Introduction
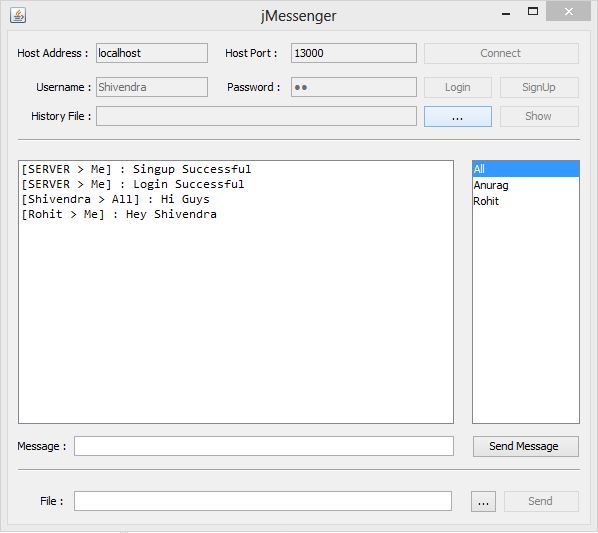
In this article I am demonstrating a chat application which can handle multiple users at the same time. It also supports file transfer.
It is entirely based on Java and consists of two parts: jMessenger (client application) and jServer (server application).
Features
- Handles multiple users at the same time
- Support for both public and private messages
- User signup and login available
- Support for file transfer
Using the code
Run the jar files jMessenger.jar and jServer.jar and do the following:
- On jServer select "data.xml" as database file. This file contains usernames and passwords.
- On jMessenger select "History.xml" as history file. This file is used to save chat history.
- In many cases, if jMessenger cannot find the server then adjust firewall to give it network access.
Both applications are written in Netbeans and you can import source files in Netbeans to view and edit them.
Message structure
Each message in jMessenger has four fields:
type: This can be set to message, login, newuser, etc.sender: The username of sendercontent: Actual content of the messageRecipient: Username of recipient of the message
jServer
There are two main classes in jServer for handling connections and messages. On startup the SocketServer runs in
a separate thread. The job of SocketServer is to wait for connections and for each connection start a new thread ServerThread. Once the connection is
established, ServerThread will listen for any messages and hand it over to SocketServer to process. Also it will forward messages
from other users to the connected user.
Message msg = (Message) streamIn.readObject();
server.handle(ID, msg);
.......
public synchronized void handle(int ID, Message msg){
if(msg.type.equals("login")){
....
}
else id(msg.type.equals("message")){
if(msg.recipient.equals("All")){ Announce("message", msg.sender, msg.content); }
else{
}
}
.......
jMessenger
jMessenger first connects to the jServer, specified by its IP-address and port number. Arriving messages are then displayed on message board along with their senders.
When a user wants to send a file, first his request is sent via a message of type upload_req. The recipient then does the following:
- The recipient side sends its reply in a message of type
upload_res - If request is accepted then the recipient opens a new port
- For positive reply, recipient's IP address and port number is sent back
- The sender, on receiving positive reply connects to this socket and starts file upload
An advantage of this approach is that the clients can chat and transfer files at the same time. Unlike messages, files do not go through jServer.
Download dwn = new Download(....);
Thread t = new Thread(dwn);
t.start();
send(new Message("upload_res", ui.username, dwn.port, msg.sender));
.........
Upload upl = new Upload(addr, port, ui.file, ui);
Thread t = new Thread(upl);
t.start();
Update
There was much confusion about two issues regarding the project. I would like to clarify that here.
1. Chat History is not complete. The project's main purpose was to demonstrate networking concepts and due to deadline limitation it was not completed.
2. Many people are confused why chat over different networks is not possible. To understand this, take the example of any web-server. For any browser to connect to a web-server, this server needs to have a global IP address so that it is visible on the Internet. Similarly jServer also is a application server and for chat over two different networks (say a campus LAN and DSL at your house), it also need to be run on a computer with a global IP address.
About this project
This is a class project which I wanted to share with others. Source code is licensed under The Code Project Open License (CPOL).
The purpose of this project was to demonstrate Java sockets, so the whole History feature is not
implemented as good as I would have liked. If this article proves to be any help, please let me know.
