Decorator Pattern is a structural pattern. It is used to attach additional responsibilities to an object dynamically. Decorators provide a flexible alternative to subclassing for extending functionality.
Decorator pattern is used in .Net. The following collection classes are the decorators of the ArrayList class:
- SyncArrayList: This denotes a synchronized arraylist which can be used multithreading scenario. This arraylist is to be used when multiple threads are to modify a single instance of arraylist.
- FixedSizeArrayList: This denotes a fixed size arraylist. The size of the array list cannot be changed. Elements cannot be added and removed. Existing elements can be replaced.
- ReadOnlyArrayList: This denotes a read-only arraylist. Elements cannot be added and removed. Existing elements cannot be replaced.
All the above decorators are defined as following:
private class [Sync/Fixed/ReadOnly]ArrayList : ArrayList
{
internal [Sync/Fixed/ReadOnly]ArrayList(ArrayList arrayList) {...}
}
The above structure is the proof of all the aboved mentioned classes to be a deocorator of the ArrayList class.
All the above deocorators are private and can be instantiated using the static methods provided on ArrayList class:
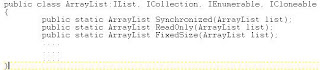 All the decorators override appropriate virtual methods and adds the additional behavior. Below shows the sample code snippet for the Synchronized arraylist the decorators:
All the decorators override appropriate virtual methods and adds the additional behavior. Below shows the sample code snippet for the Synchronized arraylist the decorators:

Similarly ReadOnlyArrayList overrides the virtual method of the ArrayList class and throws exception to restrict any modifications in the list.
In a similar manner FixedSizeArrayList overrides the virtual method of the ArrayList class and throws exception to restrict any changes to the size of the list.
This is how the decorator pattern is being used in .net framework. There are possibilities of decorator pattern being used at multiple places in the framework. It can be found out by studying the framework thoroughly and understanding the patterns used in the framework.
