Introduction
How many times have you felt the need to grant restricted access to your SQL Server databases to external users and felt unsafe about doing it? External users might be downstream consumers of your data or a team under the same organization that needs access to your database for their apps/databases to work. What if the external users try to hack into your database and read data that they’re not supposed to, or even worse, gain write access to it? What if they destroy/damage your data?
This post describes a method to create a Facade Database to provide restricted access to specific tables in your databases to specific users without granting direct access to any of the underlying databases/tables. SQL Server provides a feature called Cross-database Ownership Chaining that can help us achieve this. The examples provided in this article have been developed and tested on a SQL Server 2008 R2 Server. This feature is supported in older versions of SQL Server too, but we’ll limit the discussion to the following versions:
- SQL Server 2005
- SQL Server 2008
- SQL Server 2008 R2
- SQL Server 2012
- SQL Server 2014
Ownership Chaining
When a script accesses multiple database objects sequentially, the sequence is known as a chain. Although such chains do not independently exist, when SQL Server traverses the links in a chain, it evaluates permissions on the constituent objects differently than it would if it were accessing the objects separately. These differences have important implications for managing access and security.
When an object is accessed through a chain, SQL Server first compares the owner of the object to the owner of the calling object. If both objects have the same owner, permissions on the referenced object are not evaluated.
Cross Database Ownership Chaining
SQL Server can be configured to allow ownership chaining between specific databases or across all databases inside a single server of SQL Server. Cross-database Ownership Chaining is disabled by default and should not be enabled unless it is specifically required. To make Cross-database Ownership Chaining work, the databases involved must have a common owner.
Server-Level vs. Database-Level
Cross-database Chaining can be enabled at the server-level or at the individual database-levels. Enabling it at the server-level makes Cross-database Ownership Chaining work across all databases on the server, regardless of individual settings of the database. If the requirement is to enable it only for a few databases, then you should enable it at the database-level.
Server-Level Cross-Database Ownership Chaining
To enable server-level Cross-database Ownership Chaining, use the following T-SQL statements.
EXECUTE sp_configure 'show advanced', 1
GO
RECONFIGURE
GO
EXECUTE sp_configure 'cross db ownership chaining', 1
GO
RECONFIGURE
GO
To check if it is enabled already, use this query:
SELECT [name], value
FROM [sys].configurations
WHERE [name] = 'cross db ownership chaining';
A value of one indicates that it is already enabled.
Database-Level Cross-Database Ownership Chaining
To enable database-level Cross-database Ownership Chaining, use the following T-SQL statements.
ALTER DATABASE myDatabase SET DB_CHAINING ON
GO
To check if it is already enabled at the individual database-level, run:
SELECT name, is_db_chaining_on FROM sys.databases
GO
Preparing the Primary DB
Let me illustrate this with an example. Create a database named CustomerDB. Then, create a table named Customers and insert some test data.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Customers](
[CustomerId] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[CustomerName] [varchar](50) NOT NULL,
[Address] [varchar](500) NOT NULL,
[City] [varchar](50) NOT NULL,
[Country] [varchar](50) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Customers] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[CustomerId] ASC
) WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, _
IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
INSERT INTO Customers ([CustomerId], [CustomerName], [Address], _
[City], [Country]) VALUES (1, 'Michael Douglas', 'LA Home', 'Los Angeles', 'US')
INSERT INTO Customers ([CustomerId], [CustomerName], [Address], _
[City], [Country]) VALUES (2, 'Al Pacino', 'NY Home', 'New York', 'US')
INSERT INTO Customers ([CustomerId], [CustomerName], [Address], _
[City], [Country]) VALUES (3, 'James Cameroon', 'NJ Home', 'New Jersey', 'US')
Creating the Facade DB
Create a database named FacadeDB (or any other name for that matter).
Creating Views
Create Views for each table in the Primary DB that you wish to grant access to the restricted user.
CREATE VIEW [dbo].[CustomerView] AS
SELECT * FROM CustomerDB.dbo.Customers
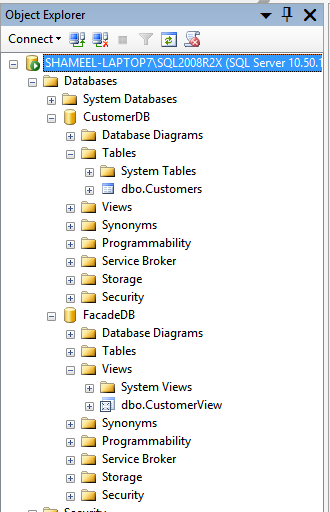
Your object explorer should look like this now:
Creating Login and Users to Streamline Access
Create the restricted user Login and its associated Users in the databases. The user must be added to the Primary Database as “public.” Otherwise, ownership chaining will not work. The user must have at least a “db_datareader” role on the Facade Database.
CREATE LOGIN [FacadeUser] WITH PASSWORD=N'facadeuser', DEFAULT_DATABASE=[FacadeDB], _
DEFAULT_LANGUAGE=[us_english], CHECK_EXPIRATION=OFF, CHECK_POLICY=OFF
GO
USE [CustomerDB]
GO
CREATE USER [FacadeUser] FOR LOGIN [FacadeUser] WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA=[dbo]
GO
USE [FacadeDB]
GO
CREATE USER [FacadeUser] FOR LOGIN [FacadeUser] WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA=[dbo]
GO
EXEC sp_addrolemember N'db_datareader', N'FacadeUser'
GO
Turning on Database Ownership Chaining on Both the Databases
ALTER DATABASE CustomerDB SET DB_CHAINING ON
GO
ALTER DATABASE FacadeDB SET DB_CHAINING ON
GO
Testing
Log in to the server as the restricted user (FacadeUser) and execute the following commands.
SELECT * FROM CustomerView
You should be able to see the rows of the underlying table.

Now, try querying the underlying table directly.
SELECT * FROM CustomerDB.dbo.Customers
You should see this error:

The SELECT permission was denied on the object 'Customers', database 'CustomerDB', schema 'dbo'.
Conclusion
If you followed the above steps, you should have a working setup where a restricted user can query the FacadeDB and view the results, but they cannot query the underlying tables in the CustomerDB.
History
- 7th September, 2019: Initial version
