In this quick tutorial, we’ll see by example how to consume a third-party API using Axios inside an Ionic 4 project based on TypeScript and React. We’ll see how to:
- Install and use Axios for sending HTTP GET requests in TypeScript and React
- Consume a third-party REST API
- Use React Hooks like
useState and useEffect - Display the data using
IonList and IonItem components - Create buttons using
IonButton
The useState() and useEffect() methods are built-in React Hooks introduced in React 16.8+; they enable developers to use state and other React features in functional React components.
Let’s get started with the prerequisites!
You need to have the following:
- Node and NPM installed on your machine
- Knowledge of TypeScript and React
- Ionic CLI v5+ and a Ionic/React project
We’ll make use of a the third-party API available from NewsAPI.org. You should register for a free account and get an API key to access the service, otherwise you can also consume any available REST API of your choice.
Step 1 – Installing Axios in Your Ionic/React Project
In this step, we’ll see how to install Axios in our Ionic/React project.
Provided that you have already created your Ionic/React project, head back to your terminal and navigate inside the project’s root folder and install Axios from npm as follows:
$ cd ./App
$ npm install axios --save
Step 2 – Sending an HTTP GET Request with Axios
In this step, we’ll use Axios to send a GET request for consuming the third-party API.
If you have generated your Ionic project based on the sidemenu template, you’ll already have a home page.
Go ahead and open the src/pages/Home.tsx file, and import the necessary APIs, i.e., axios and IonButton as follows:
import {
IonButton,
IonList,
IonItem
} from '@ionic/react';
import axios from 'axios';
Next, define the apiKEY and endpoint variables:
const apiKEY = "<YOUR_API_KEY_HERE>";
const endpoint = `https://newsapi.org/v2/top-headlines?sources=techcrunch&apiKey=${API_KEY}`;
Next, define the following method.
Next, define the sendGetRequest() method as follows:
const sendGetRequest = () => {
return axios({
url: URL,
method: 'get'
}).then(response => {
console.log(response);
return response.data;
})
};
We call the axios() method to send a GET request to the REST API endpoint.
In this step, we’ll build the UI of our home page. We’ll use Ionic components such as IonList, IonItem and IonButton, React Hooks such as useState and useEffect.
Inside the HomePage functional component and call the useState method to create a state variables named items as follows:
const HomePage: React.FunctionComponent = () => { const [items, setItems] = React.useState([]);
useState() returns the state variable, which has the empty array as its initial value and a function that we can use to change the value of the variable. We use destructuring assignment to unpack the values from the returned pair into distinct variables (i.e., articles and setArticles()).
Next, call the sendGetRequest() method inside the useEffect hook to consume the REST API:
const HomePage: React.FunctionComponent = () =>
{ const [items, setItems] = React.useState([]); React.useEffect(() =>
{ sendGetRequest().then(data => setItems(data.articles)); }, []); ```
We use use the useEffect() hook to perform a side effect in our component. The side effect is consuming data from the REST API.
The useEffect() hook is equivalent to calling the componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate and componentWillUnmount lifecycle methods combined in class-based components.
Next, iterate over the items array and render the data fetched from the REST API as follows:
const HomePage: React.FunctionComponent = () => {
const [items, setItems] = React.useState([]);
React.useEffect(() => {
sendGetRequest().then(data => setItems(data.articles));
}, []);
return (
<>
<IonHeader>
<IonToolbar color="primary">
<IonButtons slot="start">
<IonMenuButton />
</IonButtons>
<IonTitle>Home</IonTitle>
</IonToolbar>
</IonHeader>
<IonContent color="primary" >
<IonList color="primary">
{
items.map(item => {
return (
<IonItem>
{item['title']}
<IonButton href={item['url']} color="primary" slot="end">See article</IonButton>
</IonItem>
);
})
}
</IonList>
</IonContent>
</>
);
};
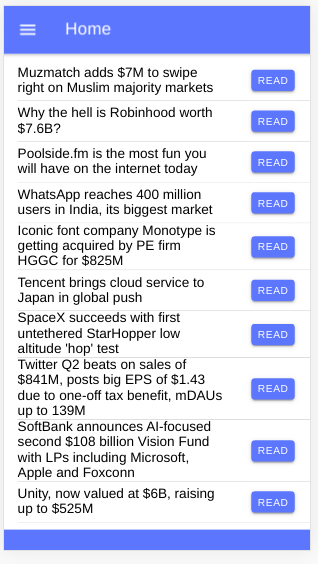
This is a screenshot of the home page UI:
Conclusion
In this quick example, we’ve seen how to use Axios to send GET requests to consume a REST API inside an Ionic/React app based on TypeScript.
We’ve used React Hooks like useState and useEffect and Ionic 4+ components like IonList, IonItem and IonButton.
