What is an Unsafe Assembly?
Assemblies which are built using normal computational functions are considered as safe assemblies. But when assemblies do external operations such as reading file information, creating files, etc., they are categorized as unsafe/external assemblies.
**Visual Studio creates safe assemblies by default.
We will create an assembly which will access the external file system, so that it will need external access. We will create a simple function which will return the file size for a given file, using the ‘FileInfo’ class.
using System;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
using System.IO;
public partial class UserDefinedFunctions {
[SqlFunction]
public static long GetFileSize(string FileName) {
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(FileName);
return fi.Length;
}
};
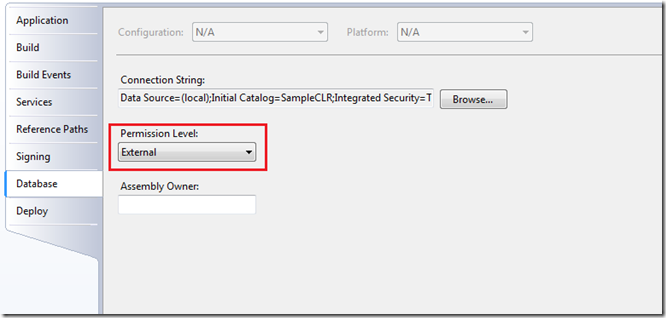
Now right click the project (from the solution explorer) and go the properties tab. From the ‘Database’ tab, select the permission level to ‘External’. (Default value is ‘Safe’.)
Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (Run it as Administrator since you are going to assign permission to the current user), and log in as a different user than the one you are trying to provide access permission to (For this example, I am logging as ‘sa’). Execute the following script:
use master;
grant external access assembly to [Domain\UserID];
use SampleCLR;
Use the appropriate values for ‘Domain’ and ‘UserID’ (and ‘SampleCLR’ is the database that I will be using).
**Please note that this is a server wide permission. Therefore the user can create any external assembly in any database on the SQL Server.
The above script will grant permission to the user to create external assemblies on the executed server. But it is not sufficient. The database should be allowed to have external access assemblies.
There are two methods of doing so:
- Making the database trusted
- Using sign assemblies
Method 1 ~ Making Database Trusted
Execute the following script (using Management Studio) in order to make the database trusted.
alter database SampleCLR set trustworthy on;
And if you inspect the database properties, you can see that the database’s ‘Trustworthy’ property value is changed to ‘True’.

Now go to Visual Studio and deploy the solution. It will succeed without any issues.
However, if you try to deploy without doing the above mentioned steps, you will get the following error:
CREATE ASSEMBLY for assembly <AssemblyName> failed because assembly <AssemblyName>
is not authorized for PERMISSION_SET = EXTERNAL_ACCESS. The assembly is authorized
when either of the following is true: the database owner (DBO) has EXTERNAL ACCESS
ASSEMBLY permission and the database has the TRUSTWORTHY database property on;
or the assembly is signed with a certificate or an asymmetric key that has a
corresponding login with EXTERNAL ACCESS ASSEMBLY permission.
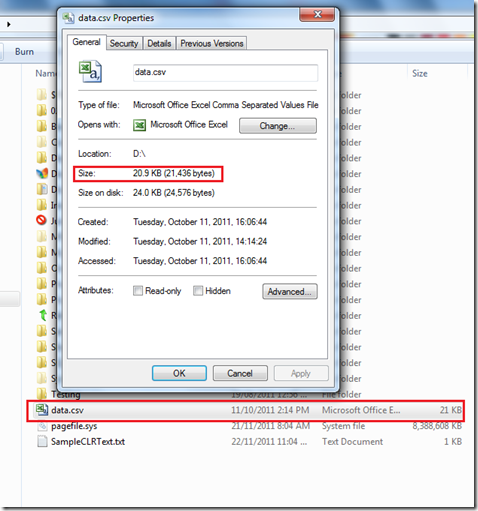
We will check the deployed assembly by executing the following script. (I have a file on my D:\ drive with the mentioned name.)
select dbo.GetFileSize(N'D:\data.csv')

And if you try to execute the function without making the database trusted, you will get the following error:
Msg 10314, Level 16, State 11, Line 1
An error occurred in the Microsoft .NET Framework while trying to load assembly id
65540. The server may be running out of resources, or the assembly may not be
trusted with PERMISSION_SET = EXTERNAL_ACCESS or UNSAFE. Run the query
again, or check documentation to see how to solve the assembly trust issues. For
more information about this error:
System.IO.FileLoadException: Could not load file or assembly 'sqlclrproject,
Version=0.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null' or one of its dependencies.
An error relating to security occurred. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x8013150A)
System.IO.FileLoadException:
at System.Reflection.Assembly._nLoad(AssemblyName fileName, String codeBase,
Evidence assemblySecurity, Assembly locationHint, StackCrawlMark& stackMark,
Boolean throwOnFileNotFound, Boolean forIntrospection)
at System.Reflection.Assembly.InternalLoad(AssemblyName assemblyRef, Evidence
assemblySecurity, StackCrawlMark& stackMark, Boolean forIntrospection)
at System.Reflection.Assembly.InternalLoad(String assemblyString, Evidence
assemblySecurity, StackCrawlMark& stackMark, Boolean forIntrospection)
at System.Reflection.Assembly.Load(String assemblyString)
Method 2 ~ Using Sign Assemblies
Set the trustworthy to false by using the following script (you only have to do this if you have made the database a trusted one in the previous example, and I am keeping it false for illustrative purposes.)
alter database SampleCLR set trustworthy off;
In order to sign an assembly, we need a public/private key file (.snk file). We will create one using the ‘sn.exe’.
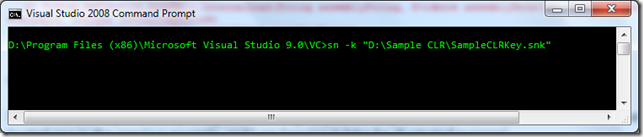
sn -k "D:\Sample CLR\SampleCLRKey.snk"
And sign the assembly using the key file that we have created now.
To sign an assembly: go to project properties => select the ‘Signing’ tab and check the ‘Sign the assembly’ check box and browse and select the created file. Save the project.
In order to deploy the assembly,
- Need to create an asymmetric key using the key file which we have created in the SQL Server
- Need to create a login using that asymmetric key
- Giving that login the permission for external access assemblies

Use the following script to create the asymmetric key using SQL Server Management Studio.
(** Please note that the key should be created on the master database.)
use master;
create asymmetric key CLRExtensionKey
from file = 'D:\Sample CLR\SampleCLRKey.snk'
encryption by password = '@Str0ngP@$$w0rd'
Now create the login using the above created key (*Please note that the login should be created on the database which you want to publish the assembly to.)
use SampleCLR;
create login CLRExtensionLogin from asymmetric key CLRExtensionKey;
Give the login permission for external access assemblies.
use master;
grant external access assembly to CLRExtensionLogin;
Now go to Visual Studio and deploy the solution. And you can use the following statement which we used in Method 1.
select dbo.GetFileSize(N'D:\data.csv')

