Introduction
la4j is an open source, single-threaded and 100% Java library for solving problems of linear algebra. It supports sparse and dense matrices and covers almost all of the linear algebra tasks.
la4j was written by the author in the process of learning Calculation Math in one Russian university.
Features
Following are the features of the current version of la4j:
- Uniform interpretation of vectors and matrices
- Sparse (CSR) and dense (2d array) matrices and vectors support
- Basic vectors and matrices operations (addition, multiplying, transposing and other)
- Linear systems solving (Gaussian Elimination, Jacobi, Gauss-Seidel and other)
- Matrices decomposition (SVD, LU, Cholesky and other)
- Inverted matrix foundation
- Matrices and vectors serialization
- I/O for vectors and matrices support (MatrixMarket format)
In addition, la4j now is 55 classes, 6700 loc, 90 tests, 50 kb (in jar).
Matrices and Vectors
See the below la4j core class diagram:
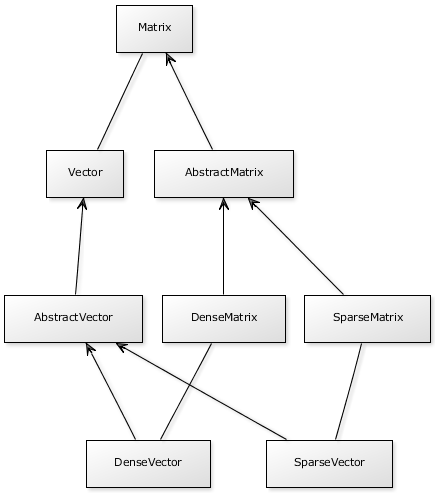
la4j provides a flexible API for working with matrices and vectors through factories - DenseFactory and SparseFactory. Here is an example:
Factory denseFactory = new DenseFactory();
Factory sparseFactory = new SparseFactory();
double array[][] = new double[][] {
{1.0, 0.0, 0.0},
{0.0, 5.0, 0.0},
{0.0, 0.0, 9.0}
};
Matrix a = sparseFactory.createMatrix(array);
Matrix b = denseFactory.createMatrix(array);
Matrix c = a.copy(denseFactory);
Matrix d = b.copy(sparseFactory);
Here is an example of basic operations:
Matrix a = sparseFactory.createMatrix(array);
Matrix b = denseFactory.createMatrix(array);
Matrix c = a.multiply(b);
Matrix d = a.multiply(b, denseFactory);
Matrix e = c.add(d).subtract(a).multiply(100);
Matrix f = a.transpose();
Matrix g = a.transpose(denseFactory);
Linear Systems
la4j supports most of the popular calculation methods for solving linear systems. See the below design of la4j.linear package:

As you can see, la4j.linear package implements the Strategy design pattern.
Here is an example of solving linear systems in la4j:
Matrix a = denseFactory.createMatrix(array);
Vector b = sparseFactory.createVector(array[0]);
LinearSystem system = new LinearSystem(a, b);
Vector x = system.solve(new GaussianSolver());
Vector y = system.solve(new JacobiSolver(), sparseFactory);
Matrix Decomposition
There are a lot of matrix decomposition methods available in the la4j.decomposition package.

This package is implemented in terms of Strategy design pattern.
Here is an example of how to use la4j for matrix decomposition:
Matrix a = denseFactory.createMatrix(array);
Matrix[] qr = a.decompose(new QRDecompositor());
Matrix[] lu = a.decompose(new LUDecompositor(), sparseFactory);
Input/Output
la4j supports I/O operations through la4j.io package. It implements Bridge Design pattern.
The current implementation supports MatrixMarket format. Here is an example of output for matrix:
0 1 0
0 2 0
0 3 0
For dense matrix, it will be:
%%MatrixMarket matrix array real general
3 3
0
1
0
0
2
0
0
3
0
For sparse matrix, it will be:
%%MatrixMarket matrix coordinate real general
3 3 3
0 1 1
1 1 2
2 1 3
la4j provides two classes: MMInputStream and MMInputStream, which can be used instead of ObjectInputStream and ObjectOutputStream in serialization algorithms. For example:
Matrix a = denseFactory.createMatrix(array);
ObjectOutput mmos = new MMOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("file.mm"));
mmos.writeObject(a);
mmos.close();
ObjectInput mmis = new MMInputStream(new FileInputStream("file.mm"));
Matrix b = (Matrix) mmis.readObject();
mis.close();
Links
You can find the la4j project at Google Code. Also you can visit la4j development blog at Blogger.
History
- 14th November, 2011: Initial post
