Introduction
This article discusses the construction of a simple utility that may be used to locate and evaluate paths within an XML document, and to test queries against those paths. The application allows the user to open an XML document into a TreeView control for easy viewing of the structure; the user may right click on any node within the TreeView to expose a context menu that will allow the user to copy the current path to that node. The user may then open a test window up and paste the copied path into an expression text box. Once the path has been pasted into the text box, the user may test the path directly, or may edit the path and test the edit.
The project includes a collection of sample XML documents which may be used to try out the application.
To use the application, open the main form and use the file menu to open an XML document. The document will be displayed in the main form using a TreeView control. The user may click on any node in the TreeView and the path to that node as well as the node type will be displayed in the status bar at the bottom of the window. The user may right click on any selected node and select from one of three options:
- Copy only the text contained in the current node
- Copy the path to the node formatted as a query for that attribute value, and
- Copy the full path exactly as it is
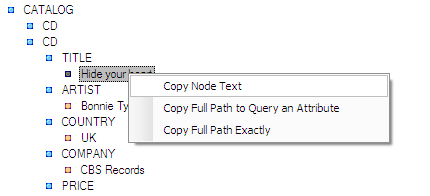
Figure 1: Context Menu

Figure 2: The Main Form

Figure 3: The Test Form (Example shows use
of the “Copy Full Path to Query an Attribute” context menu option)

Figure 4: Editing a path manually to test alternative paths
(“/description” added to path shown in Figure 3)
The intent of the application was to provide a simple tool that may be used to test paths for XPath based queries; it is intended to simplify viewing the XML and to make it easier to identify specific paths within an XML document.
Getting Started
In order to get started, unzip the included project and open the solution in the Visual Studio 2005 environment. In the solution explorer, you should note these files:

Figure 3: Solution Explorer
The Main Form (frmXmlPathfinder.cs)
The main form is used to open XML documents and to display them in TreeView format; form also provides the interface necessary to copy node paths and to open a test window which may be used to test XPath based queries against the XML document’s content. The code is annotated and should be easy enough to follow from the descriptions provided:
If you’d care to open the code view up in the IDE, you will see that the code file begins as follows:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.XPath;
The imports are primarily per the default configuration for a Windows application; the System.Xml and System.Xml.XPath library import are the only departure from the default.
Following the imports, the namespace and class are defined and a constructor added. A local string variable is declared and used to hold the path to the XML document.
namespace XmlPathfinder
{
public partial class frmXmlPathfinder : Form
{
private string mFilePath;
public frmXmlPathfinder()
{
InitializeComponent();
mFilePath = string.Empty;
}
Next up is the method used to exit the application.
private void tspExit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
The next section of the code is used to load the XML document into the TreeView control.
private void PushToTreeView(XmlNode currentNode, TreeNodeCollection
nodCollection)
{
TreeNode insertNode = nodCollection.Add(currentNode.Name);
switch (currentNode.NodeType)
{
case XmlNodeType.Element:
insertNode.Text = currentNode.Name;
insertNode.Tag = "Element";
insertNode.ImageIndex = 1;
break;
case XmlNodeType.Attribute:
insertNode.Text = "@" + currentNode.Name;
insertNode.Tag = "Attribute";
insertNode.ImageIndex = 2;
break;
case XmlNodeType.Text:
insertNode.Text = currentNode.Value;
insertNode.Tag = "Text";
insertNode.ImageIndex = 3;
break;
case XmlNodeType.CDATA:
insertNode.Text = currentNode.Value;
insertNode.Tag = "CDATA";
insertNode.ImageIndex = 4;
break;
case XmlNodeType.Comment:
insertNode.Text = currentNode.Value;
insertNode.Tag = "Comment";
insertNode.ImageIndex = 5;
break;
case XmlNodeType.Entity:
insertNode.Text = currentNode.Value;
insertNode.Tag = "Entity";
insertNode.ImageIndex = 6;
break;
case XmlNodeType.Notation:
insertNode.Text = currentNode.Value;
insertNode.Tag = "Notation";
insertNode.ImageIndex = 7;
break;
default:
break;
}
if (currentNode.Attributes != null &&
currentNode.Attributes.Count > 0)
{
foreach (XmlAttribute attribute in currentNode.Attributes)
{
PushToTreeView(attribute, insertNode.Nodes);
}
}
if (currentNode.HasChildNodes)
{
foreach (XmlNode childNode in currentNode.ChildNodes)
{
PushToTreeView(childNode, insertNode.Nodes);
}
}
}
The next method is used to load up a new XML document into the form.
private void tspOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
openFileDialog1.Title = "Open XML File";
openFileDialog1.Filter = "XML Files|*.xml";
openFileDialog1.DefaultExt = "XML";
openFileDialog1.FileName = "";
openFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
if (openFileDialog1.FileName == "")
return;
mFilePath = openFileDialog1.FileName;
treeXml.Nodes.Clear();
this.Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor;
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
try
{
doc.Load(mFilePath);
this.Text = "XML Pathfinder - " + mFilePath;
this.Cursor = Cursors.Default;
}
catch (Exception ex1)
{
this.Cursor = Cursors.Default;
MessageBox.Show(ex1.Message);
return;
}
PushToTreeView(doc, treeXml.Nodes);
this.Cursor = Cursors.Default;
}
catch (Exception ex2)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex2.Message, "Unable to Open Document");
}
}
The next bit of code is used display the selected node’s path within the context of the XML document; the path shown is a cleaned up version of what appears in the TreeView. This code will display both the path as well as the selected node’s type (e.g., Element or Attribute).
private void treeXml_AfterSelect(object sender, TreeViewEventArgs e)
{
try
{
string tmp = treeXml.SelectedNode.FullPath;
tmp = tmp.Replace("#document", "/");
statusPath.Text = "Selected Path: " + tmp;
statusType.Text = " Selected Type: " +
treeXml.SelectedNode.Tag;
}
catch { }
}
The next three methods are used to format the path and to copy it into the clipboard making it possible to then paste the selected path directly into the expression test text box on the test form.
private void copyTextToClipboardToolStripMenuItem_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
string tmp = treeXml.SelectedNode.Text;
Clipboard.SetDataObject(tmp, true);
}
private void copyFullPathToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
try
{
string tmp = treeXml.SelectedNode.FullPath;
tmp = tmp.Replace("#document", "/");
int pos = 0;
pos = tmp.LastIndexOf('@');
pos = pos - 1;
if (pos != 0)
{
tmp = tmp.Remove(pos, 1);
tmp = tmp.Insert(pos, "[");
int posSlash =
treeXml.SelectedNode.FullPath.LastIndexOf('/');
if (posSlash < pos)
{
tmp += "='KeyValueHere']";
}
else
{
tmp = tmp.Remove(posSlash-8,1);
tmp = tmp.Insert(posSlash-8, "='");
tmp += "']";
}
}
Clipboard.SetDataObject(tmp, true);
}
catch
{
string tmp = treeXml.SelectedNode.FullPath;
tmp = tmp.Replace("#document", "/");
Clipboard.SetDataObject(tmp, true);
}
}
private void copyFullPathAsIsToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
try
{
string tmp = treeXml.SelectedNode.FullPath;
tmp = tmp.Replace("#document", "/");
Clipboard.SetDataObject(tmp, true);
}
catch
{
}
}
The last two methods in the main form are used to either open a help window or to open a test window.
private void openTestWindowToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (mFilePath != string.Empty)
{
frmTest f = new frmTest(mFilePath);
f.Show();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Open an xml document prior to starting a
test.", "Invalid File");
}
}
private void helpToolStripMenuItem1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
frmHelp f = new frmHelp();
f.ShowDialog();
}
The Text Form (frmTest.cs)
The test form is used to test paths within open XML documents and to display of any XPath type queries executed against the XML document.
If you’d care to open the code view up in the IDE, you will see that the code file begins as follows:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.XPath;
The imports are primarily per the default configuration for a Windows application; the System.Xml and System.Xml.XPath library import are the only departure from the default.
Following the imports, the namespace and class are defined and a constructor added. A local string variable is declared and used to hold the path to the XML document.
namespace XmlPathfinder
{
public partial class frmTest : Form
{
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
public frmTest(string filePath)
{
InitializeComponent();
try
{
doc.Load(filePath);
this.Text = "Testing - " + filePath;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Open File Error");
return;
}
}
The next bit of code is the button click event handler for the test itself. This code uses the expression text box content as path; whatever is captured from the resulting query is displayed in the result section of the form. This is accomplished by creating an XPathNavigator and using the XML document’s CreateNavigator method. Once the navigator is declared, we can send the expression search term directly to the navigator’s select method to test it.
private void btnTest_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
rtbResults.Text = string.Empty;
XPathNavigator navigator = doc.CreateNavigator();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try
{
XPathNodeIterator nodes =
navigator.Select(txtTestExpression.Text);
while (nodes.MoveNext())
{
XPathNavigator node = nodes.Current;
if (optInnerXml.Checked == true)
{
sb.Append(node.InnerXml + Environment.NewLine);
}
else if (optOuterXml.Checked == true)
{
sb.Append(node.OuterXml + Environment.NewLine);
}
else
{
sb.Append(node.Value + Environment.NewLine);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "XPath Error");
}
rtbResults.Text = sb.ToString();
}
The last bit of the class is used to close the form.
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Dispose();
}
The only remaining forms are used to display the help. The help file contains access to an RTF document which contains instructions and samples.
Summary
This application was provided as a starter utility application that may be used to evaluate paths when writing XPath based queries against an existing XML document.
