OpenCV is a library for (real-time) image processing. This module gives a short introduction to OpenCV and demonstrates its object detection functionality.
Introduction
This is the fifth module in our series on learning Python and its use in machine learning and AI. We just took a quick look at some interesting libraries, let's now get started hands-on with OpenCV!
Installation
OpenCV can be installed through pip, by running the following in a Jupyter Notebook cell:
!pip install --upgrade opencv-python
pip is Python's default package manager and a standalone executable, but running it this way ensures that the package gets installed into the Anaconda environment.
If the package installed correctly, this Python code should run without errors:
import cv2
Because we’re going to want to display images in our Jupyter Notebook, we should also ensure that matplotlib is installed:
!pip install --upgrade matplotlib
Reading and plotting an image
Reading an image that OpenCV can work with is simple:
import cv2
im = cv2.imread("path/to/image.jpg")
OpenCV supports a variety of image formats, and when it fails to parse an image, the result of imread will be None. Note that if the image file isn’t found, no error will be raised — the result will be None as well.
Assuming the image is found, we can then plot it inside the Jupyter Notebook using matplotlib. To do so, we'll use this helper function:
from matplotlib import pyplot
def plot_img(img):
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
pyplot.imshow(rgb)
OpenCV reads images in the BGR color format, but matplotlib wants them in RGB, so first we have to convert the image. Then it can be plotted.
You can use this function as follows:
plot_img(im)
OpenCV and matplotlib integrate so cleanly because an OpenCV image is, in fact, just a multi-dimensional NumPy array containing the pixel values, and matplotlib can work with that.
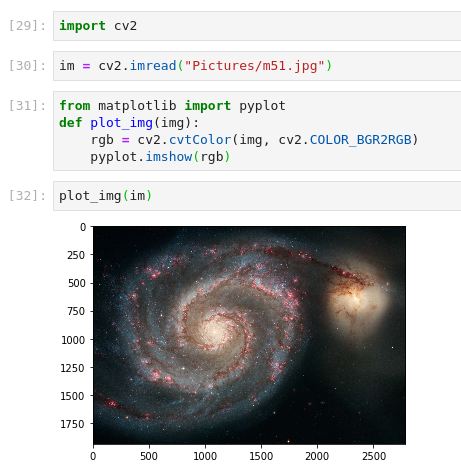
Image credit: NASA
Object Detection
There’s a lot that OpenCV can do. We're going to focus specifically on object detection.
Object detection works with so-called cascade classifiers. This approach uses machine learning: The classifier is trained both on images containing the desired object (positive images) and on images not containing it (negative images). You can train your own classifier, but OpenCV also offers several pre-trained models downloadable from their GitHub.
Let's try out the pre-trained classifier for Russian car plates, haarcascade_russian_plate_number.xml. If you want an image to test, you can use this image of a Lada Vesta by Sergey Rodovnichenko.
We can read the image and plot it to see if all went well, just like before:
car = cv2.imread("Pictures/lada-vesta.jpg")
plot_img(car)

Next, we create the classifier:
classifier = cv2.CascadeClassifier()
classifier.load("path/to/haarcascade_russian_plate_number.xml")

The detection work is done with the detectMultiScale method:
plates = classifier.detectMultiScale(car)
This returns a NumPy array. It's actually an array of arrays, with each inner array being a rectangle boundary for a detected plate, in the format [ x, y, width, height ]. To visually show them, we can draw rectangles on the image and then plot the result:
with_indicators = car
for plate in plates:
x, y, width, height = plate
with_indicators = cv2.rectangle(with_indicators, (x, y),
(x + width, y + height),
(0, 0, 255), 5)
The rectangle function takes an image, a top-left coordinate, a bottom-right coordinate, a color, and a thickness. It returns a new image with a rectangle on it. We can plot the result:
plot_img(with_indicators)

This example demonstrated OpenCV's pre-trained classifier for Russian car plates, but that's not the only one available. There are also pre-trained classifiers for faces, eyes, and more, and they’re used in exactly the same way as this classifier.
Next Steps
We’ve only scratched the surface of what OpenCV can do. OpenCV has a lot more processing functionality (transformations, filters, 2D feature detection, and so on), and it can handle video frames in real-time. There’s a lot of material available on the internet about OpenCV. The official tutorials are a good place to start, but you'll also find a lot of help if you search specifically on a problem you’d like to tackle with OpenCV.
In the next module, we'll talk about the use of the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK).
