In this post, I am going to talk about Nullable types. Actually most of developers know, in C#, we have mainly two types:
- Reference type
- Value type
But we have one more type that is called Nullable type.
Actually, it is a value type but it has feature of both reference and Value type.
As we know, a value type is allocated space on stack, and every value of type must be initialized to some value during declaration. If you don’t provide by yourself, C# does it for you. So every value type is assigned some value whether you initialize it or not.
Nullable type has a capability to hold a value or can have null reference, means there is no value. Nullable types were introduced in .NET 2.0.
We can declare and initialize a Nullable type as:
Nullable<int> t = 5;
C# also provides a short hand syntax for this as:
int? i = 5;
If you would not assign a value, you can do it with Nullable types as we can do it with reference types.
Now let’s see it in the reflector how it got implemented. Here you can see the Class declaration as:

public struct Nullable<T> where T: struct
It means Nullable can be used over struct type, i.e., value type.
Here we will see some of the main properties of Nullable type and leave default ones. Now let's go to the details of method public Nullable(T value). This is parameterised constructor. Now let's see what is inside this code:
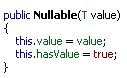
Here you can see that this is assigning value to the variable and setting hasValue as true.
So it actually has one property hasValue that does the entire job. By default, it is set to false and once we assign some value in it, it is set as true. So whenever one accesses it without assigning it a value, it returns null reference.
Now let's see the HasValue property.

It is just returning the hasValue.
Now let's see public T Value { get; } what it does:

As you can see whether hasValue is true or not. If false, throw some exception else it returns the value.
Also let's have a view at two more next methods public T GetValueOrDefault() and public T GetValueOrDefault(T defaultValue). As the method name suggests, that returns the existing value and if it is not set then return the type’s defult value. The definition is like this:


So you can see that it checks the hasValue and based on this, returns the result. Similarly if you want to see public override bool Equals(object other) method, it has the code like:

This also checks the hasValue before comparing it.
There are two operator’s method you can see at last. You all must be knowing this is Operator Overloading. But what is this for? Let's see the code below:
int i = 5;
Nullable<int> t = i;
Actually, here I have declared and intialised an int variable and created a nullable type and assigned the int variable to it. This is actually accomplished with the help of the operators.
So it means we can assign a value type to a Nullable type whose underlying type is the same as the underlying type of a Nullable type without any casting.
But vice versa is not possible. You have to do explicit cast as:
Nullable<int> t = 5;
int i = (int)t;
But you always write as:
Nullable<int> t = 5;
int i = t.Value;
So I think you all must have enjoyed. There are a lot more things still remaining which I’ll cover in my next post.
Cheers,
Brij








