Introduction
XML is widely used for storing and formatting data. By using the current APIs, it is slightly cumbersome to handle and play with XML data.
LINQ to XML (.NET 3.5) makes handling XML easier through query experience similar to SQL.
Background
In this article, we will see basic things on how to work with XML using LINQ, where we will deal with storing and reading server information in XML format.
Using the Code
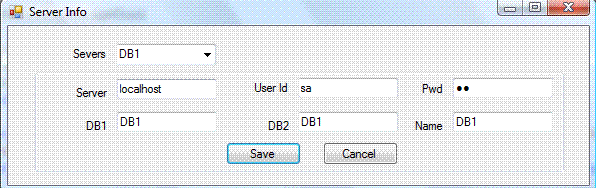
The project is a Windows application which contains a form which collects server information to be stored in the format shown below:
<servers>
<server>
<address>localhost</address>
<displayname>DB1</displayname>
<uid>sa</uid>
<pwd>sa</pwd>
<db1>DB1</db1>
<db2>DB1</db2>
</server>
</servers>
Let's look at the code below which reads the XML file and gets the server names in a list:
public static List<string> GetAllServers()
{
List<string> serversList = new List<string>();
try
{
var servers = from e in XElement.Load( path ).Elements( "server" )
select ( string )e.Element( "displayname" );
foreach ( var server in servers )
{
if ( !string.IsNullOrEmpty( server ) )
serversList.Add( server );
}
return serversList;
}
catch ( Exception ex )
{
ServerInfoDialog.ShowErrorMessage( ex.Message );
}
return serversList;
}
The above code loads the XML file by the path specified and retrieves all display names from the 'server' element.
Now, let's look at the code for updating or adding new server information into a file:
public void SaveConfig()
{
XElement doc = XElement.Load( path );
IEnumerable<XElement> serverInformation =
( from b in doc.Elements( "server" )
where ( ( string )b.Element( "displayname" ) ).Equals( DisplayName )
select b );
if ( serverInformation.Count() > 0 )
{
foreach ( XElement xe in serverInformation )
{
xe.SetElementValue( "address", Address );
xe.SetElementValue( "displayname", DisplayName );
xe.SetElementValue( "uid", UserId );
xe.SetElementValue( "pwd", Password );
xe.SetElementValue( "db1", DB1 );
xe.SetElementValue( "db2", DB2 );
}
}
else
{
XElement newServer = new XElement( "server",
new XElement( "address", Address ),
new XElement( "displayname", DisplayName ),
new XElement( "uid", UserId ),
new XElement( "pwd", Password ),
new XElement( "db1", DB1 ),
new XElement( "db2", DB2 ) );
doc.Add( newServer );
}
doc.Save( path );
}
The above code first finds whether there is already an element with the same display name. If found, that server info will be updated, else a new element is created and the file will be saved at the end.
Now let's get all the information of the server selected by the user and display it:
public void SetServerInformation( string selectedServer )
{
XDocument doc = XDocument.Load( path );
var serverInformation = from serverInfo in doc.Descendants( "server" )
where serverInfo.Element( "displayname" ).Value ==
selectedServer
select new ServerInfoService
{
Address = serverInfo.Element( "address" ).Value,
DisplayName =
serverInfo.Element( "displayname" ).Value,
UserId = serverInfo.Element( "uid" ).Value,
Password = serverInfo.Element( "pwd" ).Value,
DB1 = serverInfo.Element( "db1" ).Value,
DB2 = serverInfo.Element( "db2" ).Value
};
}
The above code loads the file and reads all element information where the display name will be the user selected server.
Conclusion
This article gives a brief introduction on using LINQ to work with XML. For more information on LINQ, refer to the links below.
References
History
