Introduction
Sometimes when we learn about a new technology or a new programming language, we look for a way to do things we did with a technology already known. This is what happened to me five years ago (or more) when I read about the C# operator overload. Operator overloads are not usual topics for VB programmers, and overloading operators for handling complex numbers are not in my job. In this article, I would like to show you a small set of classes that can generate powerful WHERE conditions in a SQL query statement, simply combining expressions and the logical operators “&”, “|”, and “!”.
The problem
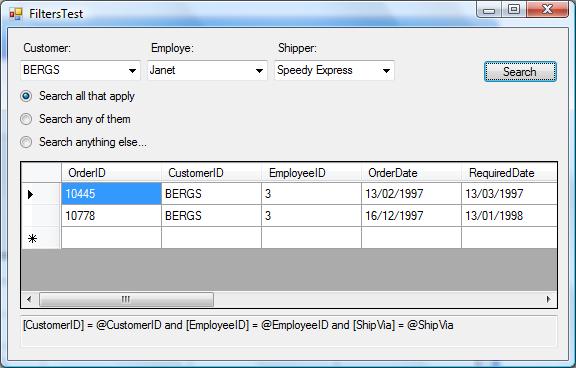
Imagine you have a user interface like the one shown above, the user can select one or more search options, and then you compose a SQL statement that retrieves the matching record.
If you compose the statement combining the values on the UI and the fields on the database table, you should be careful to add the right condition, balance parenthesis, and add the parameters to the command.
The solution: operator overload
I’ve defined a base class Expression which represents a general term in a WHERE clause. Then, I derived two classes: FieldExpression, which represents a field condition, and LiteralExpression which represents a general value based condition. The Expression base class implements all the operators necessary for the Expression comparison.
public abstract class Expression
{
public static Predicate operator ==(Expression expr1, Expression expr2)
{
return new Predicate(expr1, expr2, CompareOperator.Equal);
}
public static Predicate operator !=(Expression expr1, Expression expr2)
{
return new Predicate(expr1, expr2, CompareOperator.NotEqual);
}
public static Predicate operator >=(Expression expr1, Expression expr2)
{
return new Predicate(expr1, expr2, CompareOperator.GreaterOrEqual);
}
public static Predicate operator <=(Expression expr1, Expression expr2)
{
return new Predicate(expr1, expr2, CompareOperator.LessOrEqual);
}
}
Each operation between two Expressions produces a Predicate. Predicates could be combined with other Predicates using the logical operators “&”, “|”, and “!”, and each combination could be enclosed within parenthesis in order to obtain different evaluation precedence. Each Predicate is a tree where nodes are sets of conditions treated as AND or OR clauses, the leafs are the Expressions to evaluate. The predicate class is able to iterate recursively through its own hierarchy and render the basic WHERE statement. When a leaf node is reached (i.e., a Predicate where the attribute kind is NodeKind.Expression), it calls a callback function using ExpressionRenderDelegate.
private void Render(ExpressionRenderDelegate target,
StringBuilder filter, int nestedlevel)
{
if (this.kind == NodeKind.Expression)
{
target(filter, this.left, this.right, this.compare);
}
else
{
string comma = "";
if (this.kind == NodeKind.And)
{
foreach (Predicate p in this.siblings)
{
filter.Append(comma);
p.Render(target, filter, nestedlevel + 1);
comma = " and ";
}
}
if (this.kind == NodeKind.Or)
{
filter.Append("(");
foreach (Predicate p in this.siblings)
{
filter.Append(comma);
p.Render(target, filter, nestedlevel + 1);
comma = " or ";
}
filter.Append(")");
}
}
}
I’ve used this strategy for statement rendering, because I want to leave the Predicate class quite abstract, and have specialized classes for generating database specific WHERE clauses (see for example the two implementations: DataRowFilterRender and SqlFilterRender). That’s all.
The demo project
You can test the Filter library using the included FiltersTest application. It requires a connection to the famous Northwind SQL Server database, so please modify the connection string in the FiltersTest.exe.config file to suit your database server. Then, if you go in Form1.cs, you can see an example of how to use the library in the button1_Click shown below.
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Predicate p, p1 = null, p2 = null, p3 = null;
if(cmbcust.SelectedIndex >= 0) {
p1 = (FieldExpression)"CustomerID" ==
(LiteralExpression<string>)cmbcust.SelectedValue.ToString();
}
if (cmbemp.SelectedIndex >= 0)
{
p2 = (FieldExpression)"EmployeeID" ==
(LiteralExpression<int>)(int)cmbemp.SelectedValue;
}
if (cmbship.SelectedIndex >= 0)
{
p3 = (FieldExpression)"ShipVia" ==
(LiteralExpression<int>)(int)cmbship.SelectedValue;
}
if (optOr.Checked)
{
p = p1 | p2 | p3;
}
else
{
p = p1 & p2 & p3;
}
if (optExclude.Checked)
{
p = !p;
}
SqlFilterRender f = new SqlFilterRender("select * from Orders");
textBox1.Text = f.Render(p);
f.Command.Connection = this.ordersTableAdapter.Connection;
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter(f.Command);
this.northwindDataSet.Orders.Clear();
da.Fill(this.northwindDataSet.Orders);
}
Future works
The Filter library is not complete, there are a lot of operators in the SQL language not yet implemented (in, between, is null, and so on), and not all the basic data types are handled. I’m working on it, but in the meantime, feel free to add your contributions...
