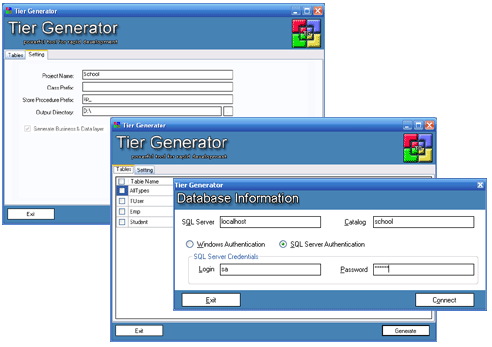
Introduction
Tier Generator is a powerful tool for generating business and data layers in C#. It is a code generation tool that helps users to rapidly generate and deploy business and data layers for their applications. The idea behind this is to provide a utility (tool) to the developer that has the capabilities of quickly generating consistent and tested source code that will help to get projects started sooner and finished faster.
Tier Generator connects to a Microsoft SQL Server database server and generates business and data layers in C#. It also generates Stored Procedures for DML operations.
Business layer
Tier Generator generates code in two layers (business and data). It generates some classes for the each table in the database in the business layer. E.g., our database contains the table Employee. Tier Generator will generate the following files:
- Employee
- EmployeeKeys
- EmployeeFactory
The Employee (business object) class contains the declaration of all instance fields along with properties. It also overrides the AddValidationRules method to associate the validation rules to the properties of the business object. It also contains an enum of all the fields.
public class Employee: BusinessObjectBase
{
#region InnerClass
public enum EmployeeFields
{
EmployeeID, Name, Password, Email, TeamID,DepartmentID, IsAdmin
}
#endregion
#region Data Members
int _employeeID;
string _name;
string _password;
string _email;
int _teamID;
int _departmentID;
bool _isAdmin;
#endregion
#region Properties
public int EmployeeID
{
get { return _employeeID; }
set
{
if (_employeeID != value)
{
_employeeID = value;
PropertyHasChanged("EmployeeID");
}
}
}
public string Name
{
get { return _name; }
set
{
if (_name != value)
{
_name = value;
PropertyHasChanged("Name");
}
}
}
.
.
.
#endregion
#region Validation
internal override void AddValidationRules()
{
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleNotNull("EmployeeID",
"EmployeeID"));
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleNotNull("Name",
"Name"));
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleStringMaxLength("Name",
"Name",50));
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleStringMaxLength("Password",
"Password",50));
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleStringMaxLength("Email",
"Email",100));
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleNotNull("TeamID",
"TeamID"));
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleNotNull("DepartmentID",
"DepartmentID"));
ValidationRules.AddRules(new Validation.ValidateRuleNotNull("IsAdmin",
"IsAdmin"));
}
#endregion
}
The EmpolyeesKeys (business object keys) class contains the list of primary keys of the table.
public class EmployeeKeys
{
#region Data Members
int _employeeID;
#endregion
#region Constructor
public EmployeeKeys(int employeeID)
{
_employeeID = employeeID;
}
#endregion
#region Properties
public int EmployeeID
{
get { return _employeeID; }
}
#endregion
}
The EmployeeFactory (business factory) class contains the methods for the Insert, Delete, Update, and Select operations. It provides the following methods for the DML operations:
public bool Insert(Employee businessObject)public bool Update(Employee businessObject)public Employee GetByPrimaryKey(EmployeeKeys keys)public List<Employee> GetAll()public List<Employee> GetAllBy(Employee.EmployeeFields fieldName, object value)public bool Delete(EmployeeKeys keys)public bool Delete(Employee.EmployeeFields fieldName, object value)
The factory class performs the DML operations with the help of the data layer.
public class EmployeeFactory
{
#region data Members
EmployeeSql _dataObject = null;
#endregion
#region Constructor
public EmployeeFactory()
{
_dataObject = new EmployeeSql();
}
#endregion
#region Public Methods
public bool Insert(Employee businessObject)
{
if (!businessObject.IsValid)
{
throw new InvalidBusinessObjectException(
businessObject.BrokenRulesList.ToString());
}
return _dataObject.Insert(businessObject);
}
public bool Update(Employee businessObject)
{
if (!businessObject.IsValid)
{
throw new InvalidBusinessObjectException(
businessObject.BrokenRulesList.ToString());
}
return _dataObject.Update(businessObject);
}
public Employee GetByPrimaryKey(EmployeeKeys keys)
{
return _dataObject.SelectByPrimaryKey(keys);
}
public List<Employee> GetAll()
{
return _dataObject.SelectAll();
}
public List<Employee> GetAllBy(Employee.EmployeeFields fieldName,
object value)
{
return _dataObject.SelectByField(fieldName.ToString(), value);
}
public bool Delete(EmployeeKeys keys)
{
return _dataObject.Delete(keys);
}
public bool Delete(Employee.EmployeeFields fieldName, object value)
{
return _dataObject.DeleteByField(fieldName.ToString(), value);
}
#endregion
}
Data Layer
The data access file generated by the Tier Generator contains the methods for DML operations. It uses Stored Procedures for DML operations. The factory class methods call the data layer methods for insertion and deletion.
class EmployeeSql : DataLayerBase
{
#region Public Methods
public bool Insert(Employee businessObject)
{
SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand();
sqlCommand.CommandText = "dbo.[sp_Employee_Insert]";
sqlCommand.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
sqlCommand.Connection = MainConnection;
try
{
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@EmployeeID", SqlDbType.Int, 4,
ParameterDirection.Output,
false, 0, 0, "",
DataRowVersion.Proposed,
businessObject.EmployeeID));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@Name", SqlDbType.NVarChar,
50, ParameterDirection.Input,
false, 0, 0, "",
DataRowVersion.Proposed,
businessObject.Name));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@password", SqlDbType.NVarChar,
50, ParameterDirection.Input,
false, 0, 0, "",
DataRowVersion.Proposed,
businessObject.Password));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@Email", SqlDbType.NVarChar,
100, ParameterDirection.Input,
false, 0, 0, "",
DataRowVersion.Proposed,
businessObject.Email));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@TeamID", SqlDbType.Int,
4, ParameterDirection.Input,
false, 0, 0, "",
DataRowVersion.Proposed,
businessObject.TeamID));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@DepartmentID", SqlDbType.Int,
4, ParameterDirection.Input,
false, 0, 0, "",
DataRowVersion.Proposed,
businessObject.DepartmentID));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@IsAdmin", SqlDbType.Bit,
1, ParameterDirection.Input,
false, 0, 0, "",
DataRowVersion.Proposed,
businessObject.IsAdmin));
MainConnection.Open();
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
businessObject.EmployeeID =
(int)sqlCommand.Parameters["@EmployeeID"].Value;
return true;
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception("Employee::Insert::Error occured.", ex);
}
finally
{
MainConnection.Close();
sqlCommand.Dispose();
}
}
#endregion
}
How to use
The code generated by the Tier Generator is easy to use. Open the generated project in Visual Studio 2005 and compile it. Run the Stored Procedures script in the the database which is generated by the Tier Generator. You can find the SQL script file in the generated folder.
Add a new Windows/web project in the existing project and add the DLL of the generated code to it. Add app.config for Windows applications and web.config for web applications. Get the connection string from the generated app.config file. You will get this file in the generated folder.
<appSettings>
<add key="Main.ConnectionString"
value="Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=School;
User Id=sa;Password=sa" />
</appSettings>
Here is the code sample for inserting a new record:
public void AddNewRecord()
{
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.EmployeeID = 1;
emp.FirstName = "Shakeel";
emp.LastName = "Iqbal";
.
.
.
.
EmployeeFactory empFact = new EmployeeFactory();
empFact.Insert(emp);
}
The code sample for selecting all the records:
public void SelectAll()
{
EmployeeFactory empFact = new EmployeeFactory();
List<Employee> list = empFact.GetAll();
dataGrid1.DataSource = list;
}
Future enhancements
I have some future enhancements planned for the Tier Generator, and I have plans to launch the next version of the Tier generator. In this version, I will improve my business and data layers, and I will also provide the following features:
- Generate Windows application.
- Generate Web application.
- Generate Web Services.
