Few Points to Ponder!
- Always start on Green Light! i.e., Start merging when both Trunk and Branch are fully committed and they are showing green color.
- Merging always takes place within a working copy, i.e., in trunk.
- In every commit, do not forget to add comment in the comment box. Mind it, this is important!
Use Case for Merging
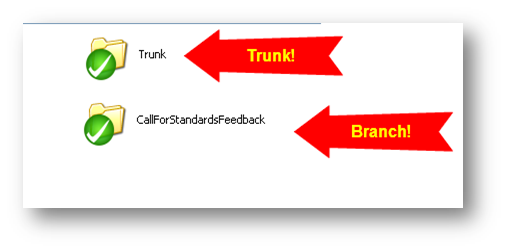
- We have a main trunk
- We have taken a branch named “
CallForStandardFeedBack” branch. - After taking this branch, codes in both trunk and branch are modified by concerned developers.
- Now we want to merge “
CallForStandardFeedback” branch back to trunk and we have lots of changes both in trunk and merge.
Merging Step: 1
- All files are committed and we have green tick mark in our folder. Now we can start merging.
Merging Step: 2
- Right click on Trunk go to TortoiseSVN->Merge and Click Merge.

Merging Step: 3
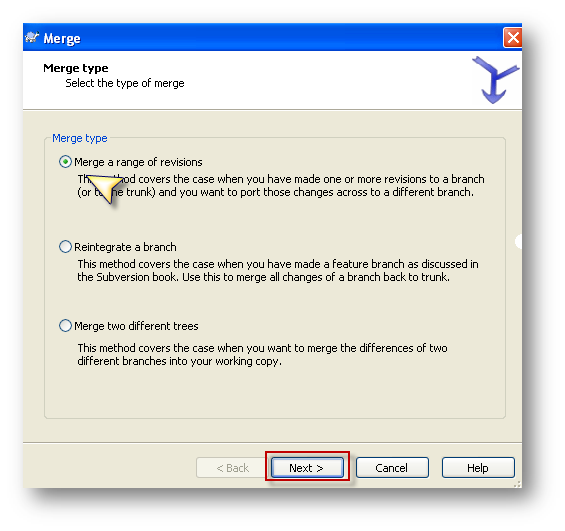
- Select “Merge a range of revisions” and click next.
Merging Step 4
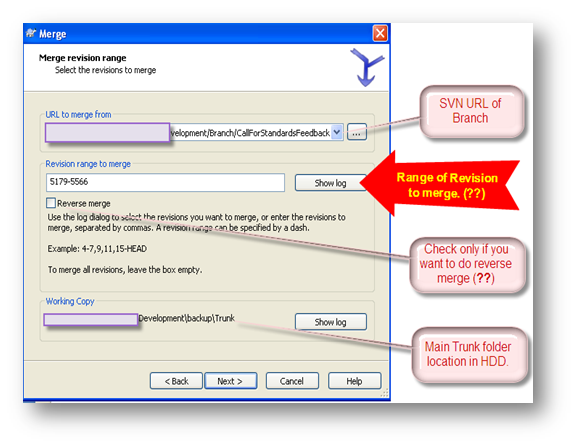
- Select the value as appropriate in the picture below:
Explaining ??
- Range Of Revision: Range of revision is actually all those range of changes that we want to merge with trunk. As we are merging a full branch with trunk, so we will select all the ranges like below:

- Reverse Merge: Reverse Merge is basically to decouple the changes that were committed with trunk before while merging one particular branch with trunk. Say for example, we have implemented one menu in one branch and merged it with trunk. After a few days, it is needed to rollback every code related with that branch. In that case, we will use reverse Merge.
Merge Step 5
- Use the default value in this form and click merge to get the job done!

After merging, you will get the result like below. Now handle only conflicted files and do an integration test!
Happy merging!
CodeProject






