Introduction
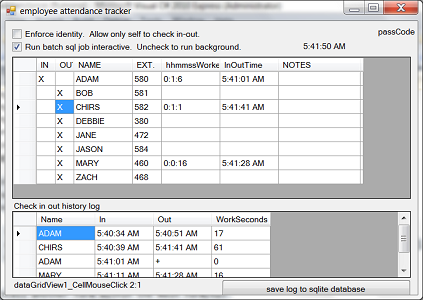
The above screen shot shows Adam checked-in, worked 17 seconds, took a 10 seconds break then checked-in again. Chirs worked 61 seconds and Mary worked 16 seconds. Currently, Adam is the only one still in office.
Last Friday, I was casually browsing codeproject site and was entertained by a question and answer that were posted a long time ago. Seeker looked for an attendance tracking program and got one replied that “no, we do not do your home work.” and I totally agreed with the replier.
But by Sunday, I woke up to a delicious morning, when the whole body is one sense, and imbibes delight through every pore(Walden Pond), with the add of a cup of hot coffee (Walden Pond author despised), I found myself coded away the employee attendance tracker project.
I coded to demonstrate following features (Microsoft C# 2010 Express) I learned recently:
- connect datagrideview with xml data source.
- call a form within an active form
- save persistent data to sqlite database
- organize code into a class to ease programming
- use a timer object to control the programming flow
- run batch job interactively or in background
The design scenarios for EAT
I designed program with the following two scenarios in mind.
scenario 1, a small shop only has one computer used by everyone to check in and out.
scenario 2, an office that everyone have their own computer and can check-in and out from their own desktop.
How does the program work?
EAT records employee work time in seconds and displays to user as HH:MM:SS.
The employee can check in out several times a day. The work time will be accumulated.
Once the employee checks-in, the work time will start to increase; once checked-out, the time stopped.
The time of check-in, check-out will be recorded and displayed.
Program enforced a security of passcode with four letters as the ATM passcode.
If passcode is enforced, user needs to enter the right passcode to Check-in, out and view report.
employee can click on IN, OUT, NAME column to indicate Check-in, Check-out and obtains a history report.
For the simplicity and this demo, program displays the history on the bottom view immediately.
A Timer object
A timer can simplify the flow of program execution and make program more responsive to user’s command. Without timer, programmer needs to introduce some artificial delay, such as sleep for a few micro seconds or doing some looping which can cause problem.
I use one timer in the following fashion:
Every second, timer will do the increment of the employee’s work time if an employee has checked in. It checks if user has done typing in Enter Passcode form. Without timer, the flow of control is difficult to coordinate between two forms because Windows does not wait for the Child form to finish.
Three SortedDictionary Objects
dTimeWorked and
dTimeSection use employee name as a key to store the accumulate total seconds worked and each check-in out total seconds worked.
dCheckedIn uses employee name as a key to store the true or false value to indicate if an employee is check-in or check-out.
SortedDictionary<string, int> dTimeWorked = new SortedDictionary<string, int>();
SortedDictionary<string, int> dTimeSection = new SortedDictionary<string, int>();
SortedDictionary<string, bool> dCheckedIn = new SortedDictionary<string, bool>();
XML Datasource
It is effortless to maintain employee's name and passcode in
employees.xml file, just edit it with a notepad. "EXT." is for employee's phone extension.
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>ADAM</NAME><EXT.>580</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1580</PASSCODE></ROW>
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>BOB</NAME><EXT.>581</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1581</PASSCODE></ROW>
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>CHIRS</NAME><EXT.>582</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1582</PASSCODE></ROW>
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>DEBBIE</NAME><EXT.>380</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1380</PASSCODE></ROW>
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>JANE</NAME><EXT.>472</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1472</PASSCODE></ROW>
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>JASON</NAME><EXT.>584</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1584</PASSCODE></ROW>
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>MARY</NAME><EXT.>460</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1460</PASSCODE></ROW>
<ROW><IN></IN><OUT>X</OUT><NAME>ZACH</NAME><EXT.>468</EXT.><hhmmssWorked></hhmmssWorked><InOutTime></InOutTime><NOTES></NOTES><PASSCODE>1468</PASSCODE></ROW>
The following code loadDGViewFromXML reads employees.xml and assigns to dataGridView1, connecting data with the ROW tag in employees.xml.
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
loadDGViewFromXML("employees.xml");
attendance = new DBAttendance();
dataGridView2.DataSource = attendance.atbl;
chkBoxViewBatch.Checked = true;
chkBoxSecurity.Checked = false;
timerStart()
}
public void loadDGViewFromXML(string filePath)
{
DataSet dsRows = new DataSet("ROW");
dsRows.ReadXml(filePath);
dataGridView1.DataSource = dsRows;
dataGridView1.DataMember = "ROW";
setdataGridView1ColumnWidth();
}
Enforced Security Mode
When program runs in the security mode, following prompt will pop up when employee tries to check-in or check-out.

Switching value between two columns
private void swapValue(int row, int col1, int col2)
{
string temp = dataGridView1.Rows[row].Cells[col1].Value.ToString();
dataGridView1.Rows[row].Cells[col1].Value = dataGridView1.Rows[row].Cells[col2].Value;
dataGridView1.Rows[row].Cells[col2].Value = temp;
}
Call another form within the main form
There are three steps to make this happening:
private void checkPassCode()
{
lblPassCode.Text = "";
Form2 subForm = new Form2(this);
subForm.Show();
}
Form1 mainForm;
public Form2(Form1 mainForm)
{
this.mainForm = mainForm;
InitializeComponent();
}
private void textBox1_KeyUp(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text.Length == 4)
{
mainForm.lblPassCode.Text = textBox1.Text;
this.Close();
}
}
Save log to sqlite database
If program is in interactive mode, the following screen will appear. Press a key to go on. Use d.bat, debug.sql to debug the sqllite.

d.bat
cls
sqlite3 employeeattendance.db < debug.sql
pause
debug.sql
SELECT * FROM sqlite_master;
SELECT * FROM worklog order by ename;
.quit
References
MSDN Form
Using-SQLite-in-your-C-Application
History
30-Jan-2012 - First version.
