Introduction
It is possible to host WPF controls in a Win32 application, and the other way around, but because of the differences between these technologies, there are various issues that can appear. One of these is handling of keyboard input. Without diving too much into differences between WPF and Win32, I will show how to provide keyboard input for WPF controls hosted in a Win32 applications. For reading about the differences and the interoping between the two, I suggest WPF and Win32 Interoperation.
Hosting a WPF Control in Win32
To host a WPF control in a Win32 application, you need to follow several steps.
- Create a new HwndSource, setting the parent window as its parent. This is a key object, that enables displaying of WPF content in a Win32 window.
- Instantiate the WPF control or window.
- Assign the reference to this instance of the WPF control or window
RootVisual property of the HwndSource object.
To simplify this process, I have this small helper class:
#pragma once
#include <vcclr.h>
class CWpfControlWrapper
{
HWND m_hwndWPF;
gcroot<System::Windows::Interop::HwndSource^> m_source;
gcroot<System::Windows::Controls::Control^> m_control;
public:
CWpfControlWrapper(void):m_hwndWPF(NULL) {}
~CWpfControlWrapper(void) {}
template <typename T>
T^ Control()
{
System::Windows::Controls::Control^ obj = m_control;
return dynamic_cast<T^>(obj);
}
BOOL CreateControl(System::Type^ type,
HWND parent,
DWORD style,
int x, int y,
int width, int height)
{
System::Windows::Interop::HwndSourceParameters^ sourceParams =
gcnew System::Windows::Interop::HwndSourceParameters("WpfControlWrapper");
sourceParams->PositionX = x;
sourceParams->PositionY = y;
sourceParams->Height = height;
sourceParams->Width = width;
sourceParams->ParentWindow = System::IntPtr(parent);
sourceParams->WindowStyle = style;
m_source = gcnew System::Windows::Interop::HwndSource(*sourceParams);
m_control =
(System::Windows::Controls::Control^)System::Activator::CreateInstance(type);
m_source->RootVisual = m_control;
m_hwndWPF = (HWND)m_source->Handle.ToPointer();
return m_hwndWPF == NULL ? FALSE : TRUE;
}
};
With this class, I can create WPF controls like this:
CWpfControlWrapper btn1;
btn1.CreateControl(System::Windows::Controls::Button::typeid,
m_hWnd,
WS_CHILD|WS_VISIBLE|WS_TABSTOP,
10, 10, 210, 24);
btn1.Control<System::Windows::Controls::Button>()->Content = "Button 1";
Enabling Keyboard Input
While you can use the mouse with these WPF controls added like this, the keyboard in not enabled. To provide keyboard input for the WPF controls, we need to hook the HwndSource, adding a handler that receives all window messages. We must handle the WM_GETDLGCODE message to let the system know what kind of messages we want to handle on our own (in the WPF control).
This is how we add the hook:
m_source->AddHook(gcnew System::Windows::Interop::HwndSourceHook(
&CWpfControlWrapper::ChildHwndSourceHook));
And this is how the hook procedure looks (defined as a static member of my CWpfControlWrapper):
static System::IntPtr ChildHwndSourceHook(
System::IntPtr hwnd,
int msg,
System::IntPtr wParam,
System::IntPtr lParam,
bool% handled)
{
if (msg == WM_GETDLGCODE)
{
handled = true;
return System::IntPtr
(DLGC_WANTCHARS | DLGC_WANTTAB | DLGC_WANTARROWS | DLGC_WANTALLKEYS);
}
return System::IntPtr::Zero;
}
By returning all these dialog codes will let the system know that the window wants to process arrow keys, tab keys, all keys and receive the WM_CHAR message.
Enabling TAB Navigation
Even though the WPF controls now have keyboard input, it turns out that navigating with TAB (forward) or TAB+SHIFT (backwards) does not work.
Here is an example where I have an MFC application with four WPF controls, two buttons and two text boxes. One button and one text box, as well as the OK and CANCEL buttons have tab stops.
CWpfControlWrapper btn1;
btn1.CreateControl(System::Windows::Controls::Button::typeid,
m_hWnd,
WS_CHILD|WS_VISIBLE|WS_TABSTOP,
10, 10, 210, 24);
btn1.Control<System::Windows::Controls::Button>()->Content = "Button 1 (tab stop)";
CWpfControlWrapper btn2;
btn2.CreateControl(System::Windows::Controls::Button::typeid,
m_hWnd,
WS_CHILD|WS_VISIBLE,
10, 40, 210, 24);
btn2.Control<System::Windows::Controls::Button>()->Content = "Button 2 (no tab stop)";
CWpfControlWrapper edit1;
edit1.CreateControl(System::Windows::Controls::TextBox::typeid,
m_hWnd,
WS_CHILD|WS_VISIBLE|WS_TABSTOP,
10, 70, 210, 24);
edit1.Control<System::Windows::Controls::TextBox>()->Text = "edit 1 (tab stop)";
CWpfControlWrapper edit2;
edit2.CreateControl(System::Windows::Controls::TextBox::typeid,
m_hWnd,
WS_CHILD|WS_VISIBLE,
10, 100, 210, 24);
edit2.Control<System::Windows::Controls::TextBox>()->Text = "edit 2 (no tab stop)";
The sample dialog box looks like this:
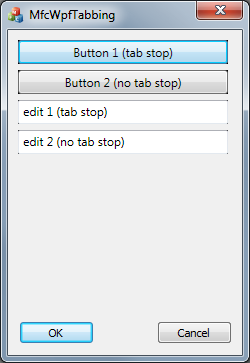
Pressing the TAB key should allow navigating from button 1 to edit 1, then button OK, button CANCEL and then back to button 1. Button 2 and edit 2, not having the tab stop style defined, should not be included in the navigation.
As already mentioned, this does not work, however. After reading about a solution for this problem, it looked like the key lied in the IKeyboardInputSink interface, that both HwndSource and HwndHost implement. This interface provides a keyboard sink for components that manage tabbing, accelerators, and mnemonics across interop boundaries and between HWNDs. Apparently, the solution was to:
- derive the
HwndSource class - override the TabInto method (actually, since this is a
sealed method, you’d have to define a new override for it) and implement the tabbing logic there - use this derived
HwndSource to present WPF content in a Win32 window
Though I tried several things, I didn’t manage to make it work. However, since I already had a hook for all window messages, and explicitly asked for receiving WM_CHAR, it was possible to use this to handle TAB and TAB+SHIFT. So, here is an addition to the ChildHwndSourceHook above:
else if(msg == WM_CHAR)
{
if(wParam.ToInt32() == VK_TAB)
{
handled = true;
HWND nextTabStop = FindNextTabStop((HWND)hwnd.ToPointer(),
(GetKeyState(VK_SHIFT) & 0x8000) != 0x8000);
if(nextTabStop)
::SetFocus(nextTabStop);
}
}
So if we get a WM_CHAR and the wParam is VK_TAB, then we query the parent for the next tab stop (for forward navigation if SHIFT was not pressed, or backwards navigation if SHIFT was also pressed). If there is such a tab stop, we set focus on that window.
The FindNextTabStop method (added as a member of the CWpfControlWrapper class) looks like this:
static HWND FindNextTabStop(HWND wnd, bool forward)
{
HWND nextstop = NULL;
HWND nextwnd = wnd;
do
{
nextwnd = ::GetWindow(nextwnd, forward ? GW_HWNDNEXT : GW_HWNDPREV);
if(nextwnd == NULL)
nextwnd = ::GetWindow(wnd, forward ? GW_HWNDFIRST : GW_HWNDLAST);
if(nextwnd == wnd)
break;
DWORD style = ::GetWindowLongPtr(nextwnd, GWL_STYLE);
if((style & WS_TABSTOP) == WS_TABSTOP)
nextstop = nextwnd;
}while(nextstop == NULL);
return nextstop;
}
It does the following:
- It gets the next/previous window in the z-order (which defines the tab stop order).
- When it reaches the end/top of the z-order, it starts all over again, which enables looping through the child windows of the parent.
- If the next child in the z-order is the current control, then it finished looping through the children of the parent and it stops.
- If the current child in the z-order has the
WS_TABSTOP style set, then this is the window we are looking for.
With this defined, it is possible to use the TAB key to navigate between the WPF controls on a Win32 window.
Here is the MFC demo application that you can try.
History
- 15th October, 2012: Initial version
