Introduction
As discussed in Components, Aspects, and Dynamic Decorator, application development involves tasks specific to an application type and tasks independent of an application type. This separation of tasks is significant in not only helping you decide on processing strategy, deployment strategy, test strategy, UI strategy, etc., based on specific technologies associated with an application type, but also in helping you address the application-type-independent, a.k.a. common, tasks like designing/extending components and addressing cross-cutting concerns systematically. Several guidelines are discussed for development of these common tasks. The Dynamic Decorator is used to address these tasks by following these guidelines. A WinForms application is used as an example.
In this article, I demonstrate how the principles and guidelines are applied to a different application type - MVC/AJAX/REST application - by using the Dynamic Decorator.
Choose Application Type
There are several application types in the .NET world: WinForms, ASP.NET, ASP.NET MVC, and Silverlight. A WinForms application offers rich user interactions and client processing power. An ASP.NET application has the advantages of deployment and maintenance via the Web. ASP.NET MVC offers testability plus advantages of ASP.NET. A Silverlight application offers a rich user interface over the Web. Different types of applications have different technology specifics, which may or may not meet your requirements. You should choose your application type based on your processing strategy, deployment strategy, maintenance strategy, test strategy, UI strategy, etc.
In addition, AJAX technologies can be employed to enhance web applications (ASP.NET, ASP.NET MVC, or Silverlight) to create a more interactive user experience.
Different application types also have different application programming models, UI elements, state management, event processing models, etc. You need to address tasks related to an application type once you select the application type for your application.
Address Common Tasks
In addition to the tasks specific to an application type, there are also tasks independent of a particular application type in application development. For instance, regardless of application types, you face tasks like designing, extending components, and addressing cross-cutting concerns. They are common for all application types.
A set of principles are given for the development of these common tasks in the article Components, Aspects, and Dynamic Decorator. They are listed here again as follows:
- Design components to meet business requirements in a general way
- Design aspects as global methods in their own modules
- Add aspects to objects as needed
- Extend objects as needed
Please refer to Components, Aspects, and Dynamic Decorator for details of the discussion about these principles. You may also need to read the article Dynamic Decorator Pattern to understand the Dynamic Decorator, and read the article Add Aspects to an Object Using Dynamic Decorator to understand Aspects programming using Dynamic Decorator.
Example
In the following sections, an example application is discussed to demonstrate how the above principles are applied to an MVC/AJAX/REST application by using the Dynamic Decorator.
The same problem discussed in Components, Aspects, and Dynamic Decorator as an example is used here. This time, we choose an MVC/AJAX/REST application as the application type instead of a WinForms application. For convenience, I state the problem again as follows.
Problem
Displays employees based on the selection of a department.
Components
Assume there are two components, Employee and Department. For Employee, there is a corresponding RepositoryEmployee component to contain a collection of objects of Employee. For Department, there is a corresponding RepositoryDepartment component to contain a collection of objects of Department. The code of these components is listed as follows.
public interface IEmployee
{
System.Int32? EmployeeID { get; set; }
System.String FirstName { get; set; }
System.String LastName { get; set; }
System.DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
System.Int32? DepartmentID { get; set; }
System.String FullName();
System.Single Salary();
}
public class Employee : IEmployee
{
#region Properties
public System.Int32? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public System.String FirstName { get; set; }
public System.String LastName { get; set; }
public System.DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public System.Int32? DepartmentID { get; set; }
#endregion
public Employee(
System.Int32? employeeid
, System.String firstname
, System.String lastname
, System.DateTime bDay
, System.Int32? departmentID
)
{
this.EmployeeID = employeeid;
this.FirstName = firstname;
this.LastName = lastname;
this.DateOfBirth = bDay;
this.DepartmentID = departmentID;
}
public Employee() { }
public System.String FullName()
{
System.String s = FirstName + " " + LastName;
return s;
}
public System.Single Salary()
{
System.Single i = 10000.12f;
return i;
}
}
public interface IDepartment
{
System.Int32? DepartmentID { get; set; }
System.String Name { get; set; }
}
public class Department : IDepartment
{
#region Properties
public System.Int32? DepartmentID { get; set; }
public System.String Name { get; set; }
#endregion
public Department(
System.Int32? departmentid
, System.String name
)
{
this.DepartmentID = departmentid;
this.Name = name;
}
public Department() { }
}
public interface IRepository<T>
{
List<T> RepList { get; set; }
void GetAll();
}
public class RepositoryEmployee : IRepository<IEmployee>
{
private List<IEmployee> myList = null;
public List<IEmployee> RepList
{
get { return myList; }
set { myList = value; }
}
public RepositoryEmployee()
{
}
public void GetAll()
{
myList = new List<IEmployee> {
new Employee(1, "John", "Smith", new DateTime(1990, 4, 1), 1),
new Employee(2, "Gustavo", "Achong", new DateTime(1980, 8, 1), 1),
new Employee(3, "Maxwell", "Becker", new DateTime(1966, 12, 24), 2),
new Employee(4, "Catherine", "Johnston", new DateTime(1977, 4, 12), 2),
new Employee(5, "Payton", "Castellucio", new DateTime(1959, 4, 21), 3),
new Employee(6, "Pamela", "Lee", new DateTime(1978, 9, 16), 4) };
}
}
public class RepositoryDepartment : IRepository<IDepartment>
{
private List<IDepartment> myList = null;
public List<IDepartment> RepList
{
get { return myList; }
set { myList = value; }
}
public RepositoryDepartment()
{
}
public void GetAll()
{
myList = new List<IDepartment> { new Department(1, "Engineering"),
new Department(2, "Sales"),
new Department(3, "Marketing"),
new Department(4, "Executive") };
}
}
In this application, the data for employees and departments is hard-coded in two lists to simplify our discussion. In a real world application, these data are normally persisted in a relational database. Then, you will need to create a data layer to retrieve them and put them in lists.
It is worth noting that the employee list is populated by the inserting order without any kind of sorting in place. It is difficult to anticipate what kinds of sorting to support for this component at this time. In applications, an object of the component may need to sort by last name. Another may need to sort by birth day. A third may not need to sort at all. So, it is better to defer the implementation of sorting until the component is used in an application. By designing the component RepositoryEmployee without concerning about sorting, the Principle "Design components to meet business requirements in a general way" is followed. This way, the component is stable and closed.
HRMVCAjax
Normally, a response from a web application refreshes the entire page. For example, when a department is selected, the entire page is refreshed to display the employees associated with the selected department. It is more desirable that only part of the page, the employee table, is refreshed when a department is selected. This can be achieved using AJAX.
AJAX is a set of client-side technologies within a web application. You can apply AJAX to different types of web applications: ASP.NET, ASP.NET MVC, PHP, etc. For this example, we choose ASP.NET MVC as our web application. Also, you have a few choices in terms of implementing AJAX: native JavaScript, ASP.NET AJAX Framework, jQuery, etc. For our example, we use jQuery. Last, you have to decide on how to serve the AJAX requests. For this example, we choose WCF REST service to serve AJAX requests.
HRMVCAjax is an ASP.NET MVC application which uses the above components to display employees based on the selection of a department. Since it is an ASP.NET MVC application, it follows ASP.NET MVC's application programming model and event model. The Controller code is listed as follows:
public class DepEmployeesController : Controller
{
private IRepository<IEmployee> rpEmployee = null;
private IRepository<IDepartment> rpDepartment = null;
public DepEmployeesController()
{
rpEmployee = new RepositoryEmployee();
rpDepartment = new RepositoryDepartment();
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
rpDepartment.GetAll();
rpEmployee.GetAll();
List<SelectListItem> depList = new List<SelectListItem>();
SelectListItem sli = null;
sli = new SelectListItem();
sli.Value = "";
sli.Text = "";
depList.Add(sli);
foreach (IDepartment d in rpDepartment.RepList)
{
sli = new SelectListItem();
sli.Value = d.DepartmentID.Value.ToString();
sli.Text = d.Name;
depList.Add(sli);
}
ViewData["depSel"] =
new SelectList(depList, "Value", "Text");
return View(rpEmployee.RepList);
}
}
The View code is listed as follows:
<%@ Page Title="" Language="C#"
MasterPageFile="~/Views/Shared/Site.Master" Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewPage<dynamic>" %>
<asp:Content ID="Content2" ContentPlaceHolderID="MainContent" runat="server">
<% Html.BeginForm("Index", "DepEmployees"); %>
<span>Department</span><br />
<%= Html.DropDownList("depSel")%>
<br /> <br />
<span>Employees</span><br />
<div id="grid">
<table cellspacing="0" rules="all" border="1"
id="GridView1" style="border-collapse:collapse;">
<tr>
<th>EmployeeID</th><th>FirstName</th>
<th>LastName</th><th>DateOfBirth</th><th>DepartmentID</th>
</tr>
<% foreach (var itm in Model) { %>
<tr>
<td><%= itm.EmployeeID %></td><td><%= itm.FirstName%></td>
<td><%= itm.LastName%></td><td><%= itm.DateOfBirth%></td>
<td><%= itm.DepartmentID%></td>
</tr>
<% } %>
</table>
</div>
<% Html.EndForm(); %>
<script type='text/javascript'>
$(document).ready(function () {
$("select").change(function () {
$.get("HRRestService?dep=" + $(this).val(), function (data) {
$("#grid").html(
'<table cellspacing="0" rules="all" border="1" id="emp"
style="border-collapse:collapse;">' +
'<tr>' +
'<th>EmployeeID</th><th>FirstName</th><th>LastName</th>
<th>DateOfBirth</th><th>DepartmentID</th>' +
'</tr>');
$(data).find("Employee").each(function() {
$("#emp").append(
'<tr>' +
'<td>' + $(this).find("EmployeeID").text() + '</td><td>' +
$(this).find("FirstName").text() + '</td><td>' +
$(this).find("LastName").text() + '</td><td>' +
$(this).find("DateOfBirth").text() + '</td><td>' +
$(this).find("DepartmentID").text() + '</td>' +
'</tr>'
);
});
$("#grid").append('</table>');
});
});
})
</script>
</asp:Content>
Pay attention to the above Javascript code written in jQuery. When a department is selected, an AJAX request is sent to a service HRRestService with the selected department ID as query string. The service returns an XML data file which contains a list of employees associated with the selected department. The callback function parses the XML data and uses that to update the employee table in the page.
The code for the HRRestService service is as follows:
[ServiceContract]
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(
RequirementsMode = AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)]
[ServiceBehavior(InstanceContextMode = InstanceContextMode.PerCall)]
public class HRRestService
{
private static int iStaticDep = 0;
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "?dep={dep}")]
public List<Employee> EmployeesByDepartment(string dep)
{
IRepository<IEmployee> rpEmployee = null;
IRepository<IDepartment> rpDepartment = null;
rpEmployee = new RepositoryEmployee();
rpDepartment = new RepositoryDepartment();
rpDepartment.GetAll();
rpEmployee.GetAll();
IDepartment dpSel = rpDepartment.RepList[Convert.ToInt16(dep) - 1];
iStaticDep = dpSel.DepartmentID.Value;
List<IEmployee> empSel = null;
if (rpEmployee.RepList != null)
{
empSel = rpEmployee.RepList.FindAll(
(IEmployee emp) => { return emp.DepartmentID.Value == iStaticDep; });
}
List<Employee> empObj = new List<Employee>();
foreach (IEmployee i in empSel)
{
empObj.Add((Employee)i);
}
return empObj;
}
}
This is a WCF REST service. It accepts a department ID and returns a list of employees to the client.
When a browser accesses the application the first time, the MVC controller creates both the department list and the employee table, and sends the response back to the client. Then, when a department is selected, the jQuery code makes an AJAX request to the REST service with the selected department ID. Once the service responds back, the callback function refreshes the employee table to display the employees associated with the selected department.
When it runs, all employees are displayed as follows:
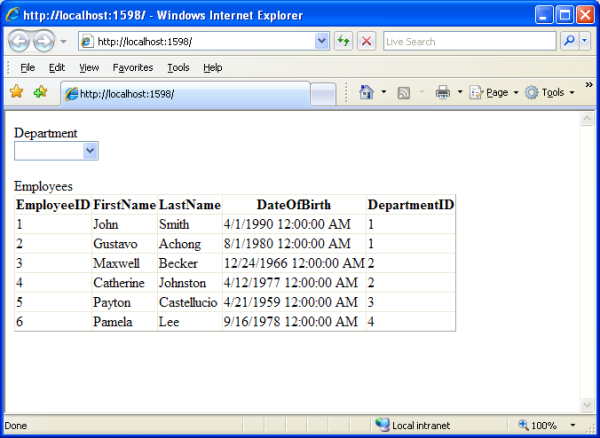
When a department is selected, the employees for that department are displayed.

Note that only the employee table is refreshed while the department dropdown control is not, and therefore is still highlighted.
Sort Employee List
Now, let's say you want the object rpEmployee, an instance of the RepositoryEmployee component, to have the functionality of sorting employees by last name. Here is what you need to do.
First, you create a comparer class for the sorting, as follows:
internal class EmployeeLastnameComparer : IComparer<IEmployee>
{
public int Compare(IEmployee e1, IEmployee e2)
{
return String.Compare(e1.LastName, e2.LastName);
}
}
Then, call the Dynamic Decorator just before the rpEmployee.GetAll() in the action Index of the DepEmployeesController, as follows:
rpEmployee = (IRepository<IEmployee>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpEmployee,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
null,
new Decoration((x, y) =>
{
object target = x.Target;
if (target.GetType().ToString() == "ThirdPartyHR.RepositoryEmployee")
{
List<IEmployee> emps = ((IRepository<IEmployee>)target).RepList;
IEnumerable<IEmployee> query = emps.OrderByDescending(emp => emp,
new EmployeeLastnameComparer()).ToList<IEmployee>();
((IRepository<IEmployee>)target).RepList = (List<IEmployee>)query;
}
}, null));
The above code needs to be applied to the EmployeesByDepartment method of HRRestService just before rpEmployee.GetAll().
That's it. Now, your HRMVCAjax displays employees sorted by their last names. Build it and run it. You will see that the employees are displayed and ordered by their last names, as follows.

When you select a department, the employees associated with this department are displayed and ordered by their last names.

Note that a Lambda expression is used to provide an anonymous method for this employee repository object to add sorting capability. Of course, you can use a normal method for the sorting logic. However, since this sorting logic is particularly for the employee repository object rpEmployee and not shared by other objects, it is more concise to keep it in an anonymous method.
There are a few points worth noting here. First, the Principle "Extend objects as needed" is followed. When we designed the component RepositoryEmployee, the sorting requirements were not clear yet. By the time we used the object rpEmployee in the application, it was clear that we need to sort the employee list by employee's last name. So, we extended this object to sort employee list by employee's last name. Second, the sorting capability was attached to the object rpEmployee without modifying its component or deriving from it. Third, the object rpEmployee is the one and the only one instance of the RepositoryEmployee component which has sorting functionality, independent of other instances created by RepositoryEmployee.
Design Aspects
Say, you want your HRMVCAjax application to address cross-cutting concerns of entering/exiting logging and security checking. By following the Principle "Design aspects as global methods in their own modules", these aspects are put in a class SysConcerns as individual public methods and packed in their own module. The following is the code for these concerns.
public class SysConcerns
{
public static void EnterLog(AspectContext ctx, object[] parameters)
{
StackTrace st = new StackTrace(new StackFrame(4, true));
Console.Write(st.ToString());
IMethodCallMessage method = ctx.CallCtx;
string str = "Entering " + ctx.Target.GetType().ToString() +
"." + method.MethodName + "(";
int i = 0;
foreach (object o in method.Args)
{
if (i > 0)
str = str + ", ";
str = str + o.ToString();
}
str = str + ")";
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.Out.Flush();
}
public static void ExitLog(AspectContext ctx, object[] parameters)
{
IMethodCallMessage method = ctx.CallCtx;
string str = "Exiting " + ctx.Target.GetType().ToString() +
"." + method.MethodName + "(";
int i = 0;
foreach (object o in method.Args)
{
if (i > 0)
str = str + ", ";
str = str + o.ToString();
}
str = str + ")";
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.Out.Flush();
}
public static void AdminCheck(AspectContext ctx, object[] parameters)
{
Console.WriteLine("Has right to call");
return;
}
}
The EnterLog writes entering logs while ExitLog writes exiting logs. The AdminCheck writes a log and returns.
You may need to modify these methods based on your system requirements. You can also enhance them by accessing various information in the context, the target, and the input parameters. To see how the context, target, and input parameters are used to enhance your aspects, please refer to Add Aspects to Object Using Dynamic Decorator.
Use Aspects
With aspects defined, you can add them to objects as needed in the application.
Say you want to add the security checking aspect before calling the GetAll method of the repository object rpDepartment of the component RepositoryDepartment. You also want to add the entering log and exiting log to the same object. You add the following code right before rpDepartment.GetAll() in the method Index of DepEmployeesController.
rpDepartment = (IRepository<IDepartment>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpDepartment,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.AdminCheck),
new object[] { Thread.CurrentPrincipal }),
null);
rpDepartment = (IRepository<IDepartment>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpDepartment,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.EnterLog), null),
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.ExitLog), null));
Then, assume you want to add entering log and exiting log to the GetAll method of the object rpEmployee of the RepositoryEmployee component; just insert the following code before rpEmployee.GetAll() in the method Index of DepEmployeesController.
rpEmployee = (IRepository<IEmployee>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpEmployee,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.EnterLog), null),
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.ExitLog), null));
Finally, assume you want to track which department is accessed; you can add the following code in the method EmployeesByDepartment of HRRestService just before using the department ID property of the selected object dpSel of the Department component iStaticDep = dpSel.DepartmentID.Value.
dpSel = (IDepartment)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
dpSel,
new String[] { "get_DepartmentID" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.EnterLog), null),
null);
Now, the cross-cutting concerns are addressed for the HRMVCAjax application.
Note that the aspects are added to the objects when needed. There is no change in the component classes. And only the objects decorated with Dynamic Decorator have the aspects, independent of other objects of the component classes. Also, an aspect can be applied to different objects, of either the same type or different types. For example, SysConcerns.EnterLog is used for rpDepartment (an object of RepositoryDepartment), rpEmployee (an object of RepositoryEmployee), and dpSel (an object of Department).
HRMVCAjax Extended
Since all the new functionality (sorting and aspects) is added to the server side in the MVC Controller or WCF REST service, there is no change for the client-side jQuery code.
For convenience, the code of DepEmployeesController after extended is listed as follows:
public class DepEmployeesController : Controller
{
internal class EmployeeLastnameComparer : IComparer<IEmployee>
{
public int Compare(IEmployee e1, IEmployee e2)
{
return String.Compare(e1.LastName, e2.LastName);
}
}
private IRepository<IEmployee> rpEmployee = null;
private IRepository<IDepartment> rpDepartment = null;
public DepEmployeesController()
{
rpEmployee = new RepositoryEmployee();
rpDepartment = new RepositoryDepartment();
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
rpDepartment = (IRepository<IDepartment>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpDepartment,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.AdminCheck),
new object[] { Thread.CurrentPrincipal }),
null);
rpDepartment = (IRepository<IDepartment>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpDepartment,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.EnterLog), null),
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.ExitLog), null));
rpDepartment.GetAll();
rpEmployee = (IRepository<IEmployee>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpEmployee,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
null,
new Decoration((x, y) =>
{
object target = x.Target;
if (target.GetType().ToString() == "ThirdPartyHR.RepositoryEmployee")
{
List<IEmployee> emps = ((IRepository<IEmployee>)target).RepList;
IEnumerable<IEmployee> query = emps.OrderByDescending(emp => emp,
new EmployeeLastnameComparer()).ToList<IEmployee>();
((IRepository<IEmployee>)target).RepList = (List<IEmployee>)query;
}
}, null));
rpEmployee = (IRepository<IEmployee>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpEmployee,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.EnterLog), null),
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.ExitLog), null));
rpEmployee.GetAll();
List<SelectListItem> depList = new List<SelectListItem>();
SelectListItem sli = null;
sli = new SelectListItem();
sli.Value = "";
sli.Text = "";
depList.Add(sli);
foreach (IDepartment d in rpDepartment.RepList)
{
sli = new SelectListItem();
sli.Value = d.DepartmentID.Value.ToString();
sli.Text = d.Name;
depList.Add(sli);
}
ViewData["depSel"] = new SelectList(depList, "Value", "Text");
return View(rpEmployee.RepList);
}
}
The code for HRRestService after extended is listed as follows:
[ServiceContract]
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(
RequirementsMode = AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)]
[ServiceBehavior(InstanceContextMode = InstanceContextMode.PerCall)]
public class HRRestService
{
internal class EmployeeLastnameComparer : IComparer<IEmployee>
{
public int Compare(IEmployee e1, IEmployee e2)
{
return String.Compare(e1.LastName, e2.LastName);
}
}
private static int iStaticDep = 0;
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "?dep={dep}")]
public List<Employee> EmployeesByDepartment(string dep)
{
IRepository<IEmployee> rpEmployee = null;
IRepository<IDepartment> rpDepartment = null;
rpEmployee = new RepositoryEmployee();
rpDepartment = new RepositoryDepartment();
rpDepartment.GetAll();
rpEmployee = (IRepository<IEmployee>)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
rpEmployee,
new String[] { "GetAll" },
null,
new Decoration((x, y) =>
{
object target = x.Target;
if (target.GetType().ToString() == "ThirdPartyHR.RepositoryEmployee")
{
List<IEmployee> emps = ((IRepository<IEmployee>)target).RepList;
IEnumerable<IEmployee> query = emps.OrderByDescending(emp => emp,
new EmployeeLastnameComparer()).ToList<IEmployee>();
((IRepository<IEmployee>)target).RepList = (List<IEmployee>)query;
}
}, null));
rpEmployee.GetAll();
IDepartment dpSel = rpDepartment.RepList[Convert.ToInt16(dep) - 1];
dpSel = (IDepartment)ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy(
dpSel,
new String[] { "get_DepartmentID" },
new Decoration(new DecorationDelegate(SysConcerns.EnterLog), null),
null);
iStaticDep = dpSel.DepartmentID.Value;
List<IEmployee> empSel = null;
if (rpEmployee.RepList != null)
{
empSel = rpEmployee.RepList.FindAll(
(IEmployee emp) => { return emp.DepartmentID.Value == iStaticDep; });
}
List<Employee> empObj = new List<Employee>();
foreach (IEmployee i in empSel)
{
empObj.Add((Employee)i);
}
return empObj;
}
}
One thing to notice is that the object returned by ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy is assigned back to the variable originally pointed to the target. For example, rpEmployee originally was assigned an object of RepositoryEmployee - the target. After calling ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy, it is assigned the returned object, which is a proxy of the target. It is subtle but important. The returned object of ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy is a proxy of the target. By using the same variable for both the target and its proxy, the original code is in tact. That means that the target and its proxy are interchangeable. If the variable is pointed to the target, the target is used as is. If the variable is pointed to the proxy of the target, additional functionality is executed before or after the target is used. Actually, if you remove all the code that is calling ObjectProxyFactory.CreateProxy, you get the original code before you extended the object and added the aspects to the objects.
Last, before running the application, you need to modify the Global.asax method to redirect console output to a file hrlog.txt. These changes are for this application only since the entering/exiting logging aspects use the console. Your application may use a different logging mechanism. In that case, you may need to make the corresponding changes. The modified application class is listed below.
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.Add(new ServiceRoute("HRRestService",
new WebServiceHostFactory(), typeof(Services.HRRestService)));
routes.MapRoute(
"Default",
"{controller}/{action}/{id}",
new { controller = "DepEmployees", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
FileStream fileStream = null;
string path = Path.GetDirectoryName(Server.MapPath("~"));
if (!File.Exists(path + "\\hrlog.txt"))
{
fileStream = new FileStream(path + "\\hrlog.txt", FileMode.Create);
}
else
fileStream = new FileStream(path + "\\hrlog.txt", FileMode.Truncate);
TextWriter tmp = Console.Out;
Application["origOut"] = tmp;
StreamWriter sw1 = new StreamWriter(fileStream);
Console.SetOut(sw1);
Application["logStream"] = sw1;
}
protected void Application_End(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TextWriter origStrm = (TextWriter)Application["origOut"];
Console.SetOut(origStrm);
StreamWriter tmp = (StreamWriter)Application["logStream"];
Stream fileStream = tmp.BaseStream;
tmp.Close();
fileStream.Close();
}
}
When the application runs, you will see the following output in the file hrlog.txt.
at HRMVCAjax.Controllers.DepEmployeesController.Index()
in C:\CBDDynDecoratorAJAX\HRMVCAjax\Controllers\DepEmployeesController.cs:line 47
Entering ThirdPartyHR.RepositoryDepartment.GetAll()
Has right to call
Exiting ThirdPartyHR.RepositoryDepartment.GetAll()
at HRMVCAjax.Controllers.DepEmployeesController.Index()
in C:\CBDDynDecoratorAJAX\HRMVCAjax\Controllers\DepEmployeesController.cs:line 72
Entering ThirdPartyHR.RepositoryEmployee.GetAll()
Exiting ThirdPartyHR.RepositoryEmployee.GetAll()
at HRMVCAjax.Services.HRRestService.EmployeesByDepartment(String dep)
in C:\CBDDynDecoratorAJAX\HRMVCAjax\Services\HRRestService.cs:line 73
Entering ThirdPartyHR.Department.get_DepartmentID()
at HRMVCAjax.Services.HRRestService.EmployeesByDepartment(String dep)
in C:\CBDDynDecoratorAJAX\HRMVCAjax\Services\HRRestService.cs:line 73
Entering ThirdPartyHR.Department.get_DepartmentID()
Points of Interest
The philosophy of "Add aspects to objects as needed" and "Extend objects as needed" is applied to an MVC/AJAX/REST application. MVC/AJAX/REST developers may find the following principles useful for addressing common tasks with the Dynamic Decorator:
- Design components to meet business requirements in a general way
- Design aspects as global methods in their own modules
- Add aspects to objects as needed
- Extend objects as needed
