This article shows how to register and manage System-Global hotkeys in WinForm and WPF applications and perform some keyboard manipulation from your app and has a custom hotkey control.
Introduction
Sometimes, your form or window (depending on if you're building a WinForm or a WPF application) may need to respond to a hotkey or shortcut (used interchangeably in this article) regardless of if the app is focused or running in the background.
Also, if you want to register multiple hotkeys, within and or outside your application, it gets a tad bit difficult. In this article, we’ll be creating a library that’ll allow an app process hotkeys and perform other keyboard manipulations.
Terminologies
HotKeys: These are the keys the user presses on the keyboard that may need to be processed by your app.LocalHotKeys: A class that manages regular hotkeys within your app; they have a key and or modifier (modifiers are optional for LocalHotkeys), they work only when the application is focused. An example is Control + C (used for copying in most cases)GlobalHotKeys: A class that manages hotkeys outside of your application, regardless of whether your form or window has focus or is running in background. They are regular hotkeys that has a key AND modifier and are processed as long as the application is running (whether it is focused, minimized or running in background). An example is Window + L (used for locking the computer)ChordHotKeys: A class of advanced LocalHotKeys, more like two LocalHotKeys; the BASE and the CHORD. The base must have a BaseKey AND a BaseModifier that start the Chord when they are pressed, the Chord has a key and also an optional Modifier. An example is Control + K, Control + D (used for indenting code in the Visual Studio IDE), in this case Control + K is the base while Control + D is the hotkey of chord. Like LocalHotKeys, they work only when the app is focused.HotKeyManager: This class manages the above classes; it keeps tracks of their changes and raises events when the hotkey associated with them are pressed on the keyboard. In addition, the HotKeyManager class can listen to all key presses from the keyboard, reports them to our app and can also simulate a keypress.
* Registering a HotKey means subscribing the Hotkey to a HotKeyManager.
HotKeyControl: A UserControl that allows a user set a hotkey via input.
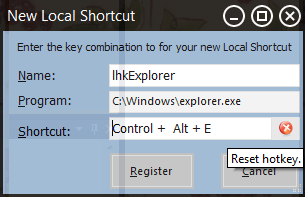
HotKey control for WinForm

HotKeyControls for WPF
* The HotKeyControl does not regard the WindowKey as a modifier, rather treats it as a key exactly like in the Key(s) enum.
Background
Before I started using .NET, I wanted to disable some keys on the keyboard, especially Control + Alt + Delete for a computer based test app I created, I looked into ways of doing that programmatically but found none until I resulted to use ScanCodeMap, (now don’t get too excited, the HotKeyManager cannot do that either) only caveat was I had to restart Windows when I want to enable or disable those keys. I also had trouble in .NET implement global shortcuts and making the keys changeable. This library was created to speed things up, allow you perform manipulations on the keyboard with ease, and manage numerous dynamic hotkeys at the same time like in VLC player and other applications.
The Source Files
The HotKeyManager class for WPF has most if not all of the functionalities of the WinForm equivalent and though it would probably be easier to create the class for both platforms in the same project, however, if you were creating a program in WinForm and wanted to reference the DLL, you’ll be required to also import:
PresentationCorePresentationFramework andWindowsBase
Which are WPF’s core libraries and also if you were creating a program in WPF, you’ll be required to import:
System.Windows.Forms andSystem.Drawing.
with the version depending on the ones used in writing the project, this would make your project clogged with unnecessary references and that is why I have writting the library in two separate projects keeping the code usage exactly the same. The source files (in C# but compatible with VB) contains 5 projects: a library for WinForm in C# 2.0, a library for WPF in C# 3.0 and 4.0 (this was just because I wanted to create a better control for WPF) and two demo projects, one each for WinForm and WPF.
* I'm working on creating another library for WinForm, converting the classes into components so that they can be added and validated at design time instead of writing them in code.
Getting to Work
A shortcut consists of a modifier (can be one or more) and a single key. The modifiers keys are: Shift Key, Alt Key, the Control Key and the Window Key (this isn't exactly a modifier and should be used only when creating GlobalShortcuts), please note that this is regardless of whether it is the left or right key, the right Alt key in WinForm sends ‘Control + Alt’ , WPF sends LeftCtrl but with a few adjustments sends the same key as WinForm.
A reference is added to Microsoft.VisualBasic which we’ll be using to perform some string manipulations and getting some keyboard key states.
We define a modifier enum and mark it with the flags attribute which specifies that the enum can be treated as a bit field and the second enum defines when we want our local hotkey events to be raised.
#region **Modifiers and constants.
[Flags]
public enum Modifiers
{
NoModifier = 0x0000,
Alt = 0x0001,
Ctrl = 0x0002,
Shift = 0x0004,
Win = 0x0008
}
public enum RaiseLocalEvent
{
OnKeyDown = 0x100,
OnKeyUp = 0x101
}
#endregion
WPF already has its own modifiers keys in the namespace System.Windows.Input as ModifierKeys, and also has the flags attribute set, so this would not be necessary.
The flags attribute allows the modifiers to be combined via XOR so one could write a statement in WinForm as:
Modifiers modifier = Modifiers.Control | Modifiers.Shift;
Dim modifier as Modifiers = Modifiers.Control Xor Modifiers.Shift
And in WPF:
ModifierKeys modifier = ModifierKeys.Control | ModifierKeys.Shift;
Dim modifier as ModifierKeys = ModifierKeys.Control Xor ModifierKeys.Shift
Meaning that the modifier is ‘Control + Shift’.
The RaiseLocalEvent enum will determine when a LocalHotKey event should be raised, when the key is down (OnKeyDown) or when it is released (OnKeyUp).
public class HotKeyAlreadyRegisteredException : Exception
public class HotKeyUnregistrationFailedException : Exception
public class HotKeyRegistrationFailedException : Exception
public class HotKeyInvalidNameException : Exception
HotKeyAlreadyRegisteredException: As the name implies, this exception is thrown when an attempt is made to re-register hotkey (with the same name, key and or modifier) with the HotKeyManager. For GlobalHotKeys, this exception is thrown when the key and modifier of the global hotkey is in use by another application. For instance, an attempt to register Window + L raises this exception. When using the library, an attempt to register a ChordHotKey with a base key and base modifier that is being used by a LocalHotKey throws a HotKeyAlreadyRegisteredException, also, an attempt to register a LocalHotKey with its key and modifier already registered as the base key and modifier of a ChordHotKey throws the same exception. Precedence is given to the HotKey that’s first registered.
HotKeyUnregistrationFailedException: This is thrown when a HotKey cannot be unregistered. Same for HotKeyRegistrationFailedException, thrown when a HotKey cannot be registered, also occurs when you attempt to register HotKeys like Control + Escape.
HotKeyInvalidNameException: This exception is thrown when you attempt to register a HotKey with an invalid name; hotkeys in this library are treated more like controls, you are required to assign every hotkey with a name, same as in Visual Studio, a valid HotKey name does not start with a number or contain space. The names are checked in the function..
public static bool IsValidHotkeyName(string text)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(text)) return false;
if (text.Contains(" ") || char.IsDigit((char)text.ToCharArray().GetValue(0)))
return false;
return true;
}
And of course, you can change this if you like.
The HotKey Shared Class
This is a static class that helps to perform some functions like checking the name of a HotKey control discussed earlier, splitting a string into its respective key and modifier (useful for our HotKeyControl) and reversing the process. It also contains a struct for enumerating Modifiers. The HotKeyControl will be taking hotkeys as a string which isn’t very useful to use unless we split it into its respective key and modifier, the ParseShortcut function allows us to achieve this.
The class has the static functions ParseShortcut and CombineShortcut. The former allows you strip a shortcut, say "Control + Alt + T" into its respective modifiers (Control, Alt) and key (T), while the latter does the reverse.
The ParseShortcut function is an object array that returns the Modifier of a Hotkey string in it lower bound and the Key in the upper bound.
The function public static object[] ParseShortcut(string text) has one overload.
public static object[] ParseShortcut(string text, string separator)
{
bool HasAlt = false; bool HasControl = false; bool HasShift = false;
bool HasWin = false;
Modifiers Modifier = Modifiers.None;
Keys key = 0;
string[] result;
string[] separators = new string[] { separator };
result = text.Split(separators, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (string entry in result)
{
if (entry.Trim() == Keys.Control.ToString())
{
HasControl = true;
}
if (entry.Trim() == Keys.Alt.ToString())
{
HasAlt = true;
}
if (entry.Trim() == Keys.Shift.ToString())
{
HasShift = true;
}
if (entry.Trim() == Keys.LWin.ToString())
{
HasWin = true;
}
}
if (HasControl) { Modifier |= Modifiers.Control; }
if (HasAlt) { Modifier |= Modifiers.Alt; }
if (HasShift) { Modifier |= Modifiers.Shift; }
if (HasWin) { Modifier |= Modifiers.Win; }
KeysConverter keyconverter = new KeysConverter();
key = (Keys)keyconverter.ConvertFrom(result.GetValue(result.Length - 1));
return new object[] { Modifier, key };
}
Notice that the function uses the KeysConverter class, the TypeConverter for System.Windows.Forms.Keys enum to convert a string into its Key enum representation.
Usage:
object[] Result = ParseShortcut("Control + Shift + A", " + ");
Modifiers modifier = (Modifiers)Result[0];
Keys key = (Keys)Result[1];
In VB:
Dim Result() as Object = ParseShortcut("Control + Shift + A", " + ")
Dim modifier as Modifiers = CType(Result(0), Modifiers)
Dim key as Keys = CType(Result(0), Keys)
And to reverse this process, we use the CombineShortcut function:
public static string CombineShortcut(Modifiers mod, Keys key)
{
string hotkey = "";
foreach (Modifiers a in new HotKeyShared.ParseModifier((int)mod))
{
hotkey += a.ToString() + " + ";
}
if (hotkey.Contains(Modifiers.None.ToString())) hotkey = "";
hotkey += key.ToString();
return hotkey;
}
Usage:
Modifiers modifier = Modifiers.Control | Modifiers.Shift;
CombineShortcut(modifier, Keys.A);
Dim modifier as Modifiers = Modifiers.Control Xor Modifiers.Shift
CombineShortcut(modifier, Keys.A)
The HotKey Control
The HotKeyControl is a UserControl that extends the TextBox control to catch Keys the user presses when it is active. It adds the event HotKeyIsSet which is raised when a HotKey has been set by the user and also adds the properties UserKey and UserModifer (not visible in design view) which return the key and modifer the user sets and a property ForceModifiers (visible in design view) which specifies that the user should be forced to enter a modifer when setting a hotkey if true else accepts all hotkeys.
For WinForm
The HotKey control utilizes the KeyDown and KeyUp event of the textbox to get keys pressed by the user. And uses a reset button to clear the HotKey entered.
void HotKeyControl_KeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
e.SuppressKeyPress = true;
this.Text = string.Empty;
KeyisSet = false;
if (e.Modifiers == Keys.None && forcemodifier)
{
MessageBox.Show("You have to specify a modifier like 'Control', 'Alt' or 'Shift'");
this.Text = Keys.None.ToString();
return;
}
foreach (string modifier in e.Modifiers.ToString().Split(new Char[] { ',' }))
{
if (modifier != Keys.None.ToString())
this.Text += modifier + " + ";
}
if (e.KeyCode == Keys.ShiftKey | e.KeyCode == Keys.ControlKey | e.KeyCode == Keys.Menu)
{
KeyisSet = false;
}
else
{
this.Text += e.KeyCode.ToString();
KeyisSet = true;
}
}
The KeyUp event determines if a HotKey is already set by checking the variable KeyisSet, if true raises the HotKeyIsSet event or clears the control.
void HotKeyControl_KeyUp(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
if (KeyisSet == false)
{
this.Text = Keys.None.ToString();
}
else
{
if (HotKeyIsSet != null)
{
var ex = new HotKeyIsSetEventArgs(UserKey, UserModifier);
HotKeyIsSet(this, ex);
if (ex.Cancel)
{
KeyisSet = false;
this.Text = Keys.None.ToString();
}
}
}
}
For WPF
The source file contain two HotKey controls, one built in .NET Framework 3.0 and the other in .NET Framework 4.0.
The HotKeyControl uses the PreviewKeyDown event and a hook to get the key the user presses.
public HotKeyControl()
{
this.GotFocus += new RoutedEventHandler(HotKeyControl_GotFocus);
this.hook = new HwndSourceHook(WndProc);
this.LostFocus += new RoutedEventHandler(HotKeyControl_LostFocus);
this.ContextMenu = null;
Text = Keys.None.ToString();
this.IsReadOnly = true;
this.PreviewKeyDown += new KeyEventHandler(HotKeyControl_PreviewKeyDown);
}
* The HotKeyControl does not treat the Window key as a modifier, rather treats it as a key.
HotKeys
The GlobalHotkey class implements INotifyPropertyChanged, it alerts the HotKeyManager when the Key, Modifier or the Enabled property is changed.
It also, similar to the LocalHotKey and ChordHotKey class, implements IEquatable and ISerializable.
The HotKeys raise the event HotKeyPressed when their keys are pressed on the keyboard. When GlobalHotKeys are registered, they are given a id which is returned when they are pressed.
[Serializable]
public class GlobalHotKey : INotifyPropertyChanged, ISerializable,
IEquatable<GlobalHotKey> { }
[Serializable]
public class LocalHotKey : ISerializable, IEquatable<LocalHotKey>,
IEquatable<ChordHotKey> { }
[Serializable]
public class ChordHotKey : ISerializable, IEquatable<ChordHotKey><chordhotkey>,
IEquatable<LocalHotKey><localhotkey> { }</localhotkey></chordhotkey>
* The HotKeys have to be registered with the HotKeyManager before they can work (raise events).
The HotKeyManager
The HotKeyManager class in WinForm which will manage the GlobalHotKey, LocalHotKey and ChordHotKey class implements:
IMessageFilter: will allow the class to receive windows message callbacksIDisposable: will free all resources, and unregister all HotKeys
The class will receive Windows messages by adding:
Application.AddMessageFilter(this);
In the constructor and will stop receiving Windows messages by adding:
Application.RemoveMessageFilter(this);
In the destructor.
And then the class will receive the messages by adding the function, this is as a result of implementing IMessageFilter.
public bool PreFilterMessage(ref Message m) { }
For WPF, a Hook is added to the class to allow it to recieve Windows messages.
I copied the Keys enum from WinForm to the WPF class to allow for Local and ChordHotKeys since Windows still sends the same key message as that of WinForm to WPF applications.
this.hook = new HwndSourceHook(WndProc);
this.hwndSource = (HwndSource)HwndSource.FromVisual(window);
this.hwndSource.AddHook(hook);
The class will then receive Windows messages from the function.
private IntPtr WndProc
(IntPtr hwnd, int msg, IntPtr wParam, IntPtr lParam, ref bool handled) { }
In the source file, the HotKeyManager does not have an empty contructor, this is because I want you to provide a form or a window as the case may be, because the handle of the form or window that the GlobalHotKeys are registered to is required by Windows to register or unregister them. If you want to use this library in a service or you do not intend to use GlobalHotKeys, you can add an empty constructor and make necessary changes, the library would still work just fine.
The HotKeyManager automatically disposes itself when the form or window that it registered with is closing, you don’t need to redispose in your app and no exception is thrown if you do. It can also be disabled, it still receives messages, it just doesn’t do anything with them and in WinForm, you can set the HotKeyManager to temporarily disable itself when another form is shown, probably a dialog because it still raises events, set DisableOnManagerFormInactive to true.
Now, when a key is pressed in your application, Windows sends a message containing information about the pressed key and state (whether it is held down or has been released) to our class because we have subscribed to them.
However, to get the Modifiers pressed when the key was pressed, I’ve referenced Microsoft.VisualBasic to speed things up. You can get the Modifiers pressed anytime on the keyboard like this:
Microsoft.VisualBasic.Devices.Keyboard UserKeyBoard =
new Microsoft.VisualBasic.Devices.Keyboard();
bool AltPressed = UserKeyBoard.AltKeyDown;
bool ControlPressed = UserKeyBoard.CtrlKeyDown;
bool ShiftPressed = UserKeyBoard.ShiftKeyDown;
You can see that the Window key is not treated as a modifier but rather as Key, to get the state of the Window key, you can use:
short ret = Win32.GetKeyState(0x5b);
if ((ret & 0x8000) == 0x8000) LocalModifier |= Modifiers.Window;
When any key is pressed on the keyboard, the HotKeyManager iterates through all LocalHotKeys and ChordHotKeys registered with it and raises events for the ones found.
Finding LocalHotKeys
Keys keydownCode = (Keys)(int)m.WParam & Keys.KeyCode;
LocalHotKey KeyDownHotkey = LocalHotKeyContainer.Find
(
delegate(LocalHotKey d)
{
return ((d.Key == keydownCode) && (d.Modifier == LocalModifier)
&& (d.WhenToRaise == RaiseLocalEvent.OnKeyDown));
}
);
LocalHotKey KeyDownHotkey = (from items in LocalHotKeyContainer
where items.Key == keydownCode && items.Modifier == LocalModifier
where items.WhenToRaise == RaiseLocalEvent.OnKeyDown
select items).FirstOrDefault();
* This search returns null when nothing is found.
Finding ChordHotKeys
When a LocalHotKey cannot be found, the Manager checks if a base key and modifier of any registered ChordHotKey matches the Key pressed, that is why you cannot set the same base key and modifier for any other localhotkey. If it finds one, it goes to ChordMode, and waits for another key to be pressed discarding modifiers, if the second key that is pressed matches the chordkey and modifier of any chord, it raises the event for that chord, else leaves ChordMode and gives a sound like Visual Studio does.
Finding GlobalHotKeys
To register GlobalHotKeys, there is no built in built in functionality that allows for this, but it is built into the Win32 API and .NET provides a way to call non-native libraries. The methods we’re interested in are defined in User32.dll, RegisterHotKey and UnRegisterHotKey.
RegisterHotKey and UnregisterHotKey
Now, define the important methods: The static functions that allow us to register shortcuts.
[DllImport("user32", CharSet = CharSet.Ansi, SetLastError = true, ExactSpelling = true)]
private static extern int RegisterHotKey(IntPtr hwnd, int id, int modifiers, int key);
[DllImport("user32", CharSet = CharSet.Ansi, SetLastError = true, ExactSpelling = true)]
private static extern int UnregisterHotKey(IntPtr hwnd, int id);
Note that we're not providing a method body. The method is defined in user32.dll, we're just adding a way for our application to directly call that method.
hWnd refers to the form or window handleid is the unique identifier of the hotkeymodifiers is the integer representation of the modifier keys (shift/alt/ctrl/win) that you want pressed with your key- and
key is the virtual key code for the hotkey
When a GlobalHotKey is pressed, Windows sends the ID of the GlobalHotKey assigned to it when it was registered in wParam, this ID can then be used to search through all GlobalHotKeys like we did for LocalHotKeys.
Other Functions
The HotKeyManager also supports enumeration, you can iterate through a specific hotkey; global, local or chord like this:
string message = "Global HotKeys.\n";
foreach (GlobalHotKey gh in MyHotKeyManager.EnumerateGlobalHotKeys)
{
message += string.Format("{0}{1}", Environment.NewLine, gh.FullInfo());
}
message += "\n\nLocal HotKeys.\n";
foreach (LocalHotKey lh in MyHotKeyManager.EnumerateLocalHotKeys)
{
message += string.Format("{0}{1}", Environment.NewLine, lh.FullInfo());
}
message += "\n\nChord HotKeys.\n";
foreach (ChordHotKey ch in MyHotKeyManager.EnumerateChordHotKeys)
{
message += string.Format("{0}{1}", Environment.NewLine, ch.FullInfo());
}
MessageBox.Show(message, "All HotKeys registered by this app.",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);

This will allow iteration to be easier, because we can directly iterate through all ChordHotKeys like this
as opposed to implementing IEnumerable<ChordHotKey> and iterating like this, which will require using the namespace System.Collections.Generic
foreach (ChordHotKey ch in (IEnumerable<ChordHotKey>)MyHotKeyManager)
{
message += string.Format("{0}{1}", Environment.NewLine, gh.FullInfo());
}
The HotKeyManager also utilises the Win32 API to get all keyboard presses even if your app isn’t focused and can disable them.
KeyboardHookEventHandler keyboardhandler = (sender, handler) =>
{
if (handler.Modifier == KeyboardHookEventArgs.modifiers.Shift)
{ handler.Handled = true; }
switch (handler.Key)
{
case Keys.A:
case Keys.E:
case Keys.I:
case Keys.O:
case Keys.U:
handler.Handled = true;
return;
}
};
The code above disables the vowel keys on the keyboard but disables all keys when the Shift Key is pressed.
The HotKeyManager, using Win32API can also simulate a Key press, here, we simulate pressing Control + A.
MyHotKeyManager.SimulateKeyDown(Keys.Control);
MyHotKeyManager.SimulateKeyPress(Keys.A);
MyHotKeyManager.SimulateKeyUp(Keys.Control);
The HotKey manager is disposed by unregistering all registered GlobalHotKeys registered with the class, unhooking the class from all keyboard messages from the method, HotKeyManager.Dispose.
for (int i = GlobalHotKeyContainer.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
RemoveGlobalHotKey(GlobalHotKeyContainer[i]);
}
LocalHotKeyContainer.Clear();
ChordHotKeyContainer.Clear();
KeyBoardUnHook();
Using the Code
Now, we add HotKeys to the HotKeyManager like this:
GlobalHotKey ghkNotepad = new GlobalHotKey("ghkNotepad", Keys.N,
Modifiers.Control | Modifiers.Shift);
LocalHotKey lhkNewHotkey = new LocalHotKey("lhkNewHotKey", Keys.A);
ChordHotKey chotCmd = new ChordHotKey("chotCmd", Keys.C,
Modifiers.Alt, Keys.P, Modifiers.Alt);
MyHotKeyManager.AddGlobalHotKey(ghkNotepad);
MyHotKeyManager.AddLocalHotKey(lhkNewHotkey);
MyHotKeyManager.AddChordHotKey(chotCmd);
Dim ghkNotepad as new GlobalHotKey("ghkNotepad", Keys.N, Modifiers.Control Xor Modifiers.Shift)
Dim lhkNewHotkey as new LocalHotKey("lhkNewHotKey", Keys.A)
Dim chotCmd as new ChordHotKey("chotCmd", Keys.C, Modifiers.Alt, Keys.P, Modifiers.Alt)
MyHotKeyManager.AddGlobalHotKey(ghkNotepad)
MyHotKeyManager.AddLocalHotKey(lhkNewHotKey)
MyHotKeyManager.AddChordHotKey(chotCmd)
For the HotKeyControl, the user can then use the control to set a shortcut and you can then get the associated key and modifier from HotKeyControl.UserKey and HotKeyControl.UserModifier.
The HotKeyManager can also simulate pressing a key and add a hook to the Keyboard.
You can disable a keyboard key by setting the Handled property of the key to true, the only combination of keys that seems to be left out is Control + Alt + Delete.
Download the source file to access the full code.
Points of Interest
-
When you try to create a new HotKeyManager, using WPF in the InitializeComponent method, it could cause your Window to crash, you best do this when the Window is already loaded.
-
The Library can also be extended into components so that the HotKeys can be added and verified at design time and at runtime, it will save you a lot of code. I'll try uploading the sample I've got.
If you have questions, leave a comment. The samples in the source file are shown below:


History
- 17th August, 2012: Initial version
