A web based SPA [Single Page Application] needs modal dialogs to provide the same user experience as a desktop application. This article demonstrates how to create a simple generic modal dialog container for Blazor Components and build vanilla and Bootstrap versions.
Code Repository
The code repository is here: Modal Dialog Repository
The Implementation
Overview
The implementation consists of two interfaces, four classes and an enum:
IModalOptionsIModalDialogContextModalOptionsModalResultModalResultTypeModalDialogContextModalDialogBase
The example code uses the standard Blazor template and shows how to open an edit form component from the WeatherForecast list in FetchData.
The code below demonstrates the basics: how to open a WeatherEditForm in a modal dialog. The method builds an IModalOptions object containing the Uid of the record. It calls ShowAsync<WeatherForm>(options), defining the component form to display and the options for that form, and awaits the returned Task. The Task doesn't complete until the modal closes.
private async Task EditAsync(Guid uid)
{
if (_modal is not null)
{
var options = new BsModalOptions();
options.ControlParameters.Add("Uid", uid);
var result = await _modal.Context.ShowAsync<WeatherEditForm>(options);
}
}
The form calls Close(modal result) which completes the Task and EditAsync runs to completion.
private void Close()
{
this.Modal?.Close(ModalResult.OK());
}
IModalOptions
IModalOptions defines three ways to pass data to the dialog. A modal dialog implementation can use the generic ModalOptions or define a specific IModalOptions.
public interface IModalOptions
{
public Dictionary<string, object> ControlParameters { get; }
public Dictionary<string, object> OptionsList { get; }
public object Data { get; }
}
ModalOptions
A basic implementation of IModalOptions.
public class ModalOptions: IModalOptions
{
public Dictionary<string, object>
ControlParameters { get; } = new Dictionary<string, object>();
public Dictionary<string, object> OptionsList { get; } =
new Dictionary<string, object>();
public object Data { get; set; } = new();
}
ModalResult
ModalResult is a return record that provides status and data back to the caller.
public sealed record ModalResult
{
public ModalResultType ResultType { get; private set; } = ModalResultType.NoSet;
public object? Data { get; set; } = null;
public static ModalResult OK() => new ModalResult()
{ ResultType = ModalResultType.OK };
}
And ModalResultType.
public enum ModalResultType { NoSet, OK, Cancel, Exit }
IModalDialogContext
ModalDialogContext encapsulates state and state management for a modal dialog component in a context class.
IModalDialogContext defines the interface.
public interface IModalDialogContext
{
public IModalOptions? Options { get; }
public bool Display { get; }
public bool IsActive { get; }
public Type? ModalContentType { get; }
public Action? NotifyRenderRequired { get; set; }
public Task<ModalResult> ShowAsync<TModal>(IModalOptions options)
where TModal : IComponent;
public Task<ModalResult> ShowAsync(Type control, IModalOptions options);
public bool Switch<TModal>(IModalOptions options) where TModal : IComponent;
public bool Switch(Type control, IModalOptions options);
public void Update(IModalOptions? options = null);
public void Dismiss();
public void Close(ModalResult result);
}
ModalDialogContext
ModalDialogContext implements IModalDialogContext, providing the boilerplate code for ModalDialog implementations.
It consists of properties to maintain state and methods to show, hide, switch and reset the component content.
Show:
- Ensures the passed type is a component i.e implements
IComponent. - Sets the state.
- Invokes the callback to notify the component to render: this will show the dialog framework and create the content component.
- Uses a
TaskCompletionSource to construct a manual active Task and passes the task back to the caller to await.
protected TaskCompletionSource<ModalResult> _ModalTask
{ get; set; } = new TaskCompletionSource<ModalResult>();
private Task<ModalResult> ShowModalAsync(Type control, IModalOptions options)
{
if (!(typeof(IComponent).IsAssignableFrom(control)))
throw new InvalidOperationException
("Passed control must implement IComponent");
this.Options = options;
this.ModalContentType = control;
this.Display = true;
this.NotifyRenderRequired?.Invoke();
this._ModalTask = new TaskCompletionSource<ModalResult>();
return this._ModalTask.Task;
}
Close:
- clears the state.
- invokes the callback to notify the component to render: this will hide the dialog framework and destroy the content component.
- sets the
TaskCompletionSource to complete. If the caller awaited Show, the call method will now run to completion.
private void CloseModal(ModalResult result)
{
this.Display = false;
this.ModalContentType = null;
this.NotifyRenderRequired?.Invoke();
_ = this._ModalTask.TrySetResult(result);
}
Switch:
- sets the state.
- invokes the callback to notify the component to render: this will show the dialog framework with the new content component.
private async Task<bool> SwitchModalAsync(Type control, IModalOptions options)
{
if (!(typeof(IComponent).IsAssignableFrom(control)))
throw new InvalidOperationException("Passed control must implement IComponent");
this.ModalContentType = control;
this.Options = options;
await this.InvokeAsync(StateHasChanged);
return true;
}
The full class:
public class ModalDialogContext : IModalDialogContext
{
public IModalOptions? Options { get; protected set; }
public bool Display { get; protected set; }
public bool IsActive => this.ModalContentType is not null;
public Action? NotifyRenderRequired { get; set; }
private TaskCompletionSource<ModalResult> _ModalTask
{ get; set; } = new TaskCompletionSource<ModalResult>();
public Type? ModalContentType {get; private set;} = null;
public Task<ModalResult> ShowAsync<TModal>(IModalOptions options)
where TModal : IComponent
=> this.ShowModalAsync(typeof(TModal), options);
public Task<ModalResult> ShowAsync(Type control, IModalOptions options)
=> this.ShowModalAsync(control, options);
public bool Switch<TModal>(IModalOptions options) where TModal : IComponent
=> this.SwitchModal(typeof(TModal), options);
public bool Switch(Type control, IModalOptions options)
=> this.SwitchModal(control, options);
public void Update(IModalOptions? options = null)
{
this.Options = options ?? this.Options;
this.NotifyRenderRequired?.Invoke();
}
public void Dismiss()
=> this.CloseModal(ModalResult.Cancel());
public void Close(ModalResult result)
=> this.CloseModal(result);
private Task<ModalResult> ShowModalAsync(Type control, IModalOptions options)
{
if (!(typeof(IComponent).IsAssignableFrom(control)))
throw new InvalidOperationException
("Passed control must implement IComponent");
this.Options = options;
this.ModalContentType = control;
this.Display = true;
this.NotifyRenderRequired?.Invoke();
this._ModalTask = new TaskCompletionSource<ModalResult>();
return this._ModalTask.Task;
}
private bool SwitchModal(Type control, IModalOptions options)
{
if (!(typeof(IComponent).IsAssignableFrom(control)))
throw new InvalidOperationException
("Passed control must implement IComponent");
this.ModalContentType = control;
this.Options = options;
this.NotifyRenderRequired?.Invoke();
return true;
}
private void CloseModal(ModalResult result)
{
this.Display = false;
this.ModalContentType = null;
this.NotifyRenderRequired?.Invoke();
_ = this._ModalTask.TrySetResult(result);
}
}
ModalDialogBase
ModalDialogBase implements the boilerplate code for modal dialog components.
It creates an instance of ModalDialogContext and sets the callback in SetParametersAsync: this ensures inheriting classes can't inadvertently override it.
public abstract class ModalDialogBase : ComponentBase
{
public readonly IModalDialogContext Context = new ModalDialogContext();
public override Task SetParametersAsync(ParameterView parameters)
{
parameters.SetParameterProperties(this);
this.Context.NotifyRenderRequired = this.OnRenderRequested;
return base.SetParametersAsync(ParameterView.Empty);
}
private void OnRenderRequested()
=> StateHasChanged();
}
VanillaModalDialog
VanillaModalDialog provides a basic CSS styled modal dialog component wrapper. It has:
- a clickable background
- configurable width
- uses
DynamicComponent to render the requested component
VanillaModalDialog.razor
@namespace Blazr.ModalDialog.Components
@inherits ModalDialogBase
@implements IModalDialog
@if (this.Display)
{
<CascadingValue Value="(IModalDialog)this">
<div class="base-modal-background" @onclick="OnBackClick">
<div class="base-modal-content" style="@this.Width"
@onclick:stopPropagation="true">
<DynamicComponent Type=this.ModalContentType
Parameters=this.Options?.ControlParameters />
</div>
</div>
</CascadingValue>
}
@code {
private VanillaModalOptions modalOptions =>
this.Options as VanillaModalOptions ?? new();
protected string Width
=> string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(modalOptions.ModalWidth) ?
string.Empty : $"width:{modalOptions.ModalWidth}";
private void OnBackClick()
{
if (modalOptions.ExitOnBackgroundClick)
this.Close(ModalResult.Exit());
}
}
VanillaModalDialog.razor.css:
div.base-modal-background {
display: block;
position: fixed;
z-index: 101;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow: auto;
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.4);
}
div.base-modal-content {
background-color: #fefefe;
margin: 10% auto;
padding: 10px;
border: 2px solid #888;
width: 90%;
}
BsModelDialog
BsModalDialog provides a Bootstrap styled modal dialog component wrapper.
It has a custom IModalOptions where you can set the modal size.
public sealed class BsModalOptions: IModalOptions
{
public string ModalSize { get; set; } = "modal-xl";
public Dictionary<string, object> ControlParameters { get; } =
new Dictionary<string, object>();
public Dictionary<string, object> OptionsList { get; } =
new Dictionary<string, object>();
public object Data { get; set; } = new();
}
BsModalDialog.razor
@namespace Blazr.ModalDialog.Components
@inherits ModalDialogBase
@if (this.Context.Display)
{
<CascadingValue Value="(IModalDialogContext)this.Context">
<div class="modal show-modal" tabindex="-1">
<div class="modal-dialog @this.Size">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-body">
<DynamicComponent Type=this.Context.ModalContentType
Parameters=this.Context.Options?.ControlParameters />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</CascadingValue>
}
@code {
private BsModalOptions modalOptions =>
this.Context.Options as BsModalOptions ?? new();
protected string Size => modalOptions.ModalSize;
}
and BsModalDialog.razor.css:
.modal-body {
padding: 0;
}
.show-modal {
display: block;
background-color: rgb(0,0,0,0.6);
}
Demonstration
The demonstration uses the FetchData page, adding a modal dialog editor for the weather forecasts. You can view all the code in the repository, including the updated WeatherForecastService.
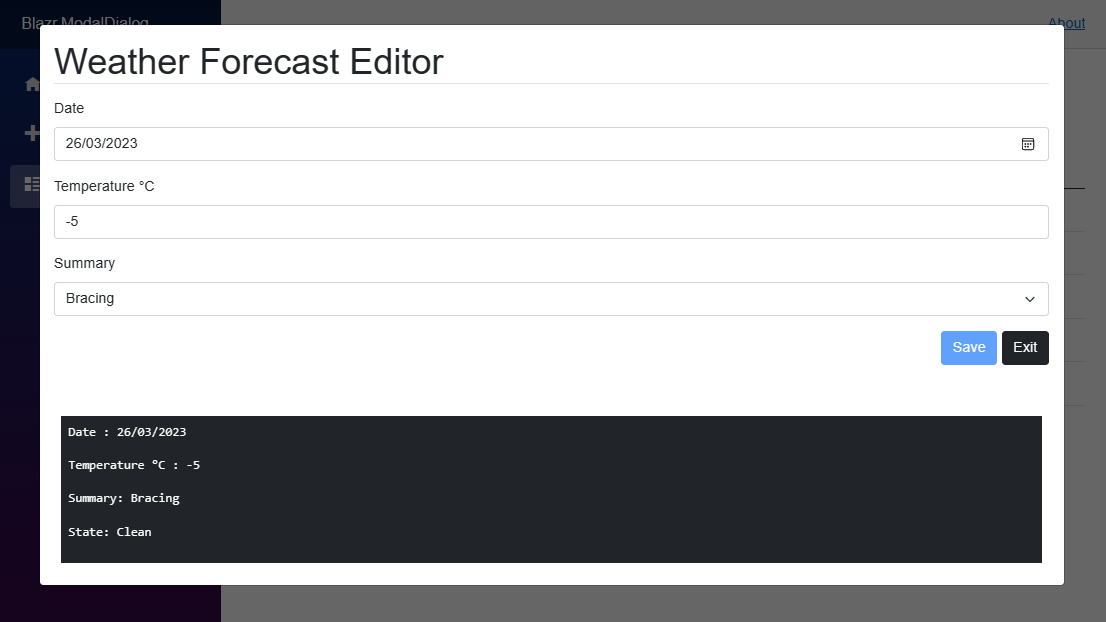
WeatherEditForm
WeatherEditForm is the edit form for a WeatherForecast record.
It:
- captures the cascaded
IModalDialogContext. - throws an expection if there's no cascaded
IModalDialogContext: the form is designed to run in a modal dialog context. - uses
EditStateTracker. This tracks the edit state and is detailed here Blazr.EditStateTracker. - interacts with the modal context in Save and Close.
// WeatherEditForm.razor
@inject WeatherForecastService DataService
<div class="p-3">
<div class="mb-3 display-6 border-bottom">
Weather Forecast Editor
</div>
<EditForm Model=this.model OnSubmit=this.SaveAsync>
<DataAnnotationsValidator/>
<EditStateTracker LockNavigation EditStateChanged=this.OnEditStateChanged />
<div class="mb-3">
<label class="form-label">Date</label>
<InputDate class="form-control" @bind-Value=this.model.Date />
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label class="form-label">Temperature °C</label>
<InputNumber class="form-control" @bind-Value=this.model.TemperatureC />
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label class="form-label">Summary</label>
<InputSelect class="form-select" @bind-Value=this.model.Summary>
@if (model.Summary is null)
{
<option disbabled selected value="null">
-- Select a Summary -- </option>
}
@foreach (var summary in this.DataService.Summaries)
{
<option value="@summary">@summary</option>
}
</InputSelect>
</div>
<div class="mb-3 text-end">
<button disabled="@(!_isDirty)" type="submit"
class="btn btn-primary" @onclick=SaveAsync>Save</button>
<button disabled="@_isDirty" type="button"
class="btn btn-dark" @onclick=Close>Exit</button>
</div>
</EditForm>
</div>
<div class="bg-dark text-white m-4 p-2">
<pre>Date : @this.model.Date</pre>
<pre>Temperature °C : @this.model.TemperatureC</pre>
<pre>Summary: @this.model.Summary</pre>
<pre>State: @(_isDirty ? "Dirty" : "Clean")</pre>
</div>
@code {
[Parameter] public Guid Uid { get; set; }
[CascadingParameter] private IModalDialogContext? Modal { get; set; }
private WeatherForecast model = new();
private bool _isDirty;
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(Modal);
model = await this.DataService.GetForecastAsync(this.Uid) ?? new()
{ Date = DateOnly.FromDateTime(DateTime.Now), TemperatureC = 10 };
}
private void OnEditStateChanged(bool isDirty)
=> _isDirty = isDirty;
private async Task SaveAsync()
{
await this.DataService.SaveForecastAsync(model);
this.Modal?.Close(ModalResult.OK());
}
private void Close()
=> this.Modal?.Close(ModalResult.OK());
}
And FetchData
- adds an Edit button to each row.
- adds the
BsModalDialog component to the page. - calls
ShowAsync on the modal component to open the modal dialog with the Edit Form.
@page "/fetchdata"
@using Blazr.ModalDialog.Data
@inject WeatherForecastService ForecastService
<PageTitle>Weather forecast</PageTitle>
<h1>Weather forecast</h1>
<p>This component demonstrates fetching data from a service.</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Date</th>
<th>Temp. (C)</th>
<th>Temp. (F)</th>
<th>Summary</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var forecast in forecasts)
{
<tr>
<td>@forecast.Date.ToShortDateString()</td>
<td>@forecast.TemperatureC</td>
<td>@forecast.TemperatureF</td>
<td>@forecast.Summary</td>
<td><button class="btn btn-sm btn-primary"
@onclick="() => EditAsync(forecast.Uid)">Edit</button></td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
<BsModalDialog @ref=_modal />
@code {
private IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> forecasts =
Enumerable.Empty<WeatherForecast>();
private BsModalDialog? _modal;
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
forecasts = await ForecastService.GetForecastAsync();
}
private async Task EditAsync(Guid uid)
{
if (_modal is not null)
{
var options = new BsModalOptions();
options.ControlParameters.Add("Uid", uid);
var result = await _modal.Context.ShowAsync<WeatherEditForm>(options);
}
}
}
Wrap Up
This implementation demonstrates several techniques and practices in developing Blazor components.
- How to use
TaskCompletionSource to manage showing and hiding the dialog. - Separation of component state into a context class, so you can cascade the state context and not the component.
- The example code demonstrates both Edit state tracking and Navigation locking.
History
- 19th November, 2020: Initial version
- 25th March, 2023: Revision 2
