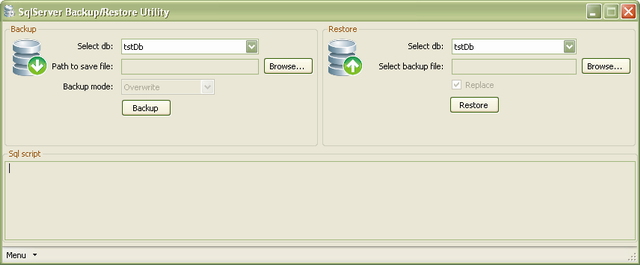
Introduction
Sometimes you need to migrate the database from the server where Management Studio is not installed (for example, when you use SQL Server Express Edition). This utility helps you to instantly backup, then restore to database server.
Using the Application
Before running an application, edit connectionStrings section in BackupRestore.exe.config file to connect your database.
Using the Code
At first, you need to get a list of available databases using the default connection string. The list of databases is bound to two combo boxes used for selecting database to backup or restore.
sqlConn = new SqlConnection(Properties.Settings.Default.masterConnectionString);
sqlServer = new Server(new ServerConnection(sqlConn));
dbList = new List<database>();
foreach (Database db in sqlServer.Databases)
{
dbList.Add(db);
}
cmbBackupDb.DataSource = dbList;
cmbRestoreDb.DataSource = dbList;
Database Backup

Database backup process is performed using the Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Backup class. When user selects database and file to save the backup to, the following method will be executed:
private void BackupDb()
{
dbName = ((Database)cmbBackupDb.SelectedItem).Name;
Backup dbBackup = new Backup();
try
{
dbBackup.Action = BackupActionType.Database;
dbBackup.Database = dbName;
dbBackup.BackupSetName = string.Format("{0} backup set.", dbName);
dbBackup.BackupSetDescription = string.Format("Database: {0}. Date: {1}.",
dbName, DateTime.Now.ToString("dd.MM.yyyy hh:m"));
dbBackup.MediaDescription = "Disk";
BackupDeviceItem device = new BackupDeviceItem
(saveBakFile.FileName, DeviceType.File);
dbBackup.Devices.Add(device);
txtBackupSql.Text = dbBackup.Script(sqlServer);
progBar.Visible = true;
progBar.Value = 0;
dbBackup.Complete += new ServerMessageEventHandler(dbBackup_Complete);
dbBackup.PercentCompleteNotification = 10;
dbBackup.PercentComplete +=
new PercentCompleteEventHandler(PercentComplete);
dbBackup.SqlBackup(sqlServer);
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
dbBackup.Abort();
MessageBox.Show(string.Format
("Exception occurred.\nMessage: {0}", exc.Message));
}
finally
{
sqlConn.Close();
}
}
Database Restore

Database restore process is performed using the Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Restore class. When user selects database and the file to restore from, the following method will be processed:
private void RestoreDb()
{
Database restoreDb = (Database)cmbRestoreDb.SelectedItem;
dbName = restoreDb.Name;
Restore dbRestore = new Restore();
dbRestore.Database = restoreDb.Name;
dbRestore.Action = RestoreActionType.Database;
dbRestore.ReplaceDatabase = true;
string fileLocation = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["SqlFileLocations"];
try
{
BackupDeviceItem device = new BackupDeviceItem
(openBakFile.FileName, DeviceType.File);
dbRestore.Devices.Add(device);
DataTable dtFiles = dbRestore.ReadFileList(sqlServer);
string backupDbLogicalName = dtFiles.Rows[0]["LogicalName"].ToString();
RelocateFile dbRf = new RelocateFile
(backupDbLogicalName, string.Format("{0}\\{1}.mdf", fileLocation, dbName));
RelocateFile logRf = new RelocateFile(string.Format("{0}_log",
backupDbLogicalName), string.Format("{0}\\{1}_Log.ldf",
fileLocation, dbName));
dbRestore.RelocateFiles.Add(dbRf);
dbRestore.RelocateFiles.Add(logRf);
string sql = string.Empty;
StringCollection scriptColl = dbRestore.Script(sqlServer);
foreach (string str in scriptColl)
{
sql += str;
}
txtBackupSql.Text = sql;
progBar.Visible = true;
progBar.Value = 0;
dbRestore.Complete += new ServerMessageEventHandler(dbRestore_Complete);
dbRestore.PercentComplete +=
new PercentCompleteEventHandler(PercentComplete);
dbRestore.SqlRestore(sqlServer);
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
dbRestore.Abort();
MessageBox.Show(string.Format
("Exception occurred.\nMessage: {0}", exc.Message));
}
finally
{
sqlConn.Close();
}
}
History
- 9th June, 2009: Initial post
