We all work with databases and while working with databases, we all have most probably one version or the another of SQL Server. Today, in this post, we will see how to retrieve the size of data files of all databases present in SQL Server and the actual amount used in these files. As you know, when you create a database, there are 2 files created on hard disk with extensions as below:
- .mdf — This is the data file where all data is stored.
- .ldf — This is the log file used by SQL Server.
SQL Server provides some DBCC statement that will help us write this query. We will use “DBCC SHOWFILESTATS” statement to build this query. To get an idea on what this DBCC statement returns, try running the below query in SQL Server Management Studio and you shall see the effect:
USE master;
DBCC SHOWFILESTATS;
This will give you an output something similar to the below:
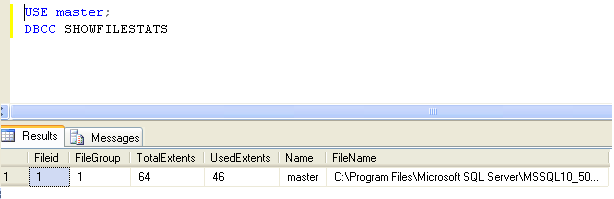
The output returns the following columns for our use:
TotalExtents — Identifies the total file size on hard diskUsedExtents – Identifies the actual file size in use on hard diskName – Identifies the name of the databaseFileName — Identifies the location of the physical file on hard disk
From MSDN, Extents are the basic unit in which space is managed. An extent is eight physically contiguous pages, or 64 KB. This means that each extent equals to 64 Kilobytes of memory. Applying the calculation on the output, we get the TotalExtent of the master database is 64 x 64=4096 KB and the UsedExtent is 46 x 64 = 2944KB.
This gives us an idea of which database is using how much size on the hard disk.
Note: To be able to run this query, you should have administrator privileges on SQL Server.
Hope you enjoyed reading this post! Cheers!
