Table of Contents
Introduction
If you read some of my CodeProject articles, probably you know that I'm not very much bashful to share with you, what I learned? Actually if I find something interesting, I will always try to share this with you. I'm not well experienced on article writing, but I try because of the wonderful knowledge sharing platform of CodeProject. I hope that everybody will agree with me that CodeProject provides us an excellent platform to share knowledge.
Before I start about this article in detail, I would like to share a little incident; few months ago, I was working to update an ERP system, where I found huge bugs of Transact-SQL and table design. Most of the time, the system fails to process data transaction. To find out the reason, I assign one of my team members. After few days, he reports to me that some of the main reasons are data type mismatch, data conversion error, stored procedure parameters issues, etc. So we decided that at first we have to find out the sources of the error and the types of error as well. So the question is how we can achieve this?
When we started to work on that, we were very confused, Should we maintain a text file to keep a log or create a table where we stored the log but the problem is a number of stored procedures will work with various OLE objects. So finally, we decided that we need to use Windows event log API. This article is about how to create a Windows event log and write a custom message using Transact-SQL.
A Little Basic Knowledge on OLE Object
When I start to learn about Microsoft OLE Objects, I found a huge theoretical explanation on Online resources specially on Microsoft Development Network (MSDN). I just try to give you some summary from them.
You can also find some more detail on OLE automation from my CodeProject article. The links are given below:
What is an OLE Object
OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) is Microsoft's framework for a compound document technology. Briefly, a compound document is something like a display desktop that can contain visual and information objects of all kinds: text, calendars, animations, sound, motion video, 3-D, continually updated news, controls, and so forth. Each desktop object is an independent program entity that can interact with a user and also communicate with other objects on the desktop. Part of Microsoft's ActiveX technologies, OLE takes advantage and is part of a larger, more general concept, the Component Object Model (COM) and its distributed version, DCOM. An OLE object is necessarily also a component (or COM object).
So we can define an OLE object as “OLE is a compound document standard developed by Microsoft Corporation. It enables you to create objects with one application and then link or embed them in a second application. Embedded objects retain their original format and links to the application that created them.”
More details can be found at this link.
Using the Code
This is a very simple way. I wrote some methods to create or write any custom message in a Windows event log. The methods with a short description are given below:
Methods
GetAuthor IsExist CreateLog Write_INFO_EventLog Write_WARNING_EventLog Write_FAILUR_EventLog Write_SUCCESS_EventLog Write_ERROR_EventLog
More details can be found at this link.
GetAuthor
This is a simple method, actually when I start writing code at first I write this method which just returns a string type data. It was just for testing purposes.
IsExist
This method will check whether the requested log name is registered or not. If it is registered, then it will return true otherwise false.
Arguments: string_expression is an expression of the type string / varchar
Return type: bool
Sample Code Example
private bool IsExist(string strLogName)
{
bool Reasult = false;
if (System.Diagnostics.EventLog.SourceExists(strLogName)) return Reasult = true;
return Reasult;
}
CreateLog
This method will create a new Windows event log if the requested log name is not registered. Once it successfully registers the log, it will return true otherwise false.
Arguments (Log name): string_expression is an expression of the type string / varchar
Return type: bool
Sample Code Example
public bool CreateLog(string strLogName)
{
bool Reasult = false;
try
{
if (!this.IsExist(strLogName))
{
System.Diagnostics.EventLog.CreateEventSource(strLogName, strLogName);
System.Diagnostics.EventLog SQLEventLog =
new System.Diagnostics.EventLog();
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.Log = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry("The " + strLogName +
" was successfully initialize component.",
EventLogEntryType.Information);
Reasult = true;
}
}
catch
{
Reasult = false;
}
return Reasult;
}
Write_INFO_EventLog
This method writes a user defined string into the specified registered event log as an information message.
Arguments
- Event log name as
string - Message source as
string - Message detail as
string
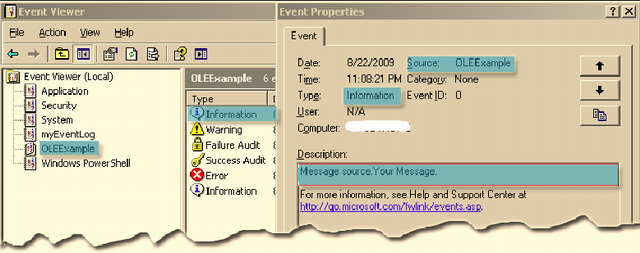
Figure - 1 showing the output of the method "Write_INFO_EventLog".
Sample Code Example
public void Write_INFO_EventLog(string strLogName
, string strSource
, string strErrDetail)
{
if (this.IsExist(strLogName))
{
System.Diagnostics.EventLog SQLEventLog =
new System.Diagnostics.EventLog();
try
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString(strSource)
+ Convert.ToString(strErrDetail),
EventLogEntryType.Information);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString("INFORMATION: ")
+ Convert.ToString(ex.Message),
EventLogEntryType.Information);
}
finally
{
SQLEventLog.Dispose();
SQLEventLog = null;
}
}
}
Write_WARNING_EventLog
This method writes a user defined string into the specified registered event log as a warning message.
Arguments
- Event log name as
string - Message source as
string - Message detail as
string

Figure - 2 showing the output of the method "Write_WARNING_EventLog"
Sample Code Example
public void Write_WARNING_EventLog(string strLogName
, string strSource
, string strErrDetail)
{
if (this.IsExist(strLogName))
{
System.Diagnostics.EventLog SQLEventLog =
new System.Diagnostics.EventLog();
try
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString(strSource)
+ Convert.ToString(strErrDetail),
EventLogEntryType.Warning);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString("WARNING: ")
+ Convert.ToString(ex.Message),
EventLogEntryType.Warning);
}
finally
{
SQLEventLog.Dispose();
SQLEventLog = null;
}
}
}
Write_FAILUR_EventLog
This method writes a user defined string into the specified registered event log as a failure audit message.
Arguments
- Event log name as
string - Message source as
string - Message detail as
string
Sample Code Example
public void Write_FAILUR_EventLog(string strLogName
, string strSource
, string strErrDetail)
{
if (this.IsExist(strLogName))
{
System.Diagnostics.EventLog SQLEventLog =
new System.Diagnostics.EventLog();
try
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString(strSource)
+ Convert.ToString(strErrDetail),
EventLogEntryType.FailureAudit );
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString("FAILUR: ")
+ Convert.ToString(ex.Message),
EventLogEntryType.FailureAudit );
}
finally
{
SQLEventLog.Dispose();
SQLEventLog = null;
}
}
}
Write_SUCCESS_EventLog
This method writes a user defined string into the specified registered event log as a success audit message.
Arguments
- Event log name as
string - Message source as
string - Message detail as
stri<code>ng
Sample Code Example
public void Write_SUCCESS_EventLog(string strLogName
, string strSource
, string strErrDetail)
{
if (this.IsExist(strLogName))
{
System.Diagnostics.EventLog SQLEventLog =
new System.Diagnostics.EventLog();
try
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString(strSource)
+ Convert.ToString(strErrDetail),
EventLogEntryType.SuccessAudit );
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString("FAILUR: ")
+ Convert.ToString(ex.Message),
EventLogEntryType.SuccessAudit );
}
finally
{
SQLEventLog.Dispose();
SQLEventLog = null;
}
}
}

Figure - 3 showing the output of the methods "Write_SUCCESS_EventLog" and "Write_FAILUR_EventLog".
Write_ERROR_EventLog
This method writes a user defined string into the specified registered event log as an error message.
Arguments
- Event log name as
string - Message source as
string - Message detail as
string
Sample Code Example
public void Write_ERROR_EventLog(string strLogName
, string strSource
, string strErrDetail)
{
if (this.IsExist(strLogName))
{
System.Diagnostics.EventLog SQLEventLog =
new System.Diagnostics.EventLog();
try
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString(strSource)
+ Convert.ToString(strErrDetail),
EventLogEntryType.Error);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SQLEventLog.Source = strLogName;
SQLEventLog.WriteEntry(Convert.ToString("ERROR: ")
+ Convert.ToString(ex.Message),
EventLogEntryType.Error);
}
finally
{
SQLEventLog.Dispose();
SQLEventLog = null;
}
}
}

Figure - 4 showing the output of the method "Write_ERROR_EventLog".
OLE Automation
To know about OLE automation, I would like to request you to read my CodeProject article at this link.
Transact-SQL Script
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[spEventLog]
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @intResult INT
DECLARE @comHandle INT
DECLARE @errorSource VARCHAR(8000)
DECLARE @errorDescription VARCHAR(8000)
DECLARE @inputText VARCHAR(500)
DECLARE @Author VARCHAR(500)
DECLARE @isSuccess INT
EXEC @intResult = sp_OACreate 'OLEExample.ClsExample', @comHandle OUTPUT, 1
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle, 'GetAuthor',@Author OUTPUT
SELECT @Author
SET @isSuccess = -1
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle,
'CreateLog',@isSuccess OUTPUT, 'OLEExample'
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle,
@errorSource OUTPUT, @errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
SELECT @isSuccess
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle,
'Write_INFO_EventLog',@isSuccess OUTPUT, 'OLEExample',_
'Message source. ','Your Message.'
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle,
@errorSource OUTPUT, @errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle,
'Write_WARNING_EventLog',@isSuccess OUTPUT, _
'OLEExample','WARNING Message source. ','Your WARNING Message.'
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle,
@errorSource OUTPUT, @errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle,
'Write_FAILUR_EventLog',@isSuccess OUTPUT, 'OLEExample',_
'FAILUR Message source. ','Your FAILUR Message.'
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle,
@errorSource OUTPUT, @errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle,
'Write_SUCCESS_EventLog',@isSuccess OUTPUT, 'OLEExample',_
'SUCCESS Audit Message source. ','Your SUCCESS Audit Message.'
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle,
@errorSource OUTPUT, @errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle,
'Write_ERROR_EventLog',@isSuccess OUTPUT, 'OLEExample',_
'ERROR Message source. ','Your ERROR Message.'
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle,
@errorSource OUTPUT, @errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle, @errorSource OUTPUT,
@errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC @intResult = sp_OAMethod @comHandle,
'Write_AUTHOR_EventLog',@isSuccess OUTPUT, 'OLEExample',_
'[dbo].[spEventLog]. ','AUTHOR: MD. MARUFUZZAMAN'
IF (@intResult <> 0)
BEGIN
EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @comHandle,
@errorSource OUTPUT, @errorDescription OUTPUT
SELECT [Error Source] = @errorSource, [Description] = @errorDescription
RETURN
END
EXEC sp_OADestroy @comHandle
END
GO
Conclusion
I hope that this article might be helpful to you. Enjoy!
Reference
Points of Interest
When registering COM+, we must use the following command by using Visual Studio command prompt.
Command:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0\VC>
RegAsm OLEExample.dll /tlb:OLEExample.tlb /codebase
Note: Do not use regsvr32 for registering COM+.
History
- 23rd August 2009: Initial post
