In this puzzle, we’re going to learn how to calculate moving averages by working through a hypothetical stock market example.
Solving puzzles is a great way to learn SQL. Nothing beats practicing what you’ve learned. Once you have figured out the puzzle, post you answer in the comments so we all can learn from one another. We also discuss puzzle and more in Essential SQL Learning Group on FaceBook. Be sure to find us there!
SQL Puzzle Question
It’s your first day on the job and an analyst has given you a set of closing stock quotes for Microsoft. She would like you to give her a report showing the closing data, closing price, 10-day moving average, 30-day moving average, and signal.
The signal is either “Over” or “Below” depending on whether the 10-day moving average is greater than or less than the 30-day moving average respectively.
You output should look like this:
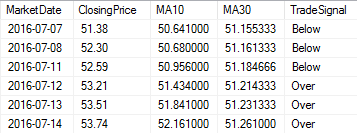
Use the following table variable to work the problem:
DECLARE @DailyQuote TABLE
(
MarketDate DATE,
ClosingPrice Decimal(10,2)
)
Download this script to create the table and populate it with sample data.
What query would you write to calculate moving averages?
Answer to Calculate Moving Averages
Before we get into the SQL let’s make sure we know what we’re calculating! To calculate the 10-day moving average of the closing price, we need to calculate the prices of current and past 9 days closing prices. We do the same for the 30-day moving average, but in that case we’ll include more days.
An easy way to calculate the moving average is to set up a window. We can do this with the OVER clause.
Below is the statement to calculate the 10-day moving average MA10:
SELECT MarketDate,
ClosingPrice,
AVG(ClosingPrice) OVER (ORDER BY MarketDate ASC ROWS 9 PRECEDING) AS MA10
FROM @DailyQuote
Within the OVER clause we order the rows by MarketDate, then use the PRECEDING clause to define the window as starting with the current row and then going nine rows up. This makes the window 10 rows in total.
You can see how this works in the diagram below:
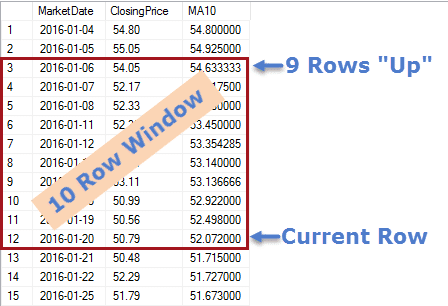
One thing that bugs me with this method is that the 10-day moving average is calculated for the first several rows in the result; the average is a one day, two day, three day moving average, and so on until we actually get to the tenth day.
Technically, it should start to calculate until we are on the tenth row. To account for this, I also compute the ROW_NUMBER, and if the ROW_NUMBER is less than 10, return NULL.
To do this, I compute the ROW_NUMBER, 10-day, 30-day within a common table expression. You’ll see this in the green portion below.
WITH CTE_DailyQuote (MarketDate, ClosingPrice, RowNumber, MA10, MA30)
AS
(
<span style="color: #339966">SELECT MarketDate,</span>
<span style="color: #339966"> ClosingPrice,</span>
<span style="color: #339966"> ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY MarketDate ASC) RowNumber,</span>
<span style="color: #339966"> AVG(ClosingPrice) OVER (ORDER BY MarketDate ASC ROWS 9 PRECEDING) AS MA10,</span>
<span style="color: #339966"> AVG(ClosingPrice) OVER (ORDER BY MarketDate ASC ROWS 29 PRECEDING) AS MA30</span>
<span style="color: #339966">FROM @DailyQuote</span>
)
SELECT MarketDate,
RowNumber,
ClosingPrice,
IIF(RowNumber > 9, MA10, NULL) MA10,
IIF(RowNumber > 29, MA30, NULL) MA30,
CASE
WHEN RowNumber > 29 AND MA10 > MA30 THEN 'Over'
WHEN RowNumber > 29 AND MA10 < MA30 THEN 'Below'
ELSE NULL
END as Signal
FROM CTE_DailyQuote
ORDER BY MarketDate
With the results from the CTE (Common Table Expression), I’m able to compare the ROW_NUMBER and return a NULL.
The last item to do is to generate the Signal. To do this I used a CASE statement. It’s a matter of simply comparing the 10-day moving average to the 30-day with the added twist of ensuring we are already at or beyond the 30th result row.
Here is a sampling of results:
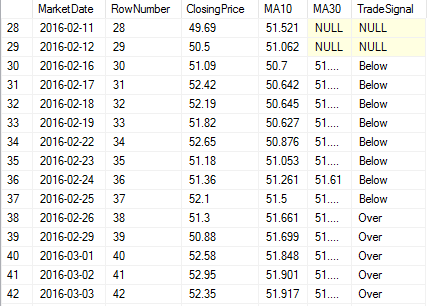
There are many other ways to calculate a Moving Average. What ways have you done? Please let me know in the comments! We also discuss puzzle and more in Essential SQL Learning Group on FaceBook. Be sure to find us there!
The post SQL Puzzle: How to Calculate Moving Averages appeared first on Essential SQL.
