal)20.0;
}
db.SubmitChanges();
Product newProduct = new Product { ProductName = "new test product" };
db.Products.InsertOnSubmit(newProduct);
db.SubmitChanges();
Product newProduct2 = (from p in db.Products
where p.ProductName == "new test product"
select p).SingleOrDefault();
if (newProduct2 != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("new product inserted with product ID {0}",
newProduct2.ProductID);
}
Product delProduct = (from p in db.Products
where p.ProductName == "new test product"
select p).FirstOrDefault();
if (delProduct != null)
{
db.Products.DeleteOnSubmit(delProduct);
}
db.SubmitChanges();
}
}
}
If you run the program, the output will be:

Deferred Execution
One important thing to remember when working with LINQ to SQL is the deferred execution of LINQ.
The standard query operators differ in the timing of their execution, depending on whether they return a singleton value or a sequence of values. Those methods that return a singleton value (for example, Average and Sum) execute immediately. Methods that return a sequence defer the query execution and return an enumerable object. Those methods do not consume the target data until the query object is enumerated. This is known as deferred execution.
In the case of methods that operate on in-memory collections, that is, those methods that extend IEnumerable<(Of <(T>)>), the returned enumerable object captures the arguments that were passed to the method. When that object is enumerated, the logic of the query operator is employed and the query results are returned.
In contrast, methods that extend IQueryable<(Of <(T>)>) do not implement any querying behavior, but build an expression tree that represents the query to be performed. The query processing is handled by the source IQueryable<(Of <(T>)>) object.
Checking Deferred Execution with SQL Profiler
There are two ways to see when the query is executed. The first is Open Profiler (All Programs\Microsoft SQL Server 2005(or 2008)\Performance Tools\SQL 2005(or 2008) Profiler); start a new trace to the Northwind database engine, then debug the program. For example, when the following statement is executed, there is nothing in the profiler:
IEnumerable<Product> beverages = from p in db.Products
where p.Category.CategoryName == "Beverages"
orderby p.ProductName
select p;
However, when the following statement is being executed, from the profiler, you will see a query is executed in the database:
Console.WriteLine("There are {0} Beverages", beverages.Count());
The query executed in the database is like this:
exec sp_executesql N'SELECT [t0].[ProductID], [t0].[ProductName], [t0].[SupplierID],
[t0].[CategoryID], [t0].[QuantityPerUnit], [t0].[UnitPrice],
[t0].[UnitsInStock], [t0].[UnitsOnOrder], [t0].[ReorderLevel], [t0].[Discontinued]
FROM [dbo].[Products] AS [t0]
LEFT OUTER JOIN [dbo].[Categories] AS [t1] ON [t1].[CategoryID] = [t0].[CategoryID]
WHERE [t1].[CategoryName] = @p0
ORDER BY [t0].[ProductName]',N'@p0 nvarchar(9)',@p0=N'Beverages'
The profiler window should be like this diagram:

From the profiler, we know under the hood that LINQ actually called sp_executesql, and it also used a left outer join to get the categories of products.
Checking Deferred Execution with SQL Logs
Another way to trace the execution time of a LINQ statement is using logs. The DataContext class provides a method to log every SQL statement it executes. To see the logs, we can first add this statement to the program in the beginning, right after Main:
db.Log = Console.Out;
Then we can add this statement right after the variable beverages is defined, but before its Count is referenced:
Console.WriteLine("After query syntax is defined, before it is referenced.");
So the first few lines of statements are now like this:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
db.Log = Console.Out;
TestTables();
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void TestTables()
{
IEnumerable<Product> beverages = from p in db.Products
where p.Category.CategoryName == "Beverages"
orderby p.ProductName
select p;
Console.WriteLine("After query syntax beverages is defined, " +
"before it is referenced.");
Console.WriteLine("There are {0} Beverages", beverages.Count());
Now if you run the program, the output will be like this:

From the logs, we see the query is not executed when the query syntax is defined. Instead, it is executed when beverages.Count() is being called.
Deferred Execution for Singleton Methods
But if the query expression will return a singleton value, the query will be executed immediately while it is defined. For example, we can add this statement to get the average price of all products:
decimal? averagePrice = (from p in db.Products
select p.UnitPrice).Average();
Console.WriteLine("After query syntax averagePrice is defined, before it is referenced.");
Console.WriteLine("The average price is {0}", averagePrice);
The output is like this:

From this output, we know the query is executed at the same time when the query syntax is defined.
Deferred Execution for Singleton Methods Within Sequence Expressions
However, just because a query is using one of those singleton methods like Sum, Average, or Count, it doesn’t mean the query will be executed when it is defined. If the query result is a sequence, the execution will still be deferred. Following is an example of this kind of query:
var cheapestProductsByCategory =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new
{
CategoryID = g.Key,
CheapestProduct =
(from p2 in g
where p2.UnitPrice == g.Min(p3 => p3.UnitPrice)
select p2).FirstOrDefault()
};
Console.WriteLine("Cheapest products by category:");
foreach (var p in cheapestProductsByCategory)
{
Console.WriteLine("categery {0}: product name: {1} price: {2}",
p.CategoryID, p.CheapestProduct.ProductName, p.CheapestProduct.UnitPrice);
}
If you run the above query, you will see it is executed when the result is being printed, not when the query is being defined. Part of the result is like this:

From this output, you can see when the result is being printed, it first goes to the database to get the minimum price for each category, then for each category, it goes to the database again to get the first product with that price. Though in a real product, you probably don’t want to write so complex a query in your application code, but put it in a Stored Procedure.
Deferred (Lazy) Loading Versus Eager Loading
In one of the above examples, we retrieved the category name of a product by this expression:
p.Category.CategoryName == "Beverages"
Even though there is no such field called category name in the Products table, we can still get the category name of a product because there is an association between the Products and Category table. On the Northwind.dbml design surface, click on the line between the Products and Categories tables and you will see all the properties of the association. Note, its participating properties are Category.CategoryID -> Product.CategoryID, meaning category ID is the key field to link these two tables.
Because of this association, we can retrieve the category for each product, and on the other hand, we can also retrieve the products for each category.
Lazy Loading by Default
However, even with the association, the associated data is not loaded when the query is executed. For example, if we retrieve all categories like this:
var categories = from c in db.Categories select c;
And later on we need to get the products for each category, the database has to be queried again. This diagram shows the execution result of the query:

From this diagram, we know that LINQ first goes to the database to query all categories, then for each category, when we need to get the total count of products, it goes to the database again to query all the products for that category.
This is because by default, lazy loading is set to true, meaning all associated data (children) are deferred loaded until needed.
Eager Loading With Load Options
To change this behavior, we can use the LoadWith method to tell the DataContext to automatically load the specified children in the initial query, like this:
DataLoadOptions dlo2 = new DataLoadOptions();
dlo2.LoadWith<Category>(c => c.Products);
NorthwindDataContext db2 = new NorthwindDataContext();
db2.Log = Console.Out;
db2.LoadOptions = dlo2;
var categories2 = from c in db2.Categories select c;
foreach (var category2 in categories2)
{
Console.WriteLine("There are {0} products in category {1}",
category2.Products.Count(), category2.CategoryName);
}
db2.Dispose();
Note: DataLoadOptions is in the namespace System.Data.Linq, so you have to add a using statement to the program:
using System.Data.Linq;
Also, we have to create a new DataContext instance for this test, because we have ran some queries again the original db DataContext, and it is no longer possible to change its LoadOptions.
Now after the category is loaded, all its children (products) will be loaded too. This can be proved from this diagram:

As you can see from this diagram, all products for all categories are loaded in the first query.
Filtered Loading With Load Options
While LoadWith is used to eager load all children, AssociateWith can be used to filter which children to load with. For example, if we only want to load products for categories 1 and 2, we can write this query:
DataLoadOptions dlo3 = new DataLoadOptions();
dlo3.AssociateWith<Category>(
c => c.Products.Where(p => p.CategoryID == 1 || p.CategoryID == 2));
NorthwindDataContext db3 = new NorthwindDataContext();
db3.LoadOptions = dlo3;
db3.Log = Console.Out;
var categories3 = from c in db3.Categories select c;
foreach (var category3 in categories3)
{
Console.WriteLine("There are {0} products in category {1}",
category3.Products.Count(), category3.CategoryName);
}
db3.Dispose();
Now if we query all categories and print out the products count for each category, we will find that only the first two categories contain products, all other categories have no product at all, like in this diagram:

Combining Eager Loading and Filtered Loading
However, from the output above, you can see it is lazy loading. If you want eager loading products with some filters, you can combine LoadWith and AssociateWith, like in the following code:
DataLoadOptions dlo4 = new DataLoadOptions();
dlo4.LoadWith<Category>(c => c.Products);
dlo4.AssociateWith<Category>(c => c.Products.Where(
p => p.CategoryID == 1 || p.CategoryID == 2));
NorthwindDataContext db4 = new NorthwindDataContext();
db4.Log = Console.Out;
db4.LoadOptions = dlo4;
var categories4 = from c in db4.Categories select c;
foreach (var category4 in categories4)
{
Console.WriteLine("There are {0} products in category {1}",
category4.Products.Count(), category4.CategoryName);
}
db4.Dispose();
The output is like this diagram:

Note for each field of an entity, you can also set its Delay Loaded property to change its loading behavior. This is different from the children lazy/eager loading, as it only affects one property of that particular entity.
Joining Two Tables
While associations are kinds of joins, in LINQ, we can also explicitly join two tables using the keyword Join, like in the following code:
var categoryProducts =
from c in db.Categories
join p in db.Products on c.CategoryID equals p.CategoryID into products
select new {c.CategoryName, productCount = products.Count()};
foreach (var cp in categoryProducts)
{
Console.WriteLine("There are {0} products in category {1}",
cp.CategoryName, cp.productCount);
}
It is not so useful in the above example because the tables Products and Categories are associated with a foreign key relationship. When there is no foreign key association between two tables, this will be particularly useful.
From the output, we can see only one query is executed to get the results:

Besides joining two tables, you can also join three or more tables, join self, create left /right outer join, or join using composite keys.
Querying With a View
Querying with a view is the same as with a table. For example, you can call the view “current product lists” like this:
var currentProducts = from p in db.Current_Product_Lists
select p;
foreach (var p in currentProducts)
{
Console.WriteLine("Product ID: {0} Product Name: {1}",
p.ProductID, p.ProductName);
}
This will get all the current products using the view.
Summary
In this article, we have learned what an ORM is, why we need an ORM, and what LINQ to SQL is. We also compared LINQ to SQL with LINQ to Entities and explored some basic features of LINQ to SQL.
The key points in this article include:
- An ORM product can greatly ease data access layer development.
- LINQ to SQL is one of Microsoft’s ORM products to use LINQ against SQL Server databases.
- The built-in LINQ to SQL designer in Visual Studio 2008 can be used to model databases.
- You can connect to a database in Visual Studio 2008 Server Explorer then drag and drop database items to the LINQ to SQL design surface.
- The class
System.Data.Linq.DataContext is the main class for LINQ to SQL applications. - LINQ methods that return a sequence defer the query execution and you can check the execution timing with Profiler, or SQL logs.
- LINQ query expressions that return a singleton value will be executed immediately while they are defined.
- By default, associated data is deferred (lazy) loaded. You can change this behavior with the
LoadWith option. - Associated data results can be filtered with the
AssociateWith option. - Options
LoadWith and AssociateWith can be combined together to eager load associated data with filters. - The
Join operator can be used to join multiple tables and views. - Views can be used to query a database in LINQ to SQL just like tables.
Note: this article is based on chapter 10 of my old book "WCF Multi-tier Services Development with LINQ" (ISBN 1847196624). Since LINQ to SQL is now not preferred by Microsoft, this book has been upgraded to using LINQ to Entities in my new book "WCF 4.0 Multi-tier Services Development with LINQ to Entities" (ISBN 1849681147). Both books are hands-on guides to learn how to build SOA applications on the Microsoft platform, with the old one using WCF and LINQ to SQL in Visual Studio 2008 and the new one using WCF and LINQ to Entities in Visual Studio 2010.
With either book, you can learn how to master WCF and LINQ to SQL/LINQ to Entities concepts by completing practical examples and applying them to your real-world assignments. They are among the first of few books to combine WCF and LINQ to SQL/LINQ to Entities in a multi-tier real-world WCF Service. They are ideal for beginners who want to learn how to build scalable, powerful, easy-to-maintain WCF Services. Both books are rich with example code, clear explanations, interesting examples, and practical advice. They are truly hands-on books for C++ and C# developers.
You don't need to have any experience in WCF or LINQ to SQL/LINQ to Entities to read either book. Detailed instructions and precise screenshots will guide you through the whole process of exploring the new worlds of WCF and LINQ to SQL/LINQ to Entities. These two books are distinguished from other WCF and LINQ to SQL/LINQ to Entities books by that, they focus on how to do it, not why to do it in such a way, so you won't be overwhelmed by tons of information about WCF and LINQ to SQL/LINQ to Entities. Once you have finished one of the books, you will be proud that you have been working with WCF and LINQ to SQL/LINQ to Entities in the most straightforward way.
You can buy either book from Amazon (search WCF and LINQ), or from the publisher's website at https://www.packtpub.com/wcf-4-0-multi-tier-services-development-with-linq-to-entities/book.
