Introduction
I was very frustrated by how difficult it was to understand the Prism EventAggregator from information available on the Internet. I had used it before, and the articles and examples just seemed to be difficult to comprehend. Since I had worked with it before, I knew it was not that difficult. I think it is now even easier with the Prism 4 library using the CompositePresentationEvent.
This is just an introduction to the EventAggregator, with a sample that is easy to understand. The sample only does communication within the form, which is silly, but this way everything is together. I found one of the problems with the existing examples is that the code is spread over many modules, making it very hard to understand what is happening.
Using Prism
The Prism 4.1 library can be installed from http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=28950. In the project, I have just taken the two DLLs I need and included them in the solution. The two used in this project are:
- Microsoft.Practices.Composite.Events
- Microsoft.Practices.Composite.Presentation.Events
There is a lot more to Prism than the <font face="Courier New">EventAggregator</font>, and Microsoft has published extensive information on Prism in Pattern and Practices: http://compositewpf.codeplex.com/releases/view/55580.
EventAggregator
The <font>EventAggregator</font> allows components in a composite application to communicate in a loosely coupled way. The Prism <font face="Courier New">EventAggregator</font> implements a publish/subscribe event mechanism. The publication/subscription to events is determined by a class used in the publish/subscribe generic. This supports good design by minimizing dependencies between modules, making them more loosely coupled. The subscribing module needs to know nothing about what module(s) will be generating the events, only the class needed to subscribe to them.
Prism is primarily intended to support desktop applications, but I view the Event Aggregator as being a lot more flexible. The Prism documentation concentrates on using the Event Aggregator for communicating with the View in a desktop or Silverlight application, and provides an integrated approach to creating a loosely coupled desktop experience.
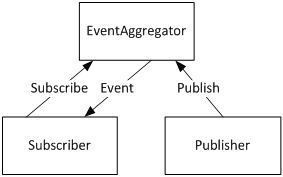
The Code
The example is a very simple application that is created with WPF and with only the code-behind. I wanted to clearly show how to implement a simple EventAggregator, so I put everything in the code-behind, including the classes needed to subscribe and publish.
using System;
using System.Windows;
using Microsoft.Practices.Composite.Events;
using Microsoft.Practices.Composite.Presentation.Events;
namespace EventAggregatorSample
{
public class test
{
}
public partial class MainWindow : Window, IDisposable
{
readonly IEventAggregator _aggregator = new EventAggregator();
private SubscriptionToken _intInt1SubscriptionToken;
private SubscriptionToken _intInt2SubscriptionToken;
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Unsubscribe(StringAction1);
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Subscribe(StringAction1);
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Subscribe(StringAction2,
ThreadOption.UIThread, false, i => i.Contains("b"));
_intInt1SubscriptionToken = _aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().
Subscribe(IntAction1, ThreadOption.UIThread, false, i => i > 0);
_intInt2SubscriptionToken = _aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().
Subscribe(IntAction1, ThreadOption.UIThread, false, i => i < 0);
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().
Subscribe(StringAction3, ThreadOption.UIThread, false,
s =>
{
int i;
return int.TryParse(s, out i);
});
}
private void StringAction1(string s) { TextBoxReceiveString1.Text = s; }
private void StringAction2(string s) { TextBoxReceiveString2.Text = s; }
private void StringAction3(string s) { TextBoxReceiveStringInt.Text = s; }
private void IntAction1(int i) { TextBoxReceiveInt.Text = i.ToString(); }
private void ButtonSendString1(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Publish(TextBoxSendString1.Text);
}
private void ButtonSendString2(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Publish(TextBoxSendString2.Text);
}
private void ButtonSendInt(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
int output;
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Publish(TextBoxSendInt.Text);
if (int.TryParse(TextBoxSendInt.Text, out output))
{
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().Publish(output);
if (output < 0)
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().Unsubscribe(_intInt2SubscriptionToken);
if (output < -1000)
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().Unsubscribe(IntAction1);
if (output == 0)
{
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().Unsubscribe(IntAction1);
_intInt1SubscriptionToken = _aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().
Subscribe(IntAction1, ThreadOption.UIThread, false, i => i > 0);
_intInt2SubscriptionToken = _aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().
Subscribe(IntAction1, ThreadOption.UIThread, false, i => i < 0);
}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("The value is not an integer");
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Unsubscribe(StringAction1);
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Unsubscribe(StringAction2);
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().Unsubscribe(_intInt1SubscriptionToken);
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleIntEvent>().Unsubscribe(_intInt2SubscriptionToken);
_aggregator.GetEvent<SampleStringEvent>().Unsubscribe(StringAction3);
}
}
public class SampleStringEvent : CompositePresentationEvent<string> { }
public class SampleIntEvent : CompositePresentationEvent<int> { }
}
In this code, I have created two Events, one that has a package of a string and one an integer (SampleStringEvent and SampleIntEvent<). There are three subscriptions to SampleStringEvent, one of which has no conditions, one that requires that the string package contains a ‘B’, and the other that requires that the string represent an integer. There are two subscriptions for SampleIntEvent, one for numbers greater than zero, and one for less (which means that a value “0” will not trigger an event). Both of these integer events use the same event handler, and both save a subscription token. I created the third subscription to the SampleStringEvent that required the string to represent an integer just to compare to the SampleIntEvent.
In the event handler for the ‘Send’ button for the integer, I check the value of integer values, and do actions according to the value:
- If the value is less than 0, the subscription token for the cases where the value is less than zero is used to Unsubscribe to the
SampleIntEvent. - If the value is zero, then re-Subscribe to both integer events.
- If the value is less than -1000, then Unsubscribe to both subscriptions using the address of the event handler.
This allows one of the special features of the subscription token to be demonstrated, and also shows that Unsubscribe works.
Results
- You will notice that I have defined two different events by creating two classes derived from
CompositePresentationEvent<T>. One of the nice things about this pattern is that many events can be defined with the same payload. The EventAggregator provides an instance for the subscribers to subscribe to events, and then the publishers to notify the subscribers that an event has occurred. The <font>GetEvent<T>()</font> method allows specific events to be accessed, the class type T defining the event. This returned object of type TEventType then can be used to subscribe/unsubscribe to the event or to fire/publish the event. - All but the first Subscribe calls use an extra argument to tell the
EventAggregator that the event is to be received on the UI thread. This can be important if the publisher is on a separate thread from the UI, and a UI element has to be updated. This is not a problem in this simple example. You can test what happens when this argument is changed to ThreadOption.BackgroundThread, a thread exception will occur because there is an attempt to update a textbox from a background thread. - You will notice there is an Unsubscribe to an event before the Subscribe in the constructor. This is to show that no exception is generated when an attempt is made to unsubscribe to an event that has not been subscribed to.
- The first two and the fifth subscriptions subscribe the same event and the other two to the other event. They use different event handlers (they write to different text boxes), and most include a filter (e.g., the second event handler will fire the event if the string contains a “b”). This is the filtering option when subscribing to the event. A lambda expression is passed as the fourth argument in the Subscribe method which will specify the filter, eliminating the need for the event handler to check if the event is applicable.
- For the third and fourth subscription, save the subscription token from the
Subscribe method. Because the subscription token is saved, the Unsubscribe method is able to use the subscription token as the argument instead of the delegate to the event handler. Using the subscription token allows one of many events using the same event handler to be unsubscribed to without unsubscribing to all the events using that event handler. By entering different numbers in the third TextBox, Unsubscribe one of the events using a subscription token, unsubscribe to both using the event handler variable, or re-subscribe to both events.< - To show good design practice, I also inherited from
IDisposable. The subscription to events in a singleton means that there is a resource that could cause memory leaks. Therefore, it is a good idea to dispose off resources using the EventAggregator. The default is for the subscriptions to be weak references, so for many applications, memory leaks will not be an issue. There is also an option (bool argument in the Subscribe method) when subscribing to keep the subscription alive when calling the constructor (strong reference). This means that memory management will not dispose of the aggregator except when specifically instructed.
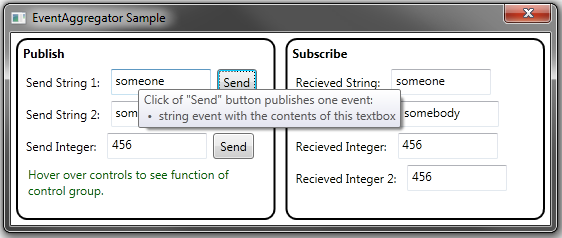
This example is extremely simple, and does not show the EventAggregator working between modules, let alone projects, but it works very well between projects. Prism is intended for large projects where the code is divided between many projects to help with management of the code development.
Advantages/Disadvantages
Disadvantages
- Registration: Having listeners do the registration adds repetitive code to each listener.
- >Discoverability/Traceability: Event aggregation is a form of indirection, which makes the system harder to understand.
- Serious memory leak issues since the
EventAggregator maintains references to subscribers. - Does not support Event Latching, meaning cannot ignore events at times, and then support updates.
- Event ordering is not guaranteed.
- Getting the event through the
GetEvent<T>() method to publish or subscribe is considered a bit clunky.
Advantages
- Ease of adding new features.
- Strong typing allows publishers and subscribers for a particular event to be quickly determined.
- Event filtering means a subscriber that is not interested in every instance can ignore those it is uninterested in. Also the filtering is done in the Event Aggregator.
- Fine grain control of what thread the processing should take place.
- A central place for instrumentation.
Note
Seems like it would be easy to add a disable method to subscriptions, and then an Enable method would allow events to be generated again without too much added cost/complexity. That removes one of the disadvantages.
Conclusion
The EventAggregator is a powerful tool in creating more maintainable applications. It can also be easily misused, creating a hard to understand application. It is part of the Prism library, but is one of those elements of the library whose usefulness extends far beyond the UI. I can see where on my current project it would have created a great simplification.
The write-up in the Microsoft Prism documentation is actually very good, but I had issues with the sample. After reviewing this article, I would recommend that you check out the information in this documentation: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff649187.aspx.
