Are you tired of attaching the Visual Studio debugger to the service application? I got the solution just for you! It’s a small helper class containing a static method which you need to invoke.
public static void Main(string[] argv)
{
if (WindowsServiceHelper.RunAsConsoleIfRequested<Service1>())
return;
}
Then go to project properties, the “Debug” tab and add “-console” as Command Arguments.
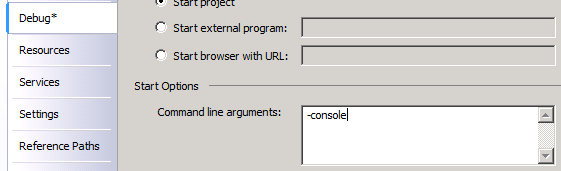
How to configure Visual Studio
That’s it! What I do is simply allocate a console using the winapi and then invoke (through reflection) the proper protected methods in your service class.
The source code for the helper class is as follows:
public static class WindowsServiceHelper
{
[DllImport("kernel32")]
static extern bool AllocConsole();
public static bool RunAsConsoleIfRequested<t>() where T : ServiceBase, new()
{
if (!Environment.CommandLine.Contains("-console"))
return false;
var args = Environment.GetCommandLineArgs().Where
(name => name != "-console").ToArray();
AllocConsole();
var service = new T();
var onstart = service.GetType().GetMethod("OnStart",
BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
onstart.Invoke(service, new object[] {args});
Console.WriteLine("Your service named '" + service.GetType().FullName +
"' is up and running.\r\nPress 'ENTER' to stop it.");
Console.ReadLine();
var onstop = service.GetType().GetMethod("OnStop",
BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
onstop.Invoke(service, null);
return true;
}
}
