This is a demonstration of how Pydroid can be used to develop and test a Django application.
Background
Django is a web application framework written in Python that helps web developers to build websites faster and without much hassle. It can be of particular use while developing complex database driven websites.
Pydroid is an easy to use and powerful Python IDE for Android. It has a lot of features to develop sophisticated python projects with ease. It also supports various libraries like PyQt5, Kivy, Jupyter, etc. It can be easily used to develop Django applications as well.
In Django, whenever the webserver receives a request for a resource, the urlresolver is used to match the URL with a list of patterns. When it finds the matching pattern, it sends the request to the related function called view. The view performs the required business logic and generates a response, which Django sends to the web browser.
Using the Code
Terminal can be started by choosing the Terminal option in the menu in Pydroid as follows:

The following command can be used to install Django after starting terminal in Pydroid:

To create a project, you can enter the following command in the directory where you want to create the project:

The following directories/files are created:
helloproj/
manage.py
helloproj/
__init__.py
settings.py
urls.py
asgi.py
wsgi.py
The outer helloproj/ directory is the main container for the project, while the inner helloproj/ directory is the Python package for the project. The helloproj/urls contains the URLs for the project.
To create an application, you can enter the following command after changing to the directory containing the manage.py file:

This will create the following directories/files:
helloapp/
__init__.py
admin.py
apps.py
migrations/
__init__.py
models.py
tests.py
views.py
Edit the helloapp/views.py file as follows:

The above code is for a simple index view, which returns an HttpResponse.
The next step is to map this view to a URL. This can be done by creating the urls.py file in the helloapp directory as follows:

After creating the urls.py file in the helloapp directory, the app directory will be as follows:
helloapp/
__init__.py
admin.py
apps.py
migrations/
__init__.py
models.py
tests.py
urls.py
views.py
The next step is to edit the root urls.py file (helloproj/urls.py) as follows:

In the above code, the include() function is used to refer to the helloapp.urls file.
Now you can run the server by the $ python manage.py runserver command as follows:

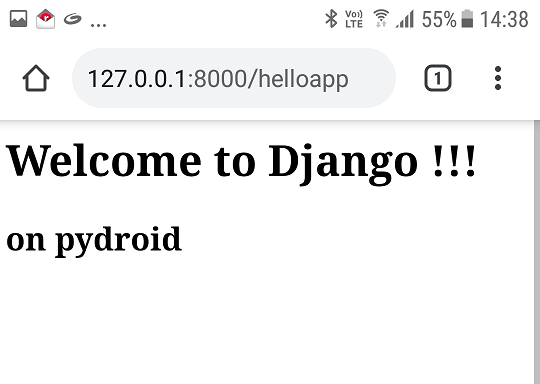
After starting the browser and entering the url http://127.0.0.1:8000/helloapp/, it will show the following output:

Points of Interest
I hope readers find this article useful and interesting.
History
- 5th May, 2020: Initial version
