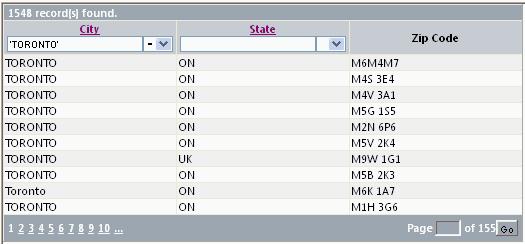
Introduction
While the out of the box GridView is enough for most applications, often there is a need to customize it. One such customization requirement is for the Top Pager to be different from the Bottom Pager. GridView allows you to customize the Pager by using a Template construct, but it uses that same template for the Top Pager as well as the Bottom Pager. Another feature missing from GridVew is filtering. Filtering allows the user to restrict the row set by specifying column values.
Background
In order to customize GridView, we need to first understand how it builds the control structure on the server side. On the client side, the GridView is rendered as a <table> within a <div> element. On the server side, the control tree is built within the GridView.controls member variable as shown:

So, we have a ChildTable at the root with all GridViewRows as its children. The very first row is the Pager row if it is needed. Next is the Header row. Then, we have one or more DataRows. This is followed by the Footer row and then the Pager row if these are needed.
Using the Code
This is how the code for the custom grid is rendered in the ASPX file. Notice that for the columns that need filtering, the headertext attribute should have a space at the end. Here we have a space for the City and State columns.
<asp:sqldatasource runat="server" id="MySource"
connectionstring="Database=****;Server=****;User=****;Password=****;"
datasourcemode="DataSet"
selectcommand="SELECT * FROM CLIENT WHERE offsysid='053'">
</asp:sqldatasource>
<cc1:HWGridView runat="server" id="MyGridView" CssClass="bc3 f2"
datasourceid="MySource"
allowpaging="True" autogeneratecolumns="False"
allowsorting="True" PageSize="10"
OnRowCommand="MyGridView_RowCommand"
OnFilterCommand="MyGridView_FilterCommand" >
<Columns>
<asp:BoundField datafield="city"
headertext="City " sortexpression="city">
<headerstyle width="170px" />
</asp:BoundField>
<asp:BoundField datafield="state"
headertext="State " sortexpression="state">
<headerstyle width="170px" />
</asp:BoundField>
<asp:BoundField datafield="zip_code" headertext="Zip Code" >
<headerstyle width="170px" />
</asp:BoundField>
</Columns>
<RowStyle CssClass="bc3" />
<PagerStyle CssClass="bc1"
ForeColor="White" HorizontalAlign="Center" />
<SelectedRowStyle BackColor="#D1DDF1"
Font-Bold="True" ForeColor="#333333" />
<HeaderStyle CssClass="bc2" Font-Bold="True" />
<AlternatingRowStyle BackColor="White" />
<EmptyDataTemplate>No records found</EmptyDataTemplate>
</cc1:HWGridView>
Design Details
The design is explained in two sections namely Custom Paging and Custom Filtering.
1. Custom Paging
When creating the Pager row (both Top and Bottom), the GridView calls a virtual method called InitializePager. We override this method and provide two new virtual methods called InitializeTopPager and InitializeBottomPager as follows:
protected override void InitializePager(GridViewRow row,
int columnSpan,
PagedDataSource pagedDataSource)
{
if (this.Controls[0].Controls.Count == 0 &&
(this.PagerSettings.Position == PagerPosition.Top ||
this.PagerSettings.Position == PagerPosition.TopAndBottom))
{
InitializeTopPager(row, columnSpan, pagedDataSource);
}
else
{
base.InitializePager(row, columnSpan, pagedDataSource);
InitializeBottomPager(row, columnSpan, pagedDataSource);
}
}
Refer to the commented line in the above code and note that we cannot use GridView.TopPagerRow to find out if IntializePager is being called for creating the Top or the Bottom pager. Reason being, whenever GridView.CreateChildControls gets called, it will in turn call InitializePager twice, first time for the top pager and the second time for the bottom pager. Now, since CreateChildControls itself may get called twice during postback/callback, first while getting created from ViewState and next when creating from the database (for a paged GridView, the user requested a new page, for example), the TopPagerRow would already exists from the previous run. So, we directly look at the control tree; if it is empty, then GridView has started creating the Top pager row.
Now, we code the top pager as shown below:
protected virtual void InitializeTopPager(GridViewRow row,
int columnSpan,
PagedDataSource pagedDataSource)
{
TableCell cell = new TableCell();
if (columnSpan > 1)
{
cell.ColumnSpan = columnSpan;
}
Literal ltrlSpan = new Literal();
ltrlSpan.Text = "<span style='float:left'> " +
pagedDataSource.DataSourceCount.ToString() +
" record(s) found.</span>";
cell.Controls.Add(ltrlSpan);
row.Cells.Add(cell);
}
We let the GridView create the Bottom pager by calling base.InitializePager. The bottom pager is created as a Table (PagerTable) with a single Row (TableRow) and a single Cell (TableCell). Then, we customize the bottom pager by adding another Cell (goToCell) to the TableRow as shown:
protected virtual void InitializeBottomPager(GridViewRow row,
int columnSpan,
PagedDataSource pagedDataSource)
{
TableCell goToCell = new TableCell();
goToCell.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.Width, "100%");
Table pagerTable = (Table)row.Cells[0].Controls[0];
pagerTable.Rows[0].Cells.Add(goToCell);
Literal ltrlSpanBegin = new Literal();
ltrlSpanBegin.Text = "<span style='float:right'>Page ";
if (m_txtPageNo == null)
{
m_txtPageNo = new TextBox();
m_txtPageNo.Width = new Unit(20);
m_txtPageNo.Style.Add("height", "10px");
m_txtPageNo.Font.Size = new FontUnit("10px");
m_txtPageNo.CssClass = this.PagerStyle.CssClass;
}
Literal ltrlText = new Literal();
ltrlText.Text = " of " + PageCount.ToString();
Button btnGo = new Button();
btnGo.Text = "Go";
btnGo.CommandName = "Page1";
btnGo.CommandArgument = "2";
btnGo.ID = "ctl_PageIndex";
btnGo.Height = new Unit("16px");
btnGo.Font.Size = new FontUnit("10px");
btnGo.CssClass = this.PagerStyle.CssClass;
if (this.PagerStyle.ForeColor!=null) {
btnGo.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.Color,
this.PagerStyle.ForeColor.ToString());
}
Literal ltrlSpanEnd = new Literal();
ltrlSpanEnd.Text = "</span>";
goToCell.Controls.Add(ltrlSpanBegin);
goToCell.Controls.Add(m_txtPageNo);
goToCell.Controls.Add(ltrlText);
goToCell.Controls.Add(btnGo);
goToCell.Controls.Add(ltrlSpanEnd);
}
We also handle the button clicks to go to a particular page by overriding the OnRowCommand method as follows:
protected override void OnRowCommand(GridViewCommandEventArgs e)
{
switch (e.CommandName)
{
case "Page1":
HandlePageCommand(e);
break;
default:
base.OnRowCommand(e);
break;
}
}
The HandlePageCommand will then read the text from the text box and set the GridView.PageIndex as shown below:
protected virtual void HandlePageCommand(GridViewCommandEventArgs e)
{
TextBox txtPageIndex;
txtPageIndex =
(TextBox)((System.Web.UI.Control)e.CommandSource).Parent.Controls[1];
Button btnPageIndex =
(Button)((System.Web.UI.Control)e.CommandSource).Parent.Controls[3];
if (txtPageIndex.Text.Length > 0)
{
try
{
int ndx = int.Parse(txtPageIndex.Text);
ndx = ndx - 1;
if (ndx >= PageCount)
ndx = PageCount - 1;
if (ndx < 0)
ndx = 0;
this.PageIndex = ndx;
btnPageIndex.CommandArgument = txtPageIndex.Text;
}
catch (Exception e1)
{
if (e1.Message.Length == 0)
return;
}
}
}
2. Custom Filtering
We add the filtering capability within the header row for each column. First, we override the InitializeRow method, and if RowType is the Header, then we call the InitializeHeaderRow method.
protected override void InitializeRow(GridViewRow row, DataControlField[] fields)
{
base.InitializeRow(row, fields);
if (row.RowType == DataControlRowType.Header)
{
InitializeHeaderRow(row, fields);
}
}
protected virtual void InitializeHeaderRow(GridViewRow row, DataControlField[] fields)
{
AddGlyph(this, row);
AddFilters(row, fields);
}
The InitializeHeaderRow method in turn calls AddGlyphs to add an up/down arrow for sorting, and then calls AddFilters to find if filtering is enabled for columns, and if it is, then it calls AddFilter to add a TextBox and a DropDownList to that column's header cell. To enable filtering for a column, include a space at the end of the column header text in the ASPX file or in the code-behind (this is kludgy).
protected virtual void AddFilters(GridViewRow headerRow,
DataControlField[] fields)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Columns.Count; i++)
{
if (Columns[i].HeaderText.EndsWith(" "))
{
AddFilter(i, headerRow.Cells[i], fields[i]);
}
}
}
protected virtual void AddFilter(int columnIndex,
TableCell headerCell,
DataControlField field)
{
if (headerCell.Controls.Count == 0)
{
LiteralControl ltlHeaderText = new LiteralControl(headerCell.Text);
headerCell.Controls.Add(ltlHeaderText);
}
LiteralControl ltlBreak = new LiteralControl("</br>");
headerCell.Controls.Add(ltlBreak);
TextBox txtFilter = null;
if (m_txtFilter.Contains(columnIndex))
{
txtFilter = (TextBox)m_txtFilter[columnIndex];
}
else
{
txtFilter = new TextBox();
txtFilter.ID = ID + "_txtFilter" + columnIndex.ToString();
if (field.ItemStyle.Width.Value != 0.0)
{
txtFilter.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.Width,
Convert.ToString(field.ItemStyle.Width.Value - 40) + "px");
}
else if (field.HeaderStyle.Width.Value != 0.0)
{
txtFilter.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.Width,
Convert.ToString(field.HeaderStyle.Width.Value - 40) + "px");
}
txtFilter.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.Height, "10px");
txtFilter.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.FontSize, "9px");
m_txtFilter[columnIndex] = txtFilter;
}
DropDownList ddlFilter;
if (m_ddlFilter.Contains(columnIndex))
{
ddlFilter = (DropDownList)m_ddlFilter[columnIndex];
}
else
{
ddlFilter = new DropDownList();
ddlFilter.ID = ID + "_ddlFilter" + columnIndex.ToString();
ddlFilter.Items.Add(" ");
ddlFilter.Items.Add("=");
ddlFilter.Items.Add("<");
ddlFilter.Items.Add(">");
ddlFilter.Items.Add("<=");
ddlFilter.Items.Add(">=");
ddlFilter.AutoPostBack = true;
ddlFilter.SelectedIndexChanged += new EventHandler(this.HandleFilterCommand);
ddlFilter.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.Width, "30px");
ddlFilter.Height = new Unit("7px");
ddlFilter.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.Height, "8px");
ddlFilter.Style.Add(HtmlTextWriterStyle.FontSize, "8px");
m_ddlFilter[columnIndex] = ddlFilter;
}
headerCell.Controls.Add(txtFilter);
headerCell.Controls.Add(ddlFilter);
}
Notice that we are triggering the filter command when the user selects an operator from DropDownList; this is done by making the DropDownList to postback whenever its selection changes.
Here is our handler for the filter:
private void HandleFilterCommand(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.RequiresDataBinding = true;
FilterCommandEventArgs filterArgs = new FilterCommandEventArgs();
filterArgs.FilterExpression = GetFilterCommand();
this.OnFilterCommand(filterArgs);
}
The important thing to note here is that we set RequiresDataBinding to true; this statement is checked by GridView during the PreRender stage and it rebinds the data to the grid if it is true. This is exactly what we want; we don’t want to bind it immediately, we delay it till the very last stage. Meanwhile, we also provide a virtual method called OnFilterCommand for derived classes/pages to hook into our filtering.
Following is the OnPreRender function:
protected override void OnPreRender(EventArgs e)
{
String filterCommand = GetFilterCommand();
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(filterCommand) == false)
{
ApplyFilterCommand(filterCommand);
}
base.OnPreRender(e);
}
Here, we call the GetFilterCommand method, which loops through all the columns to form a where clause and returns it as a filterCommand. Note that we check for a space character at the end of Columns[i].HeaderText to find if the user has enabled filtering for Columns[i].
protected virtual String GetFilterCommand()
{
String filterCommand = "";
for (int i = 0; i < this.Columns.Count; i++)
{
if (this.Columns[i].HeaderText.EndsWith(" "))
{
DataControlFieldHeaderCell headerCell =
(DataControlFieldHeaderCell)this.HeaderRow.Cells[i];
TextBox txtFilter = (TextBox)m_txtFilter[i];
DropDownList ddlFilter = (DropDownList)m_ddlFilter[i];
BoundField aColumn;
if (!(this.Columns[i] is BoundField) ||
String.IsNullOrEmpty(ddlFilter.SelectedValue.Trim()))
{
continue;
}
aColumn = (BoundField)this.Columns[i];
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtFilter.Text))
{
continue;
}
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(filterCommand))
{
filterCommand = aColumn.DataField + " " +
ddlFilter.SelectedValue + " " + txtFilter.Text;
}
else
{
filterCommand += " AND " + aColumn.DataField + " " +
ddlFilter.SelectedValue + " " + txtFilter.Text;
}
}
}
return filterCommand;
}
We then use ApplyFilterCommand to change the DataSourceView’s SelectCommand. Note that we only support SqlDataSource. I have to look into supporting ObjectDataSource.
protected virtual void ApplyFilterCommand(String filterCommand)
{
DataSourceView dsv = this.GetData();
if (dsv is SqlDataSourceView)
{
String selectCommand = ((SqlDataSourceView)dsv).SelectCommand;
if (selectCommand.Contains(filterCommand)) {
return;
}
if (selectCommand.Contains("WHERE"))
{
selectCommand += " AND " + filterCommand;
}
else
{
selectCommand += " WHERE " + filterCommand;
}
((SqlDataSourceView)dsv).SelectCommand = selectCommand;
}
}
References
Things that we can improve
- Better way of specifying the columns that need filtering in the ASPX file. We can derive from
BoundColumn and implement it. - Instead of
DropDownList using postback, it can use the callback mechanism so that the whole page doesn't repaint each time you set a column filter. For this, we can implement a custom DropDownList. - Support for
ObjectDataSource..
History
- 08/27/2008 - Initial version.
