Contents
Introduction
We will learn to write a simple web server which can send responses to the most well-known HTTP methods (GET and POST), in C#. Then we will make this server accessible from the internet. This time, we will really say "Hello world!"
Background
HTTP Protocol
HTTP is a communication protocol between servers and clients. It uses TCP/IP protocol to send/receive requests/responses.
There are a few HTTP methods and we will implement two of them; GET and POST.
GET
What happens when we write an address into the address bar of our web browser and hit enter? (We mostly don't specify a port number although it is required for TCP/IP, because it has a default value for http and it is 80. We don't have to specify it if it is 80.)
GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n
Host: atasoyweb.net\r\n
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:14.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/14.0.1\r\n
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8\r\n
Accept-Language: tr-tr,tr;q=0.8,en-us;q=0.5,en;q=0.3\r\n
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate\r\n
Connection: keep-alive\r\n\r\n
This is the GET request which is sent by our browser to the server using TCP/IP. This means the browser requests the server to send the contents of "/" from the root folder of "atasoyweb.net".
We (or browsers) can add more headers. But the most simplified version of this request is below:
GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n
Host: atasoyweb.net\r\n\r\n
POST
POST requests are similar to GET requests. In a GET request, variables are appended to the URLs using ? character. But in a POST request, variables are appended to the end of the request after 2 line break characters and total length (content-length) is specified.
POST /index.html HTTP/1.1\r\n
Host: atasoyweb.net\r\n
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:15.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/15.0.1\r\n
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8\r\n
Accept-Language: tr-tr,tr;q=0.8,en-us;q=0.5,en;q=0.3\r\n
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate\r\n
Connection: keep-alive\r\n
Referer: http://atasoyweb.net/\r\n
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\r\n
Content-Length: 35\r\n\r\n
variable1=value1&variable2=value2
Simplified version of this request:
POST /index.html HTTP/1.1\r\n
Host: atasoyweb.net\r\n
Content-Length: 35\r\n\r\n
variable1=value1&variable2=value2
Responses
When a request is received by the server, it is parsed and a response with a status code is returned:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n
Server: Apache/1.3.3.7 (Unix) (Red-Hat/Linux)\r\n
Content-Length: {content_length}\r\n
Connection: close\r\n
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8\r\n\r\n
the content of which length is equal to {content_length}
This is the response header. "200 OK" means everything is OK, requested content will be returned. There are many status codes. We will use just 200, 501 and 404:
- "
501 Not Implemented": Method is not implemented. We will implement only GET and POST. So, we will send response with this code for all other methods. - "
404 Not Found": Requested content is not found.
Content Types
Servers must specify the type of the content in their response. There are many content types and these are also called "MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) types" (because they are also used to identify non-ASCII parts of emails). Here are the content types that we will use in our implementation: (you can modify the code and add more):
- text/html
- text/xml
- text/plain
- text/css
- image/png
- image/gif
- image/jpg
- image/jpeg
- application/zip
If servers specify the wrong content types, contents will be misinterpreted. For example, if a server sends plain text using the "image/png" type, the client tries to show the text as an image.
Multithreading
If we want our server to be available even if a response is being sent to another client at that time, we must create new threads for every request. Thus, every thread handles a single request and exits after it completes its mission. (Multithreading also speeds up page loadings, because if we request a page that uses CSS and includes images, different GET requests are sent for every image and CSS file.)
Implementation of a Simple Web Server
Now we are ready to implement a simple web server. First of all, let's define variables that we will use:
public bool running = false;
private int timeout = 8;
private Encoding charEncoder = Encoding.UTF8;
private Socket serverSocket;
private string contentPath;
private Dictionary<string, string> extensions = new Dictionary<string, string>()
{
{ "htm", "text/html" },
{ "html", "text/html" },
{ "xml", "text/xml" },
{ "txt", "text/plain" },
{ "css", "text/css" },
{ "png", "image/png" },
{ "gif", "image/gif" },
{ "jpg", "image/jpg" },
{ "jpeg", "image/jpeg" },
{ "zip", "application/zip"}
};
Method to start our server:
public bool start(IPAddress ipAddress, int port, int maxNOfCon, string contentPath)
{
if (running) return false;
try
{
serverSocket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream,
ProtocolType.Tcp);
serverSocket.Bind(new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, port));
serverSocket.Listen(maxNOfCon);
serverSocket.ReceiveTimeout = timeout;
serverSocket.SendTimeout = timeout;
running = true;
this.contentPath = contentPath;
}
catch { return false; }
Thread requestListenerT = new Thread(() =>
{
while (running)
{
Socket clientSocket;
try
{
clientSocket = serverSocket.Accept();
Thread requestHandler = new Thread(() =>
{
clientSocket.ReceiveTimeout = timeout;
clientSocket.SendTimeout = timeout;
try { handleTheRequest(clientSocket); }
catch
{
try { clientSocket.Close(); } catch { }
}
});
requestHandler.Start();
}
catch{}
}
});
requestListenerT.Start();
return true;
}
Method to stop the server:
public void stop()
{
if (running)
{
running = false;
try { serverSocket.Close(); }
catch { }
serverSocket = null;
}
}
The most important part of the code:
private void handleTheRequest(Socket clientSocket)
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[10240];
int receivedBCount = clientSocket.Receive(buffer);
string strReceived = charEncoder.GetString(buffer, 0, receivedBCount);
string httpMethod = strReceived.Substring(0, strReceived.IndexOf(" "));
int start = strReceived.IndexOf(httpMethod) + httpMethod.Length + 1;
int length = strReceived.LastIndexOf("HTTP") - start - 1;
string requestedUrl = strReceived.Substring(start, length);
string requestedFile;
if (httpMethod.Equals("GET") || httpMethod.Equals("POST"))
requestedFile = requestedUrl.Split('?')[0];
else
{
notImplemented(clientSocket);
return;
}
requestedFile = requestedFile.Replace("/", @"\").Replace("\\..", "");
start = requestedFile.LastIndexOf('.') + 1;
if (start > 0)
{
length = requestedFile.Length - start;
string extension = requestedFile.Substring(start, length);
if (extensions.ContainsKey(extension))
if (File.Exists(contentPath + requestedFile))
sendOkResponse(clientSocket,
File.ReadAllBytes(contentPath + requestedFile), extensions[extension]);
else
notFound(clientSocket);
}
else
{
if (requestedFile.Substring(length - 1, 1) != @"\")
requestedFile += @"\";
if (File.Exists(contentPath + requestedFile + "index.htm"))
sendOkResponse(clientSocket,
File.ReadAllBytes(contentPath + requestedFile + "\\index.htm"), "text/html");
else if (File.Exists(contentPath + requestedFile + "index.html"))
sendOkResponse(clientSocket,
File.ReadAllBytes(contentPath + requestedFile + "\\index.html"), "text/html");
else
notFound(clientSocket);
}
}
Responses for different status codes:
private void notImplemented(Socket clientSocket)
{
sendResponse(clientSocket, "<html><head><meta
http-equiv=\"Content-Type\" content=\"text/html;
charset=utf-8\">
</head><body><h2>Atasoy Simple Web
Server</h2><div>501 - Method Not
Implemented</div></body></html>",
"501 Not Implemented", "text/html");
}
private void notFound(Socket clientSocket)
{
sendResponse(clientSocket, "<html><head><meta
http-equiv=\"Content-Type\" content=\"text/html;
charset=utf-8\"></head><body><h2>Atasoy Simple Web
Server</h2><div>404 - Not
Found</div></body></html>",
"404 Not Found", "text/html");
}
private void sendOkResponse(Socket clientSocket, byte[] bContent, string contentType)
{
sendResponse(clientSocket, bContent, "200 OK", contentType);
}
The method that will send responses to clients:
private void sendResponse(Socket clientSocket, string strContent, string responseCode,
string contentType)
{
byte[] bContent = charEncoder.GetBytes(strContent);
sendResponse(clientSocket, bContent, responseCode, contentType);
}
private void sendResponse(Socket clientSocket, byte[] bContent, string responseCode,
string contentType)
{
try
{
byte[] bHeader = charEncoder.GetBytes(
"HTTP/1.1 " + responseCode + "\r\n"
+ "Server: Atasoy Simple Web Server\r\n"
+ "Content-Length: " + bContent.Length.ToString() + "\r\n"
+ "Connection: close\r\n"
+ "Content-Type: " + contentType + "\r\n\r\n");
clientSocket.Send(bHeader);
clientSocket.Send(bContent);
clientSocket.Close();
}
catch { }
}
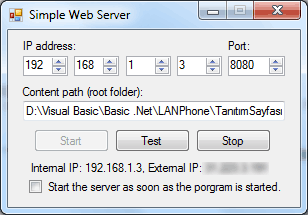
Usage
Server server = new Server();
server.start(ipAddress, port, maxconnections, contentpath);
server.stop();
Let's Say "Hello" to All The World!
Our simple web server is ready. Now we will make it accessible from the internet. To achieve this, we must redirect requests that come to our modem to our computer. It is simple if our modem supports UPnP.
- Download this UPnP Port Forwarder and run it.
- Click "Search For Devices" button. If your modem supports UPnP, it will be added to the combobox.
- Click "Update List" button to list forwarded ports.
- Then click "Add New" button and fill the form.
- If you check "IP" checkbox and type an IP, only requests from this IP will be redirected. So, do not fill it.
- Internal port must be equal to our server's port.
- "Port" and "Internal port" don't have to be equal.

From now on, all requests come to "externalip:port" will be redirected from the modem to our computer. To test the server if it is accessible from the internet, you can use www.web-sniffer.net. Just write your external IP and port as "http://externalip:port" and hit "Submit" button...

History
- 13th September, 2012: The
POST method was explained and supported - 3rd September, 2012: First version
