Introduction
In this article I am going to show how to use Authorization and Authentication using
a WCF service in Enterprise Architecting standards. This article is about advanced WCF concepts. I am using an error driven approach for better experience with the problems and the solutions.
The core aspects we cover here are:
- WCF
- ASP.NET Authentication Service
- Custom Authentication
- HTTP Cookies
- Authorization
PrincipalPermission attribute - Thread CurrentPrincipal
- Message Interceptors
You will be wondering what the above are. In a quick snap following are the activities involved.
- Create a WCF Service Application
- Add a AuthenticationService.svc reusing the ASP.NET Authentication Service
- Create a User Validator class
- Enable Custom Authentication in Global.asax
- Return Cookie if valid user
- Modify service configuration
- Try accessing the Authentication Service in the browser
- Create a UtilityService.svc with a method named
GetData(int) - Decorate
GetData(int) with the PrincipalPermission attribute for Authorized Access only - Decorate the
UtilityService class with the AspNetCompatibilityRequirements attribute - Set he Utility Service constructor to set CurrentPrincipal from the Cookie
- Create the client application and add references to both services
- Create the Authentication Service instance and invoke the
Login() method - Receive the cookie and store it
- Create the
UtilityService instance and invoke GetData() - Attach the Cookie to the
UtilityService client - Test the application and ensure proper functioning
- Move the cookie attaching code to Interceptors in the Client Application
- Move the identity setting code to Interceptors in the Service Application
- Modify the service side code to include Role instead of Name
- Use Encrypted Ticket for storing User Name and Roles
- Retest the application
Authentication and Authorization
Before starting, we should have a clear understanding about Authentication and Authorization:
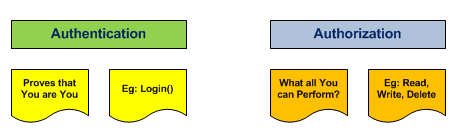
To simplify, Authentication proves the user by using his/her credentials or certificates. Authorization deals with the rights the user has. For example, the Admin user will have Read, Write, Delete privileges but an ordinary Clerk will
only have Read permissions.
In WCF we are using the Membership infrastructure of ASP.NET to implement Authentication and Authorization.
Now we can start with the steps above:
Step 1: Create a WCF Service Application

Step 2: Add a AuthenticationService.svc reusing the ASP.NET Authentication Service.
Add a new WCF Service and name it AuthenticationService.svc. Delete the associated files as we are going to expose the ASP.NET Authentication Service.
- Delete AuthenticationService.cs
- Delete IAuthenticationService.cs
Replace the contents of AuthenticationService.svc with the following:
<%@ ServiceHost
Language="C#"
Service="System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticationService"
Factory="System.Web.ApplicationServices.ApplicationServicesHostFactory" %>
Here we are exposing System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticationService through the
svc file. The associated namespace is referred to our project by default.
The Authentication Service supports the following methods:
Login()Logout()ValidateUser()
Each of these methods work with the Membership Provider to perform the functionalities. We can also customize these aspects by providing our own database of user credentials and
controlling the cookie creations.
Step 3: Create the User Validator class.
The Authentication Service will receive the User Name and Password. We need to validate this with a Custom Provider. (We are not using
the ASP.NET Membership provider here.)
Following is the class definition of it. For the time being we are hard-coding
the user name as tom and password as chicago12.
public class UserValidator
{
public bool IsUserValid(string userName, string password)
{
bool result = (userName == "tom") && (password == "chicago12");
return result;
}
}
(Later in real projects, you can change this single class to connect to a database and validate the username and password.)
Step 4: Enable Custom Authentication in Global.asax.
Add a new item, Web > Global Application Class into the project.

Replace the Appilcation_Start event as follows:
protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticationService.Authenticating +=
new EventHandler<System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticatingEventArgs>(
AuthenticationService_Authenticating);
}
Add the following event handler:
void AuthenticationService_Authenticating(object sender,
System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticatingEventArgs e)
{
e.Authenticated = new UserValidator().IsUserValid(e.UserName, e.Password);
e.AuthenticationIsComplete = true;
}
The above method extracts the User Name and Password from the Custom Credential object of
the Authentication Event Argument. Then it validates the User Name and Password
with our UserValidator class.
The property Authenticated represents true / false if a user is valid or not, respectively.
Step 5: Return Cookie if valid User.
Now we need to send back a Cookie if the user is valid. For this, add the following code in the above method.
if (e.Authenticated)
{
HttpCookie cookie = new HttpCookie(FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName);
cookie.Value = e.UserName;
HttpResponseMessageProperty response = new HttpResponseMessageProperty();
response.Headers[HttpResponseHeader.SetCookie] = cookie.Name + "=" +cookie.Value;
OperationContext.Current.OutgoingMessageProperties
[HttpResponseMessageProperty.Name] = response;
}
The above code performs the following:
- Create a cookie with the default name (.ASPXAUTH)
- Set value to the User Name
- Add the cookie to the WCF
OperationContext message property
Step 6: Modify the service configuration.
Now we need to modify the web.config file to include the following:
- Enable the Authentication Service
- Enable ASP.NET Compatibility
- Replace the contents of web.config with the following:
="1.0"
<configuration>
<system.web>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.0" />
</system.web>
<system.web.extensions>
<scripting>
<webServices>
<authenticationService enabled="true"/>
</webServices>
</scripting>
</system.web.extensions>
<system.serviceModel>
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior>
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/>
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="true"/>
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors>
<serviceHostingEnvironment multipleSiteBindingsEnabled="true" aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true" />
</system.serviceModel>
<system.webServer>
<modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests="true"/>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
Step 7: Try accessing the Authentication Service in the browser.
Now build the project and try accessing AuthenticationService.svc in a browser. If you are able to see the following page, then you are on the right track. (Else, please ensure the steps above for any corrections / use the attached source code.)

Step 8, 9, 10: Create a UtilityService.svc with a method named GetData(int).
Add a new WCF service named UtilityService.svc into our service application. Delete the existing methods inside the resulting classes and interfaces. Add the following contents to the interface and class, respectively.
[ServiceContract]
public interface IUtilityService
{
[OperationContract]
string GetData(int i);
}
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Security.Permissions;
using System.ServiceModel.Activation;
namespace EntArch_WcfService
{
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode =
AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)]
public class UtilityService : IUtilityService
{
[PrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Name = "tom")]
public string GetData(int i)
{
string result = "You Entered: " + i.ToString();
return result;
}
}
}
[PrinicalPermission] ensures that only the user with name tom is authorized to access the method
GetData(). In real world applications we will be
using the Role property to authorize a group of users.
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements] ensures that the service can be run in ASP.NET
Compatibility mode as we are
using this mode for our Authentication infrastructure needs.
Authorization can be applied in two ways:
- Imperative: Example:
if (Roles.IsUserInRole()) - Declarative:
PrincipalPermission
Step 11: Set the Utility Service constructor to set CurrentPrincipal from cookie.
The WCF Authentication Service had sent a cookie to the user. This cookie will be returned back to the Utility Service (and any new services in future) by the
client. We need to retrieve the Cookie and extract the user name out of it. This
user name has to be set to the current thread principal.
In real projects, you need to set the Roles as well.
Following are the activities involved in this step:
- Retrieve Cookie from
OperationContext Income Message properties - Extract the user name out of the Cookie
- Create a class
CustomIdentity implementing IIdentity - Set the Thread Current Principal to the
CustomIdentity instance
Modify the constructor of UtilityService as follows:
public UtilityService()
{
var messageProperty = (HttpRequestMessageProperty)
OperationContext.Current.IncomingMessageProperties[HttpRequestMessageProperty.Name];
string cookie = messageProperty.Headers.Get("Set-Cookie");
string[] nameValue = cookie.Split('=', ',');
string userName = string.Empty;
if (nameValue.Length >= 2)
userName = nameValue[1];
CustomIdentity customIdentity = new CustomIdentity();
GenericPrincipal threadCurrentPrincipal = new GenericPrincipal(customIdentity, new string[] { });
customIdentity.IsAuthenticated = true;
customIdentity.Name = userName;
System.Threading.Thread.CurrentPrincipal = threadCurrentPrincipal;
}
Following is the class definition for CustomIdentity. (You need to place it inside the service project.)
class CustomIdentity : IIdentity
{
public string AuthenticationType
{
get;
set;
}
public bool IsAuthenticated
{
get;
set;
}
public string Name
{
get;
set;
}
}
Step 12: Create the client application and add references to both services.
Now we are ready to create the client application to consume both the services. Add a new Windows Forms
application to our existing solution and name it ClientApplication.
Make sure you made the Solution Properties > Start Up Projects to start both our Server and Client Applications as shown below.

Now add Service References to the following services:
- AuthenticationService.svc
- UtilityService.svc

Step 13: Create Authentication Service instance and invoke the Login() method.
Now we are ready to test our Authentication Service. Create a button on the
Main Form and name it Authenticate. On the button click, create an instance of the
client and invoke the Login() method with the right credentials. You should get
the result as true.
private void AuthenticateButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
AuthSvc.AuthenticationServiceClient client =
new AuthSvc.AuthenticationServiceClient();
bool result = client.Login("tom", "chicago12", string.Empty, true);
MessageBox.Show(result.ToString());
}
On running the client application and clicking the button, you will receive the following output:

Step 14: Receive the Cookie and store it.
The above code just checks the result of Login(). But we need to actually have the returned cookie in case of successful validation. For this we need to replace
the above code with the following:
AuthSvc.AuthenticationServiceClient client = new AuthSvc.AuthenticationServiceClient();
using (new OperationContextScope(client.InnerChannel))
{
bool result = client.Login("tom", "chicago12", string.Empty);
var responseMessageProperty = (HttpResponseMessageProperty)
OperationContext.Current.IncomingMessageProperties[HttpResponseMessageProperty.Name];
if (result)
{
string cookie = responseMessageProperty.Headers.Get("Set-Cookie");
MessageBox.Show(result.ToString() + Environment.NewLine + cookie);
}
}
The code creates a new OperationContextScope and invokes the
Login() method. After invocation, the Cookie is extracted from the response header.
On running the client application again and clicking the button, you should be getting the following output:

The output displays the result as well as the cookie information. You can see the cookie name as .ASPXAUTH and value as tom.
Step 15: Create the UtilityService instance and invoke
GetData() by attaching stored Cookie.
Inside the client application, we can add reference to the second service (UtilityService.svc).

Now add a new button with text as Invoke Utility. On the button click handler, add the following code:
private void InvokeUtility_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UtilSvc.UtilityServiceClient utilClient = new UtilSvc.UtilityServiceClient();
string result = utilClient.GetData(10);
MessageBox.Show(result);
}
On executing the application and clicking the button, you will receive the following error:
"Request for principal permission failed."

The reason for the error is that the current thread user name is not tom. This error can be solved by doing the next step.
Step 16: Attach the Cookie to the UtilityService client.
In order to solve the above error, we need to attach the cookie from the Authentication Service to the current
OperationContext. We need to extract the variable cookie
out of the Authentication method so that it can be used in the Utility Invocation method.

Now replace the contents of InvokeUtility_Click as follows:
private void InvokeUtility_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(cookie))
{
MessageBox.Show("Please click Authenticate first.");
return;
}
UtilSvc.UtilityServiceClient utilClient = new UtilSvc.UtilityServiceClient();
using (new OperationContextScope(utilClient.InnerChannel))
{
HttpRequestMessageProperty request = new HttpRequestMessageProperty();
request.Headers[HttpResponseHeader.SetCookie] = cookie;
OperationContext.Current.OutgoingMessageProperties
[HttpRequestMessageProperty.Name] = request;
string result = utilClient.GetData(10);
MessageBox.Show(result);
}
}
The method now performs the following activities:
- Ensure the cookie field has a value (Valid Authentication Service call needed).
- Create an HTTP Request Message property to set to Cookie field.
- Attach the Message property instance to the
OperationContext.
Step 17: Test the application and ensure proper functioning.
Now we are ready with the Authentication and Authorization infrastructure. Please run the application and test the features in
two steps:

- Click the Authenticate button and wait for the response.
- Click the InvokeUtility button.
You will get the following message box on successful authorization.

If you can see the above result.. Great!! You are done with Authentication and Authorization.
Step 18: Move the Cookie attaching code to Interceptors in the Client Application.
Now we need to implement Interceptors in the client side.
Why do we need Interceptors?
This is because the above code of attaching a Cookie to the OperationContext seems to be
a tedious job every time we need to do a service call. We can move these tasks
to the background using WCF Interceptors.
MSDN: WCF Data Services enable an application to intercept request messages so that you can add custom
logic to an operation. You can use this custom logic to validate data in incoming messages. You can also use it to further restrict the scope of a query
request, such as to insert a custom authorization policy on a per request basis.
Following are the activities involved in this step.
- Add Interceptor Behavior inside client web.config
- Create the Interceptor Behavior class
- Create the Message Inspector class
- Move the code from the Form to the Message Inspector class
To start, add the following code into the Client Application app.config file. Make sure you add them just before the
</system.serviceModel> tag.
<behaviors>
<endpointBehaviors>
<behavior name="InterceptorBehaviour">
<interceptorBehaviorExtension />
</behavior>
</endpointBehaviors>
</behaviors>
<extensions>
<behaviorExtensions>
<add name="interceptorBehaviorExtension" type="ClientApplication.InterceptorBehaviorExtension,
ClientApplication, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null" />
</behaviorExtensions>
</extensions>
Change the behaviorConfiguration element of the Utility Service section as shown below:

Now we need to create the Behavior Extension and Interceptor classes inside the Client Application.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
using System.ServiceModel.Configuration;
namespace ClientApplication
{
public class InterceptorBehaviorExtension : BehaviorExtensionElement, IEndpointBehavior
{
public override System.Type BehaviorType
{
get { return typeof(InterceptorBehaviorExtension); }
}
protected override object CreateBehavior()
{
return new InterceptorBehaviorExtension();
}
public void AddBindingParameters(ServiceEndpoint endpoint,
System.ServiceModel.Channels.BindingParameterCollection bindingParameters)
{
}
public void ApplyClientBehavior(ServiceEndpoint endpoint,
System.ServiceModel.Dispatcher.ClientRuntime clientRuntime)
{
clientRuntime.MessageInspectors.Add(new CookieMessageInspector());
}
public void ApplyDispatchBehavior(ServiceEndpoint endpoint,
System.ServiceModel.Dispatcher.EndpointDispatcher endpointDispatcher)
{
}
public void Validate(ServiceEndpoint endpoint)
{
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel.Dispatcher;
using System.ServiceModel.Channels;
using System.Net;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ClientApplication
{
public class CookieMessageInspector : IClientMessageInspector
{
private string cookie;
public CookieMessageInspector()
{
}
public void AfterReceiveReply(ref System.ServiceModel.Channels.Message reply,
object correlationState)
{
}
public object BeforeSendRequest(ref System.ServiceModel.Channels.Message request,
System.ServiceModel.IClientChannel channel)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(Globals.Cookie))
{
MessageBox.Show("No Cookie Information found! Please Authenticate.");
return null;
}
HttpRequestMessageProperty requestMessageProperty = new HttpRequestMessageProperty();
requestMessageProperty.Headers[HttpResponseHeader.SetCookie] = Globals.Cookie;
request.Properties[HttpRequestMessageProperty.Name] = requestMessageProperty;
return null;
}
}
}
ApplyClientBehavior – This method enables us to attach client side behaviors to the WCF calls. We are attaching a Cookie Inspector (CookieMessageInspector) in this method.CookieMessageInspector – This class takes care of attaching the Cookie to outgoing message properties (through
the BeforeSendRequest method). The Cookie is saved in the Globals.Cookie property after the Authentication Service is called.
Step 19: Move the identity setting code to Interceptors in the Service Application.
You can remember that our UtilityService.svc has a lot of code in the constructor doing the following:
- Extracting Cookie from the current
OperationContext - Getting the user name from the Cookie
- Setting the user name to the current thread
This code for one utility seems to be fine. But in the case of dozens of utility services, the same code needs to be duplicated. We can solve this by using
background interceptors in the service side. For this we can use the same BehaviorExtension and Inspector classes with slight modifications.
Place the following files inside the WCF Service Application.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
using System.ServiceModel.Configuration;
using System.ServiceModel.Dispatcher;
namespace EntArch_WcfService
{
public class InterceptorBehaviorExtension : BehaviorExtensionElement, IServiceBehavior
{
public override Type BehaviorType
{
get { return typeof(InterceptorBehaviorExtension); }
}
protected override object CreateBehavior()
{
return new InterceptorBehaviorExtension();
}
public void AddBindingParameters(ServiceDescription serviceDescription,
System.ServiceModel.ServiceHostBase serviceHostBase,
System.Collections.ObjectModel.Collection<ServiceEndpoint> endpoints,
System.ServiceModel.Channels.BindingParameterCollection bindingParameters)
{
}
public void ApplyDispatchBehavior(ServiceDescription
serviceDescription, System.ServiceModel.ServiceHostBase serviceHostBase)
{
foreach (ChannelDispatcher dispatcher in serviceHostBase.ChannelDispatchers)
{
foreach (var endpoint in dispatcher.Endpoints)
{
endpoint.DispatchRuntime.MessageInspectors.Add(new IdentityMessageInspector());
}
}
}
public void Validate(ServiceDescription serviceDescription,
System.ServiceModel.ServiceHostBase serviceHostBase)
{
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ServiceModel.Dispatcher;
using System.ServiceModel.Channels;
using System.Net;
using System.IO;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Security.Principal;
namespace EntArch_WcfService
{
public class IdentityMessageInspector : IDispatchMessageInspector
{
public object AfterReceiveRequest(ref Message request,
System.ServiceModel.IClientChannel channel,
System.ServiceModel.InstanceContext instanceContext)
{
var messageProperty = (HttpRequestMessageProperty)
OperationContext.Current.IncomingMessageProperties[HttpRequestMessageProperty.Name];
string cookie = messageProperty.Headers.Get("Set-Cookie");
string[] nameValue = cookie.Split('=', ',');
string userName = string.Empty;
if (nameValue.Length >= 2)
userName = nameValue[1];
CustomIdentity customIdentity = new CustomIdentity();
GenericPrincipal threadCurrentPrincipal =
new GenericPrincipal(customIdentity, new string[] { });
customIdentity.IsAuthenticated = true;
customIdentity.Name = userName;
System.Threading.Thread.CurrentPrincipal = threadCurrentPrincipal;
return null;
}
public void BeforeSendReply(ref Message reply, object correlationState)
{
}
}
}
Now remove the code from the UtilityService constructor. The new constructor will look empty.
public UtilityService()
{
}
Now add the following code to the web.config file of the service just under <system.serviceModel>.
<services>
<service name="EntArch_WcfService.UtilityService" behaviorConfiguration="InterceptorBehavior"/>
</services>
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior>
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/>
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="true"/>
</behavior>
<behavior name="InterceptorBehavior">
<interceptorBehaviorExtension />
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors>
<extensions>
<behaviorExtensions>
<add name="interceptorBehaviorExtension"
type="EntArch_WcfService.InterceptorBehaviorExtension,
EntArch_WcfService, Version=1.0.0.0,
Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null" />
</behaviorExtensions>
</extensions>
Please make sure that the namespaces are correct and build the project.
Step 20: Modify the service side code to include Role instead of Name.
The current Authorization code is hardcoded for the user name Tom. But this is not feasible in the real world. We need to change the user name authorization to role based authorization.
Here each validated user will have certain roles associated with them. This role information will be fetched from the database during the Authentication process
and passed along with the Cookie to the user.
Example:
| User
| Roles
|
| tom
| Read
|
| pike
| Read, Write
|
The roles are kept as strings and we can separate methods based on the roles as given below:
[PrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Role = "Read")]
public string GetData(int i)
{}
[PrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Role = "Write")]
public string SetData(int i)
{}
To accomplish the above, we need to modify the following.
- Modify
UserValidator.IsUserVaild to return roles from the database - Modify the
AuthenticationService_Authenticating.Authentication method to include roles - Concatenate the user name and roles in the Cookie value as semicolon (;) separated
- Modify the Identity Inspector to retrieve roles from the cookie value
The modifications are given below:
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode = AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)]
public class UtilityService : IUtilityService
{
public UtilityService()
{
}
[PrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Role = "Read")]
public string GetData(int i)
{
string result = "You Entered: " + i.ToString();
return result;
}
}
public class UserValidator
{
public bool IsUserValid(string userName, string password, out IList<string> roles
)
{
roles = new List<string>();
bool result = (userName == "tom") && (password == "chicago12");
if (result)
roles.Add("Read");
return result;
}
}
private string Concatenate(string userName, IList<string> roles)
{
string result = userName + ";";
foreach (string role in roles)
result += role + ";";
return result;
}
Please note that the Read role is hardcoded in the above code:
public object AfterReceiveRequest(ref Message request,
System.ServiceModel.IClientChannel channel,
System.ServiceModel.InstanceContext instanceContext)
{
var messageProperty = (HttpRequestMessageProperty)
OperationContext.Current.IncomingMessageProperties[HttpRequestMessageProperty.Name];
string cookie = messageProperty.Headers.Get("Set-Cookie");
string[] nameValue = cookie.Split('=', ',');
string value = string.Empty;
if (nameValue.Length >= 2)
value = nameValue[1];
string userName = GetUserName(value);
string[] roles = GetRoles(value);
CustomIdentity customIdentity = new CustomIdentity();
GenericPrincipal threadCurrentPrincipal = new GenericPrincipal(customIdentity, roles);
customIdentity.IsAuthenticated = true;
customIdentity.Name = value;
System.Threading.Thread.CurrentPrincipal = threadCurrentPrincipal;
return null;
}
private string[] GetRoles(string value)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
{
List<string> roles = new List<string>();
int ix = 0;
foreach (string item in value.Split(';'))
{
if (ix > 0)
if (item.Trim().Length > 0)
roles.Add(item);
ix++;
}
return roles.ToArray<string>();
}
return new string[0];
}
private string GetUserName(string value)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
{
foreach (string item in value.Split(';'))
return item;
}
return string.Empty;
}
Once the above codes are modified and ready, you can run the application. Try changing the role inside the PrincipalPermission attitude to Write and you will get
an error on accessing the GetData() method.
Step 21: Create Cookie encryption.
As of now, our cookie contains information that is easily readable by HTTP examining
utilities like Fiddler. This makes the Cookie information prone to security threats.

In this step, we are going to add encryption to the Cookie value. The above image displays the value which we are going to encrypt (username;Role).
FormsAuthenticationTicket: The System.Web.Security namespace provides a convenient class for us. We can store the user name and roles
information inside this class instance. The ticket class also provides expiry and encryption facilities.
The following code creates the ticket:
FormsAuthenticationTicket ticket = new FormsAuthenticationTicket(
1,
e.UserName,
DateTime.Now,
DateTime.Now.AddHours(24),
true,
roles,
FormsAuthentication.FormsCookiePath);
The following code encrypts the ticket:
string encryptedValue = FormsAuthentication.Encrypt(ticket);
Now we can pass the ticket as a name value pair through the message properties:
HttpResponseMessageProperty response = new HttpResponseMessageProperty();
response.Headers[HttpResponseHeader.SetCookie] = FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName + "=" + encryptedValue;
OperationContext.Current.OutgoingMessageProperties[HttpResponseMessageProperty.Name] = response;
You need to specify the Cookie name and Machine Key properties inside the web.config as shown below:
<configuration>
<system.web>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.0" />
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms slidingExpiration="true"
name="AuthCookie"
protection="All"
timeout="20"/>
</authentication>
<machineKey
decryption="AES"
validation="SHA1"
decryptionKey="1523F567EE75F7FB5AC0AC4D79E1D9F25430E3E2F1BCDD3370BCFC4EFC97A541"
validationKey="33CBA563F26041EE5B5FE9581076C40618DCC1218F5F447634EDE8624508A129"
/>
</system.web>
In the Identity Inspector, we need to change the message property parsing code to reconstruct the
ticket. On running the client application, we can see that the message information is now encrypted.

Step 22: Retest the application.
Now perform the following activities:
- Set the property of the client app.config to Copy Always
- Execute the application
- Click on Authenticate button
- Click on Utility Invoke button
Performing the button clicks as specified in Step 17, the same results should be achieved.

We can see the result as shown below:

This concludes our article on WCF Authentication using Cookies. I hope you enjoyed the learning curves and solutions.
Note
The Membership provider used above is for learning purpose and in real world we have to go for Membership providers like ASP.NET Membership Provider, Active Directory Membership Provider etc.
References
Summary
In this article we have seen how to expose a WCF Service Application along with Authentication Service and Authorization according to Enterprise Architecting standards.
Following are the activities involved:
- The client authenticates using AuthenticationService.svc and receives
a Cookie.
- The authenticated Cookie is used in further communication.
- The Authorization part is played by the
PrincipalPermission attribute. - The WCF Interceptors do a good job by doing the Cookie attaching in the background.
You can note that the client needs to authenticate only once. Later the Cookie received is used to access other services. Based on real time requirements we need to
enable Ticket Expiry as well.
The attached source contains the projects we have explained. Please let me know any clarifications or queries you have.
In the next article, we can learn about using a Silverlight application to use the same service.
