The majority of developers have already heard about design patterns, GOF (Gang Of Four) patterns are the most popularized, and each developer has his way to learn them , we can enumerate:
- Reading a book or a magazine.
- From web sites.
- From a collegue.
- Doing a training.
Regardless of the method chosen, we can learn by heart the patterns and spent hours to memorize their UML diagrams, but sometimes when we need to use them in a real project, it becomes more problematic.
What’s very important is not to know exacly pattern names and how to implement them as described in the documentation, but what’s more relevant is the motivitations behind each pattern, because it’s from motivations that we invent the patterns.
And to master better pattern motivations, the interesting way is to study them from a real project. it’s the goal of this article , we will try to discover an open source project using them heavily.
In this first part the goal is to discover the creational patterns used by JBoss.
Analysis of JBoss
JBoss Application Server (JBoss AS, or simply JBoss) is an application server that implements the Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE).
JBoss is a big project with many modules, packages and classes, and to go deep inside its internal design we need a tool to facilitate the analysis, for this purpose we used JArchitect to analyze it, and CQLinq will help us to query code base.
After the analysis here’s a dependency graph of some JBoss modules
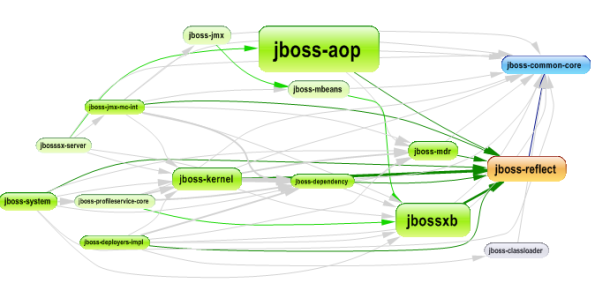
Here we go to discover creational patterns used by JBoss:
Singleton
The singleton is the most popular and the most used one. There are many variant of this pattern, let’s search with CQLinq the most documented one which has the following characteristics:
- Not an abstract type.
- Having a private constructor.
- Having an unique static field with the same type as the parent class.
from t in Application.Types
where !t.IsAbstract && t.IsClass
// All ctors of a singleton are private
where t.Constructors.Where(ctor => !ctor.IsPrivate).Count() == 0
// A singleton contains one static field of its parent type, to reference the unique instance
let staticFieldInstances = t.StaticFields.WithFieldType(t)
where staticFieldInstances.Count() == 1
select new { t, staticFieldInstance = staticFieldInstances.First() }
And here’s the result of the query

Motivation
The motivation of the singleton pattern is very simple: "Create one class instance". However, using this pattern became controversial,
and not all architects and designers recommend it, here’s an article
talking about the singleton controversy.
Factory Method
There is no mystery about factories, their goal is very clear: Create instances, and a simple factory containing a
CreateInstance method could achieve this goal, however JBoss use mainly “Factory Method” pattern for all its factories.
Here’s all factories used by JBoss:

Motivation
To understand better this pattern let’s describe a scenario where JBoss use this pattern:
JBoss define a ScopedClassPoolFactory interface which is implemented by many concrete factory classes
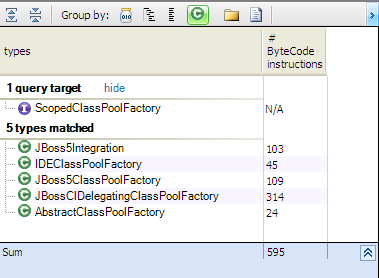
The ScopedClassPoolRepositoryImpl need a factory to create ScopedClassPool instances, for that its assigned with
setClassPoolFactory method.
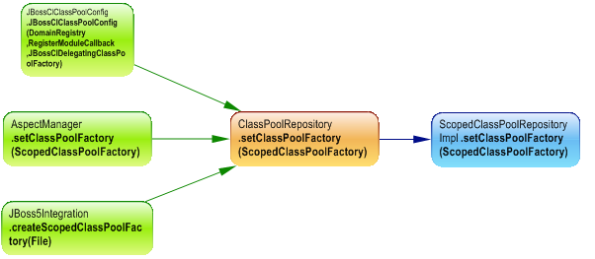
And after the selected factory is used to create the concrete ScopedClassPool.

The most important motivation is the low coupling, indeed
ScopedClassPoolRepositoryImpl need to instantiate ScopedClassPool, and it reference only this one and doesn’t know anything about concrete classes. And if
ScopedClassPoolRepositoryImpl need to works with another concrete class implementing
ScopedClassPool, we have just to add another factory implementing
ScopedClassPoolFactory.
Using a simple factory is interesting to isolate the instantiation logic, but using “Factory Method” is more suitable to enforce low coupling.
Builder
The Builder pattern permit to create an object in a step-by-step fashion. The construction process can create different object representations and provides a high level of control over the assembly of the objects.
Motivation
JBoss need to create metadata for beans, the metadata could contains many sections, and each bean could include only some of them.
The BeanMetaDataBuilder contains many methods to add sections in the metadata:
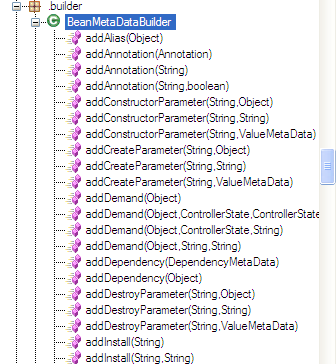
And we can construct a metadata by invoking these methods to add needed sections
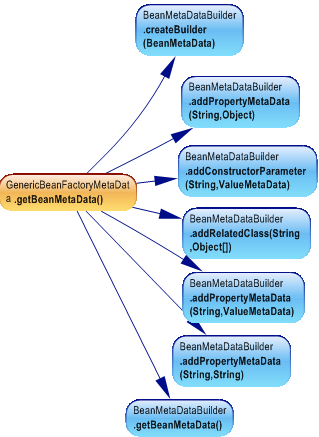
Using builder brings more flexibility when creating complex objects. this pattern is used when we need to assemble an object using multiple part.
Prototype
Prototype Design Pattern is also a pattern we use to receive an object instance for a particular class, such as builder and factory pattern. Instead of having a new fresh object every time, we can make a copy of an existed object instantly and start using it. In that way, we do not have to repeat the building process for the object we are trying to use. The new copy object is totally independent with the original prototype object, and can be used for any purpose that will not affect the original. There is no limit for copying the existing objects, any existing object can be copied.
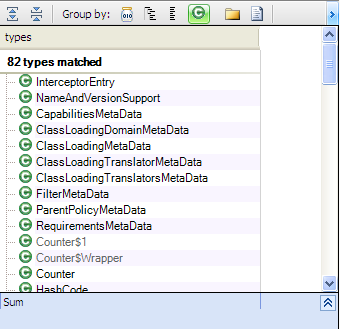
Let’s search for types implementing clone() method.
from t in Types where t.Methods.Where(a=>a.SimpleName=="clone").Count()>0
&& !t.IsThirdParty && t.IsClass
select t
Motivation
When creating an object is time consuming and a costly affair and you already have a most similar object instance in hand, then you go for prototype pattern. Instead of going through a time consuming process to create a complex object, just copy the existing similar object and modify it according to your needs.
Lazy Initialization
Lazy initialization is the tactic of delaying the creation of an object, the calculation of a value, or some other expensive process until the first time it is needed.
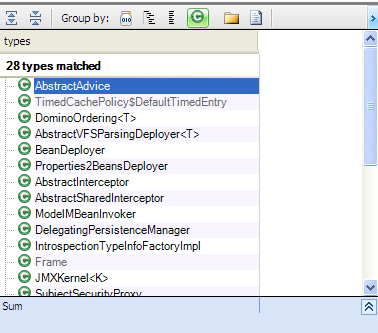
We can identify some classes using this pattern, by searching classes having init method but not invocked from the constructor.
from t in Types where t.Methods.Where(a=>a.SimpleName=="init" && a.MethodsCallingMe.Where(b=>b.IsConstructor).Count()==0).Count()>0
&& !t.IsThirdParty && t.IsClass
select t
Motivation
Like prototype pattern, Lazy Initialization is one of the performance tuning techniques.
Conclusion
Using design patterns has many advantages, but without understanding their motivations is very difficult to implement them, fortunately the motivation of creational patterns are very clear, and they are widely used, in the next article we will discover structural patterns used by JBoss.
