In this article, I’ll be showing to you a tutorial of how you can connect your app to an API using Retrofit. I’ll be using a free public API to retrieve list of regions, and under each region, the list of countries, for each country, some details like sub-region name and population, and then we will display this list into a Recycler View.
Retrofit is the best library that lets you connect to HTTP-based API services from your Android App. It leverages the OkHttp library’s core functionality, adding a bunch of features to it while eliminating the boilerplate code that should be written in case you want to only implement the OkHttp library and have any of the features that Retrofit provides.
Retrofit offers several powerful features such as the ability to cancel the request in an easy way, specify the request headers such as passing Authorization header through the annotations or intercepting the request, applying various types of Converters to convert your request/response objects to your preferred formatting, and more.
Retrofit leverages the use of Callbacks, and a callback overrides two methods, onResponse() and onFailure().
In this tutorial, I’ll be using the GsonFactoryConverter for our Retrofit implementation. Gson is a simple library that allows you to easily deal with the request/response objects of the APIs and convert them to and from Json format. The GsonFactoryConverter will handle the conversion part on your behalf, without you having to include the Gson library.
One of the great features of Retrofit is that it converts your HTTP API into a standard Interface, where every endpoint will be represented as a method with some decoration attributes that are part of the Retrofit library.
In this article, I’ll be showing to you a tutorial of how you can connect your app to an API using Retrofit, I’ll be using a free public API to retrieve list of regions, and under each region the list of countries, for each country, some details like sub-region name and population, and then we will display this list into a Recycler View.
As the title states, this article is Part 1 – Introduction to Retrofit in Android.
If you think that you already know the rudimentary concepts of Retrofit, you can navigate to the other two articles in this series:
Beginning the Tutorial
Open your Android Studio. I always recommend that you use the latest stable release of Android Studio, with all updates installed.
Start a new Project, and choose your minimum sdk level that you want, in this tutorial, let’s choose API 17: Android 4.2 (JELLY BEAN Update 2) as the minimum SDK, and API 26: Android 8.0 (Oreo) as the target SDK.
If you don’t have the above SDKs, then go to your SDK Manager and install them, otherwise you can just use whatever SDK you have available, but I would not guarantee if the code will perfectly work on whatever SDK you will be targeting or supporting.
But in general, this tutorial is about Retrofit which should fit well on all SDKs starting API 10: Android 2.3 (Gingerbread).
Now, choose an Empty Activity, and then define your activity name and layout name, and finish.
Referencing Retrofit
Open your build.gradle file, and inside the dependencies section, add a reference to the latest version of Retrofit which is 2.3.0 (until the date of writing the article), as below:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.3.0'
}
Note: We are using the syntax implementation instead of compile. This was one of the major changes introduced to Android plugin for gradle starting version 3.0.
Creating the API Interface
Then, create a new interface, and name it ILocationsApi.
public interface ILocationsApi {
@GET("all?fields=region")
Call<List<RegionModel>> getRegions();
}
This will include the needed methods which will match the endpoints which we will use within our tutorial to retrieve the regions, countries and country details.
The above method, will retrieve the regions in a List of RegionModel, which is a class that we will define to match the response of the API.
Creating the Data Model
Now, define the RegionModel class, and add one private field that will represent the ‘region’ field from the API, if you want to use a Java field name different than the API field name, then you have to use the annotation @SerializedName.
This annotation comes from the library com.google.json, so you will have to include it in your app’s gradle file, but since we will be using a Converter Factory for retrofit, then the gson annotation will be included within the library, so let’s include the retrofit’s gson converter library:
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.3.0'
You can otherwise just name the field as region, then you don’t have to use this annotation.
class RegionModel {
@SerializedName("region")
private String name;
public RegionModel(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
RegionModel that = (RegionModel) o;
return name != null ? name.equals(that.name) : that.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
}
}
We are overriding equals and hashCode, because we will need them later in this tutorial when we load the regions into HashSet, as we need the list of distinct regions.
Since now we have the Retrofit interface and the RegionModel defined, we will need to create our Retrofit instance to use it to call the endpoint that will retrieve the regions using our interface method.
Create Retrofit Instance inside ApiManager
The best way to create the Retrofit instance is by using an API Manager with a single instance method (singleton), which will guarantee that we only have one instance of the Retrofit throughout the lifetime of our running app, and the creation of this instance will happen once the application starts.
Here is how:
public class ApiManager {
private static ILocationsApi service;
private static ApiManager apiManager;
private ApiManager() {
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/")
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();
service = retrofit.create(ILocationsApi.class);
}
public static ApiManager getInstance() {
if (apiManager == null) {
apiManager = new ApiManager();
}
return apiManager;
}
public void getRegions(Callback<List<RegionModel>> callback) {
Call<List<RegionModel>> regionsCall = service.getRegions();
regionsCall.enqueue(callback);
}
}
As you can see, the getRegions method returns void. Why? Because we want to do an asynchronous call with a callback that we will pass from our main activity. The callback will handle the response from the API.
Extend Application Class
The application class is the base class that contains all activities and services in the Android app. It serves as the entrance to your app as well as a global application state container.
You can create another Class that inherits (extends) from the Application Class, however, you need to make sure that you call the new class in your AndroidManifest.xml file, in the <application> tag android:name=”.YourNewApplicationClassName”.
Extending the Application class enables you to define some injection configurations, analytics or logging configurations. As such, configurations usually come at an initial phase, upon starting the app.
Now back to our tutorial, let’s extend the Application Class, by another class with name ‘MainApplication’ , and in the onCreate method, we will create/get the instance to the ApiManager. See below:
public class MainApplication extends Application {
public static ApiManager apiManager;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
apiManager = ApiManager.getInstance();
}
}
This will guarantee that the retrofit instance will be created only once, at the start of the app, and will remain a single instance all through the lifetime of the app.
In Retrofit, you can easily choose between doing synchronous or asynchronous calls.
Synchronous calls, using the execute method, will block the thread that it is running in, and will resume once an HTTP response is returned from call (either if it was a 200 ok, or 400 bad request, or 500 internal server error). For the full list of HTTP response codes and their meanings, see here). You cannot do synchronous network call on MainThread or the UI Thread, as it will result in a NetworkOnMainThreadException.
Asynchronous calls will do the network call on a separate thread, the Main Thread will not be blocked.
Retrofit makes it super easy for you, by providing you the enqueue method. This automatically handles the threading part for you, you only have to handle the result of the network call, with providing the Callback<T> instance.
If the network call you are doing has to block the UI, then you can display a loading dialog to let the user know that there is a process being done, and you can make it not cancellable, so the user won’t be able to cancel the request.
This is useful whenever you are dealing with saving some information into db or doing a payment transaction.
So, back to our tutorial, now we need to populate the list of regions and display them nicely on a RecyclerView.
Creating the Adapter for the RecyclerView
A RecyclerView requires an adapter and a view, so let’s define our adapter that will hold the regions collection, and it will bind each region to a separate view inside this adapter.
So let’s create our RecyclerView adapter and call it ‘RegionsAdapter’:
public class RegionsAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<RegionsAdapter.RegionViewHolder> {
private Context context;
private List<RegionModel> regions;
public RegionsAdapter(Context context, List<RegionModel> regions) {
this.context = context;
this.regions = regions;
}
@Override
public RegionViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return new RegionViewHolder(LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate
(R.layout.region_item, parent, false));
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(RegionViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.setRegionItem(regions.get(position));
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return regions.size();
}
class RegionViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private TextView regionName;
RegionViewHolder(View regionItem) {
super(regionItem);
regionName = regionItem.findViewById(R.id.region_name);
}
private void setRegionItem(RegionModel region){
regionName.setText(region.getName());
}
}
}
To explain the above code: the constructor accepts a Context object, and a List of regions. The context is used as a source for the layout inflator to inflate the region item layout to be used in the ViewHolder. The list of regions is the data-set that will be used in the onBindViewHolder method to bind each region to the viewHolder’s view and set the needed layout widgets, like the textedit, and the list of regions will also be used to calculate the item count for the recycler view.
Creating the Layout for ReyclerView Item
The region_item layout needs to be defined as below:
="1.0"="utf-8"
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="@style/Base.TextAppearance.AppCompat.Large"
android:text="Sample"
android:padding="10dp"
android:id="@+id/region_name"/>
<View android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary" />
</LinearLayout>
Referencing and Adding the RecyclerView
Now we have our adapter and item defined, let’s go and create our RecyclerView inside the main activity.
The RecyclerView comes inside the Android’s v7 support library, and it should be referenced separately:
implementation 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:26.1.0'
Sync the project, then open the main activity’s layout file to add the RecyclerView widget:
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/regions_recycler_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
Calling getRegions Method in MainActivity
Then open the main activity class, and in the onCreate method, get a reference to the RecyclerView widget, and then call the getRegions method from the static instance apiManager from MainApplication:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final RecyclerView regionsRecyclerView = findViewById(R.id.regions_recycler_view);
MainApplication.apiManager.getRegions(new Callback<List<RegionModel>>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<List<RegionModel>> call,
Response<List<RegionModel>> response) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
Iterable<RegionModel> regionsIterable =
Iterables.filter(response.body(), new Predicate<RegionModel>() {
@Override
public boolean apply(RegionModel input) {
return !input.getName().trim().equals("");
}
});
HashSet<RegionModel> regionModels = Sets.newHashSet(regionsIterable);
RegionsAdapter regionsAdapter =
new RegionsAdapter(MainActivity.this, new ArrayList(regionModels));
regionsRecyclerView.setAdapter(regionsAdapter);
regionsRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager
(MainActivity.this));
} else {
try {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
response.errorBody().string(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<List<RegionModel>> call, Throwable t) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, t.getMessage(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
});
}
Let’s understand the code:
After obtaining a reference to the recycler view widget, we do the API call using our previously defined method, getRegions.
As you remember earlier in this tutorial, this method takes a callback object as a parameter, so here whenever you call it, you need to define your callback object.
The callback object overrides two methods, onResponse and onFailure.
onResponse occurs whenever the API returns a response, regardless of whether it was valid or not. It might be a 200 ok, 400 bad request, 500 internal server error, or any of the http response codes.
onFailure occurs whenever there was a connectivity issue that prevented from doing the API call, like no network available or socket was closed due to timeout. In our case, we are showing a toast message.
In the onResponse method, we are checking if the API response was successful (200 ok), if yes, then we are taking the response.body, and using it to extract the regions information, and put them within a list, and then filter them for distinct values, using the HashSet, and next passing them to the RegionsAdapter that we have created previously, and after that, we set the recycler view.
The RecyclerView requires a LayoutManager to understand how to arrange the items inside it. So we create a LinearLayoutManager and assign it to the LayoutManager of the RecyclerView.
Adding Internet Permission
For retrofit to be able to connect to the internet via your app, it will require to obtain the internet permission. So you will have to specify this permission in your manifest file:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
Even though we are targeting API level 26, the permission we are requesting here is categorized under the safe or normal permissions, that do not require the user’s deliberate consent to approve or reject the permission, and therefore, no specific runtime permission code needs to be added to use Retrofit.
Running the App
Now if you run the app, you should see the list of regions displayed properly on the screen once the app starts:
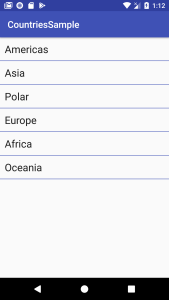
If you noticed, there was a little delay before we saw the list of regions on screen, this is the network delay, until the request was done, and a response got returned.
Adding a ProgressBar
Whenever doing an API call, it is really important to let your users know that you are doing an API call, in a friendly way, upon loading a screen or pressing a button. This can be achieved by displaying a progress bar or a loading dialog with a short message.
So, let’s include a ProgressBar widget into our example without displaying it initially:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progress_bar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="gone"
/>
Then in the code, we will take a reference to this progress bar and display it whenever we do the API call, and then hide it whenever the API returns a response or fails. See the below:
final ProgressBar progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progress_bar);
progressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
MainApplication.apiManager.getRegions(new Callback<List<RegionModel>>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<List<RegionModel>> call, Response<List<RegionModel>> response) {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
And in case of failure. We will also hide it:
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<List<RegionModel>> call, Throwable t) {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
When you run the app, you will see a progress loader spinning for a few seconds (depending on how long the network call will take), then the regions will be displayed:

Loading the Countries
After we have populated the list of regions, we would like to load the countries of each region inside another activity.
So, to do this task, first we will need to add a new method under ILocationsApi, which is getCountries, and this time, we will pass the region name:
@GET("region/{regionName}")
Call<List<CountryModel>> getCountries(@Path("regionName") String regionName);
Creating the CountryModel:
class CountryModel implements Serializable {
private String name;
@SerializedName("subregion")
private String subRegion;
private int population;
CountryModel(String name, String subRegion, int population) {
this.name = name;
this.subRegion = subRegion;
this.population = population;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getSubRegion() {
return subRegion;
}
public int getPopulation() {
return population;
}
}
Then open ApiManager, and add a new method, give it the same name, getCountries, with two arguments: one for the regionName as a String, and the other for the callback object.
public void getCountries(String regionName, Callback<List<CountryModel>> callback){
Call<List<CountryModel>> regionsCall = service.getCountries(regionName);
regionsCall.enqueue(callback);
}
Enabling Click Event on Region Item inside Regions Adapter
Now we need to do few changes on the RegionsAdapter to enable the click event on the Recycler View items ( regions).
On the RegionsAdapter constructor, add a new OnClickListener paramter, and then in the onBindViewHolder method, set the click listener of the viewHolder’s itemView to be the listener that you have passed via the constructor.
The itemView is an object of type View, that is defined inside the RegionViewHolder object, therefore, you will be able to assign a click listener to it using its method setOnClickListener. This means we are registering the click listener that we have passed from the MainActivity to the Region Item, so whenever you press on a given region, you will be able to tell which region was pressed and therefore grab some important details from it, like the region name.
Below is the final look of RegionsAdapter Class:
public class RegionsAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<RegionsAdapter.RegionViewHolder> {
private Context context;
private List<RegionModel> regions;
private View.OnClickListener listener;
public RegionsAdapter(Context context, List<RegionModel> regions,
View.OnClickListener listener) {
this.context = context;
this.regions = regions;
this.listener = listener;
}
@Override
public RegionViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return new RegionViewHolder(LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate
(R.layout.region_item, parent, false));
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(RegionViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.setRegionItem(regions.get(position));
holder.itemView.setOnClickListener(listener);
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return regions.size();
}
class RegionViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private TextView regionName;
RegionViewHolder(View regionItem) {
super(regionItem);
regionName = regionItem.findViewById(R.id.region_name);
}
private void setRegionItem(RegionModel region){
regionName.setText(region.getName());
}
}
}
Then in the MainActivity, create the onClick listener, and inside it get a reference to the region_name TextView, grab the text of it, and call the getCountries endpoint:
final TextView regionNameView = view.findViewById(R.id.region_name);
progressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
final String regionName = regionNameView.getText().toString();
MainApplication.apiManager.getCountries(regionName, new Callback<List<CountryModel>>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<List<CountryModel>> call,
Response<List<CountryModel>> response) {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
if (response.isSuccessful()){
List<CountryModel> countries = response.body();
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, CountriesActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("Countries", (Serializable) countries);
intent.putExtra("Region", regionName);
startActivity(intent);
} else {
showErrorToast(response.errorBody());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<List<CountryModel>> call, Throwable t) {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, t.getMessage(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
});
Now let’s create the other activity, name it CountriesActivity.
Inside it, we will read the countries list that was passed through the intent, and we will read the selected region name.
We will display former inside a recycler view, the same way we did for the regions list. And the latter will be used to display a proper title according to the selected region, like ‘Countries in Europe’.
The below code the CountriesActivity:
public class CountriesActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private List<CountryModel> countries;
private String region;
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.countries_activity);
parseIntent();
this.setTitle(String.format("Countries in %s", region));
RecyclerView countriesRecyclerView = findViewById(R.id.countries_recycler_view);
CountriesAdapter adapter = new CountriesAdapter(this, countries);
countriesRecyclerView.setAdapter(adapter);
countriesRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
}
private void parseIntent() {
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (!intent.hasExtra("Countries")) {
throw new RuntimeException("Countries Intent was not passed!");
}
countries = (List<CountryModel>) intent.getSerializableExtra("Countries");
region = intent.getStringExtra("Region");
}
}
And here is the xml layout for the countries_activity.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/countries_recycler_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</ScrollView>
And the CountriesAdapter is the following:
public class CountriesAdapter
extends RecyclerView.Adapter<CountriesAdapter.CountryViewHolder> {
private Context context;
private List<CountryModel> countries;
public CountriesAdapter(Context context, List<CountryModel> countries) {
this.context = context;
this.countries = countries;
}
@Override
public CountryViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return new CountryViewHolder(LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate
(R.layout.country_item, parent, false));
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(CountryViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.setCountryItem(countries.get(position));
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return countries.size();
}
class CountryViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private TextView countryName;
private TextView subRegion;
private TextView population;
CountryViewHolder(View countryItem) {
super(countryItem);
countryName = countryItem.findViewById(R.id.country_name);
subRegion = countryItem.findViewById(R.id.sub_region);
population = countryItem.findViewById(R.id.population);
}
private void setCountryItem(CountryModel country) {
countryName.setText(country.getName());
subRegion.setText(country.getSubRegion());
population.setText(String.valueOf(country.getPopulation()));
}
}
}
And here is the xml layout for the country_item.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="15dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="5dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/country_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="name"
android:textAppearance="@style/Base.TextAppearance.AppCompat.Large" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="subregion:"
android:textAppearance="@style/Base.TextAppearance.AppCompat.Medium" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/sub_region"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:text="subregion"
android:textAppearance="@style/Base.TextAppearance.AppCompat.Medium" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="population:"
android:textAppearance="@style/Base.TextAppearance.AppCompat.Medium" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/population"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:text="population"
android:textAppearance="@style/Base.TextAppearance.AppCompat.Medium" />
</LinearLayout>
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary" />
</LinearLayout>
Never forget to add the new Activity to the manifest, otherwise you will get an error at runtime.
<activity android:name=".CountriesActivity" android:label="Countries" />
Your AndroidManifest.xml file should finally look like below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="codingsonata.countriessample">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:name=".MainApplication"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".CountriesActivity" android:label="Countries" />
</application>
</manifest>
Running the App
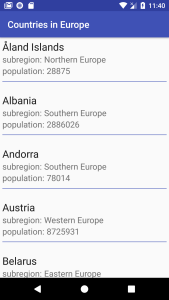
Then once the loading is done, the new activity will open, and it will display the selected region’s countries in a RecyclerView that can be scrolled.
Next Tutorial
In this tutorial, I explained how to use Retrofit to easily build an app that connects to an HTTP-based service with the use of GET method to retrieve data and display them nicely on the screen.
In the upcoming tutorial, I will explain to you how can you use Retrofit to do POST requests, and then on a subsequent tutorial, I will show you how to pass a request header (either using annotations or via an interceptor), also, we will explore the different properties of the Retrofit builder to understand the features that are available.
Stay tuned!
If you like this article, use share it in your network.
You can check my other Android related articles:
Bonus
My amazing reader and learner, listen to this wonderful piece of music that will captivate your brain while you immerse yourself while trying the code examples mentioned in this tutorial.
String Quintet in E Major, Op.11 No.5 – by Luigi Boccherini
Enjoy 
