Introduction
In this article, I would be creating a Data Access Layer using WCF. I would be using MEF to Export the Data from Data Access Layer class and then Import it.
MEF offers a nice way to create Composable apps where I can so easily Import and Export Data.
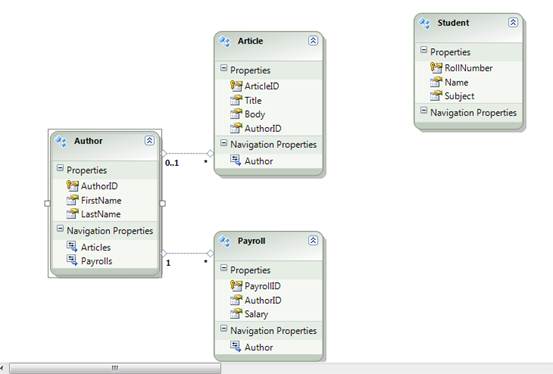
Create an ADO.NET Entity Data Model as shown in the diagram below:
Create a new WCF Service as shown below:

Two files would be added to the solution as DataService and IDataService.cs.
Add a method GetArticles() to IDataService.cs.
[ServiceContract]
public interface IDataService
{
[OperationContract]
IEnumerable GetArticles();
}
Implement the method in DataService.cs:
public IEnumerable GetArticles()
{
PublishingCompanyEntities context = new PublishingCompanyEntities();
var article = from art in context.Articles
select art.Title;
return article;
}
Creating a Data Class
- Create a class named as
Data.
class Data
{
}
- Add a property named as
Articles.
class Data
{
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set; }
}
- Add the Method
GetData(). Call the method GetArticles() of DataService.
class Data
{
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set; }
public IEnumerable GetData()
{
DataService ds = new DataService();
return Articles = ds.GetArticles();
}
}
- Add the
Export attribute on the property Articles.
class Data
{
[Export]
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set; }
public IEnumerable GetData()
{
DataService ds = new DataService();
return ds.GetArticles();
}
}
- Also add an
Export attribute on the Data Class.
[Export]
class Data
{
[Export]
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set; }
public IEnumerable GetData()
{
DataService ds = new DataService();
return ds.GetArticles();
}
}
- I need to set the value of
Articles property. I will do that in the constructor of Data class. So here is my final class:
[Export]
class Data
{
public Data()
{
Articles = GetData();
}
[Export]
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set; }
public IEnumerable GetData()
{
DataService ds = new DataService();
return Articles = ds.GetArticles();
}
}
Creating Another Class App
- Create a class
App.
class App
{
}
- Add a method
Run() and put the code to compose the container.
class App
{
public void Run()
{
var catalog = new AssemblyCatalog
(System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly());
var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
container.ComposeParts(this);
}
}
- Create a property
Articles and this time add an import attribute.
class App
{
[Import]
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set;}
public void Run()
{
var catalog = new AssemblyCatalog
(System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly());
var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
container.ComposeParts(this);
}
}
- Create an object for the
Data Class and Import it.
class App
{
[Import]
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set;}
[Import]
Data data;
public void Run()
{
var catalog = new AssemblyCatalog
(System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly());
var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
container.ComposeParts(this);
}
}
- Add a
foreach through the articles.
class App
{
[Import]
public IEnumerable Articles { get; set;}
[Import]
Data data;
public void Run()
{
var catalog = new AssemblyCatalog
(System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly());
var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
container.ComposeParts(this);
foreach (string art in Articles)
{
Console.WriteLine(art);
}
}
}
Please note that adding Export and Import attributes would need you to include the System.ComponentModel.Composition.
Call the App class now.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
App a = new App();
a.Run();
Console.ReadKey();
}
It works! Happy coding.
History
- 23rd July, 2011: Initial version
