When you need to build a working prototype for your client or your company doesn't have a budget for enterprise development, you have no choice and you need to use some shortcuts and life hacks, usually low-code or no-code approaches. In this post, I present an interesting approach on how to develop a Blazor UI very quickly using the open-source library Platz.SqlForms. SqlForms will provide SPA user experience and it will communicate with the database without any coding from your side, all you need to do is to define UI forms supplying fluent notation definition for EF entities that you want to show as UI controls.
If you are interested, you can read my other articles about Blazor dynamic forms:
New blog post coming:
Microsoft Blazor Open-source Platz.SqlForms - using Schema Builder to design and maintain SQL Server database
Platz.SqlForms Official Roadmap
### Release 0.3.0 - Current
- SqlForms custom rules to change field properties (hidden, required, read-only, etc.)
SchemaDesigner prototype, that allows to design database entities and save the schema to json- T4 template to generate
SchemaDesigner entities and data access layer - Upgrade
ObjectBuilder to support SchemaDesigner entities
### Release 0.4.0 - May'21
- UI SQL forms to enter/edit business objects
ObjectBuilder definition of business object - entity mappings and CRUD operationsObjectBuilder T4 template to generate business object CRUD operations' C# codeObjectBuilder Select functionsObjectBuilder Group By queriesObjectBuilder Subqueries
### Release 0.5.0 - Jun'21
- Usability and error data recovery for builders and designers
- Bug fixes
### Release 1.0.0 - Aug'21
- Support documentation
- Tutorials
- Bug fixes
1. Create Demo Project
1.1 DemoSqlForms.App
Let’s start by creating a Blazor Server App .NET 5.0 project DemoSqlForms.App using the Visual Studio 2019 “Create a New Project” link.
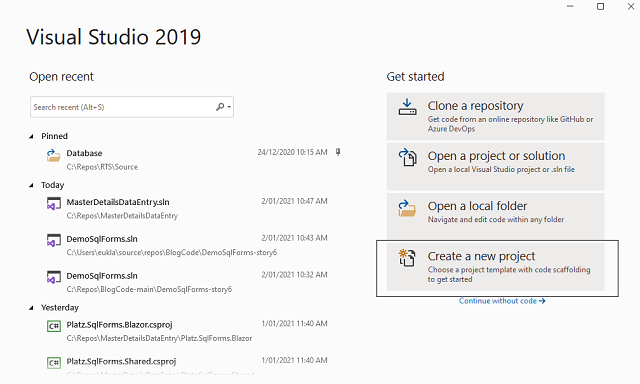
Then find the “Blazor App” template, select it and click the “Next” button.

On the next screen, specify the Project name: DemoSqlForms.App and the Solution name: DemoSqlForms and click the “Create” button.
Now select “.NET 5.0” and “Blazor Server App” templates, and click the “Create” button.

Visual Studio will create a solution with a project.
I like to spend some time deleting the example pages (Counter and FetchData) and their related code, but this is not necessary.
1.2 Platz.SqlForms NuGet Package
Now we need to add the Platz.SqlForms NuGet package, right-click on the solution project and click the “Manage NuGet Packages…” menu, then in the Browse tab, type “Platz” search pattern and you will see Platz packages. Select Platz.SqlForms and click the “Install” button. Versions 0.2.0 and 0.2.1 contained bugs, so use version 0.2.2 or later.

After installation, you will see a readme.txt file with simple instructions, follow them.
The important step is to add Platz.SqlForms initialization logic in the ConfigureServices method:
services.AddPlatzSqlForms();
1.3 Database Project
To demonstrate how to use Platz.SqlForms, we will need to create a database project.
Right-click on “DemoSqlForms” solution (the top line in Solution Explorer), click “Add” and click “New Project…”.
In the “Add a new project” wizard, find the “Class Library (.NET Core)” template, select it and click “Next”.

Type “DemoSqlForms.Database” in the Project Name and click “Create”.
Visual Studio will create a new class library project and add it to the solution.
We need to make sure that the Target Framework is “.NET 5.0”, right-click on project “DemoSqlForms.Database” and click “Properties”.

Select Target framework “.NET 5.0” and <ctrl+s> to save your changes.
2. Setup Demo Database
How to set up Demo Database you can see in the Appendix of this article - it is not related to the approach we demonstrate and many of you know how to use Entity Framework, so I would like not to spend your time on that.
I only should say that for this demo, we need SchoolContext database context and the following entities with some test data:

3. SqlForms Dynamic Pages
The main idea of SqlForms is to give developers a tool that allows them to define UI in a C# type safe way. Having Entity Framework entities or your own POCO objects means you can define which particular property to show, what UI control to use, make it mandatory or optional to submit, and also attach business rules to validate the input.
3.1 CourseEditForm and CourseEdit.razor page
Let’s start from the [Course] entity, add a new folder “Forms” to the “DemoSqlForms.App” project, and create a CourseEditForm class.
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App.Forms
{
public class CourseEditForm : DynamicEditFormBase<SchoolContext>
{
protected override void Define(DynamicFormBuilder builder)
{
builder.Entity<Course>(e =>
{
e.Property(p => p.CourseID).IsPrimaryKey().IsUnique();
e.Property(p => p.Title).IsRequired();
e.Property(p => p.Credits).IsRequired();
e.DialogButton(ButtonActionTypes.Cancel).DialogButton
(ButtonActionTypes.Submit);
e.DialogButtonNavigation("CourseList", ButtonActionTypes.Cancel,
ButtonActionTypes.Delete, ButtonActionTypes.Submit);
});
}
}
}
You can see that [CourseEditForm] is inherited from [DynamicEditFormBase<SchoolContext>] that has type parameter [SchoolContext] – this is how we tell the SqlForms engine which DbContext to use.
We override the [Define] method and provide the form definition inside it.
Code [builder.Entity<Course>] specifies [Course] type parameter, thus we inform the SqlForms engine which entity to use.
Now we need to specify how to show each property:
e.Property(p => p.CourseID).IsPrimaryKey().IsUnique();
It means that CourseID is a Primary Key and has a Unique constraint. IsRequired() means that the form will not be submitted if the value of this property is empty.
Method DialogButton is used to specify what buttons to show.
Method DialogButtonNavigation is used to assign navigation actions to a set of buttons. Thus, the next line...
e.DialogButtonNavigation("CourseList", ButtonActionTypes.Cancel,
ButtonActionTypes.Delete, ButtonActionTypes.Submit);
says that when the Cancel, Delete, or Submit buttons are clicked, the application will redirect to the link /CourseList.
Full specification of Form Definition can be found on the project wiki page:
Now when a form is defined, we can add a new razor page to the Pages folder CourseEdit.razor.
@page "/CourseEdit/{CourseId:int}"
@page "/CourseEdit"
<h1>Course Edit</h1>
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="CourseEditForm" Id="@CourseId" />
@code {
[Parameter]
public int CourseId { get; set; }
}
The <FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="CourseEditForm" Id="@CourseId" /> component expects the TForm parameter that points to form definition CourseEditForm and the Id of entity that is mapped to the page parameter CourseEdit.
Now, if you run the application and add /CourseEdit to the browser path, you will see the edit page that rendered from the definition. Because we have not supplied an Id value, it will create a new Course record in the database.
If you click “Submit”, you will see that the validation for CourseID and Title* failed.

Because CourseID is a primary key, but it is not Auto Incremented, you are able to specify any integer value except 0 and one that’s already been used, for Auto Incremented primary keys, the input is always read-only.
If you populate the form with values (100, C#, 4) and click Submit, the form will create a new record in the database and redirect to /CourseList, which is not implemented yet.
3.2 CourseListForm and CourseList.razor Page
The list form is defined a bit differently but we use a similar approach, BTW, this approach we spied in the Entity Framework entities definition, please have a look at this piece of code from SchoolContext.cs:
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Enrollment>(entity =>
{
entity.HasOne(d => d.Course)
.WithMany(p => p.Enrollments)
.HasForeignKey(d => d.CourseID)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Restrict)
.HasConstraintName("FK_Enrollment_Course");
entity.HasOne(d => d.Student)
.WithMany(p => p.Enrollments)
.HasForeignKey(d => d.StudentID)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Restrict)
.HasConstraintName("FK_Enrollment_Student");
});
}
So, the Course list form will look like this:
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App.Forms
{
public class CourseListForm : DataServiceBase<SchoolContext>
{
protected override void Define(DataServiceFormBuilder builder)
{
builder.Entity<Course>(e =>
{
e.ExcludeAll();
e.Property(p => p.CourseID).IsPrimaryKey();
e.Property(p => p.Title);
e.Property(p => p.Credits);
e.ContextButton("Edit", "CourseEdit/{0}").ContextButton
("Delete", "CourseDelete/{0}");
e.DialogButton("CourseEdit/0", ButtonActionTypes.Add);
});
builder.SetListMethod(GetCourseList);
}
public List<Course> GetCourseList(params object[] parameters)
{
using (var db = GetDbContext())
{
var query =
from s in db.Course
select new Course
{
CourseID = s.CourseID,
Title = s.Title,
Credits = s.Credits
};
var result = query.ToList();
return result;
}
}
}
}
Class CourseListForm is inherited from DataServiceBase<SchoolContext> now, and again we need to override the Define method, in which we place the form definition.
Firstly, we use e.ExcludeAll(); to remove all the properties from the definition, we do it when we don’t want to show everything.
Secondly, we specify all columns that we want to show in the order we want to see them.
Next, we define the context menu in line:
e.ContextButton("Edit", "CourseEdit/{0}").ContextButton("Delete", "CourseDelete/{0}");
where we supply buttons text and navigation links. The link part “{0}” is a placeholder for the record’s primary key, when users click on this button on some row, the primary key value will be extracted from the row and placed to the placeholder, for example for primary key value 17, we will get the resulting navigation link “CourseEdit/17”.
Then, we use the DialogButton to present an “Add” button with link “CourseEdit/0” and “0” says that the edit page executed to create a new record.
Finally, we need to specify the method (“SetListMethod”) that returns data to show on the page. GetCourseList uses LINQ to return all courses from the database.
When the definition is ready, we can add the razor page:
@page "/CourseList"
<h1>Courses</h1>
<FormDataServiceListComponent TForm="CourseListForm"/>
@code {
}
We use FormDataServiceListComponent and set our definition to TForm parameter.
We also need to modify NavMenu.razor in the Shared folder and include the CourseList page in the left side menu, also I included a link to StudentList page, which we will implement next.
<li class="nav-item px-3">
<NavLink class="nav-link" href="StudentList">
<span class="oi oi-people" aria-hidden="true"></span> Student List
</NavLink>
</li>
<li class="nav-item px-3">
<NavLink class="nav-link" href="CourseList">
<span class="oi oi-bell" aria-hidden="true"></span> Course List
</NavLink>
</li>
If you run the application now, you will see:

If you click on Course List, you will see:

You can use the “Add” button to add more courses to the database or the Actions context menu to Edit records.
We can also delete course records if we add the CourseDelete.razor page.
@page "/CourseDelete/{CourseId:int}"
<h1>Delete Course</h1>
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="CourseEditForm" Id="@CourseId" ForDelete="true" />
@code {
[Parameter]
public int CourseId { get; set; }
}
This page has the route [@page "/CourseDelete/{CourseId:int}" and it reuses the CourseEditForm but also we supply ForDelete="true", and this parameter tells the SqlForms that the form should be read-only and contain a “Delete” button.

As you can see, all insert, update, and delete operations are done for us by SqlForms, we only needed to create the query to select course records.
3.3 StudentListForm and StudentList.razor Page
Form definition for the student list is very similar to CourseList.
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App.Forms
{
public class StudentListForm : DataServiceBase<SchoolContext>
{
protected override void Define(DataServiceFormBuilder builder)
{
builder.Entity<StudentDetails>(e =>
{
e.ExcludeAll();
e.Property(p => p.ID).IsPrimaryKey();
e.Property(p => p.FirstMidName);
e.Property(p => p.LastName);
e.Property(p => p.EnrollmentDate).Format("dd-MMM-yyyy");
e.Property(p => p.EnrollmentCount);
e.ContextButton("Edit", "StudentEdit/{0}").ContextButton
("Delete", "StudentDelete/{0}").ContextButton
("Enrollments", "EnrollmentList/{0}");
e.DialogButton("StudentEdit/0", ButtonActionTypes.Add);
});
builder.SetListMethod(GetStudentList);
}
public class StudentDetails : Student
{
public int EnrollmentCount { get; set; }
}
public List<StudentDetails> GetStudentList(params object[] parameters)
{
using (var db = GetDbContext())
{
var query =
from s in db.Student
select new StudentDetails
{
ID = s.ID,
FirstMidName = s.FirstMidName,
LastName = s.LastName,
EnrollmentDate = s.EnrollmentDate,
EnrollmentCount = (db.Enrollment.Where
(e => e.StudentID == s.ID).Count())
};
var result = query.ToList();
return result;
}
}
}
}
Notice the format Format("dd-MMM-yyyy") that specifies how to show the EnrollmentDate property.
Also, sometimes, you need to show more columns than your entity has, then we need to create a business object – a class that will contain all the required properties. I created StudentDetails class that inherits all properties from Student and also, I added the EnrollmentCount property.
GetStudentList returns all student data and calculates the number of enrollments for each student.
The razor page will look like this:
@page "/StudentList"
<h1>Students</h1>
<FormDataServiceListComponent TForm="StudentListForm"/>
@code {
}
If you run the application and click the Student List menu item, you will see:

To get Add, Edit, Delete working, we need to add StudentEditForm.
3.4 StudentEditForm and StudentEdit.razor Page
StudentEditForm definition is very similar to CourseEditForm but I added business rules to have additional validation when a new student is entered or edited.
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App.Forms
{
public class StudentEditForm : DynamicEditFormBase<SchoolContext>
{
protected override void Define(DynamicFormBuilder builder)
{
builder.Entity<Student>(e =>
{
e.Property(p => p.ID).IsReadOnly();
e.Property(p => p.FirstMidName).IsRequired();
e.Property(p => p.LastName).IsRequired();
e.Property(p => p.EnrollmentDate).Rule
(DefaultDate, FormRuleTriggers.Create).Rule(CheckDate);
e.DialogButton(ButtonActionTypes.Cancel).DialogButton
(ButtonActionTypes.Validate).DialogButton(ButtonActionTypes.Submit);
e.DialogButtonNavigation("StudentList", ButtonActionTypes.Cancel,
ButtonActionTypes.Delete, ButtonActionTypes.Submit);
});
}
public FormRuleResult DefaultDate(Student model)
{
model.EnrollmentDate = new DateTime(DateTime.Now.Year, 9, 1);
return null;
}
public FormRuleResult CheckDate(Student model)
{
if (model.EnrollmentDate < new DateTime(2015, 1, 1))
{
return new FormRuleResult("EnrollmentDate is incorrect");
}
return null;
}
}
}
Rule Rule(DefaultDate, FormRuleTriggers.Create) says that when new student records are created, the DefaultDate method will be executed, this method sets EnrollmentDate to 01-Sep of the current year.
Rule CheckDate will be executed when the EnrollmentDate property changes or the form is submitted. This rule will fire a validation error when the entered value is before 01-Jan-2015.
StudentEdit.razor page is very simple as usual:
@page "/StudentEdit/{Id:int}"
@page "/StudentEdit"
<h1>Student Edit</h1>
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="StudentEditForm" Id="@Id" />
@code {
[Parameter]
public int Id { get; set; }
}
If you run the application now, select the Student List page and click on the “Add” button. You can play with default and validation rules.

For the delete functionality, we need to add StudentDelete.razor page.
@page "/StudentDelete/{Id:int}"
<h1>Delete Student</h1>
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="StudentEditForm" Id="@Id" ForDelete="true" />
@code {
[Parameter]
public int Id { get; set; }
}
When you run the application, the delete page will look like this:

Now we need to create Enrollment pages and I would like to demonstrate how the list form creation can be simplified.
4. Platz.ObjectBuilder
Platz.ObjectBuilder can be used to visually build complex LINQ queries with joins, subqueries, conditions and generate C# code for the queries and business objects returned by the queries.
To show how to use the Platz.ObjectBuilder, we need to create another Blazor Server Application with target framework .NET 5.0 and name it “DemoSqlForms.ObjectBuilder.App”.
Then we need to install Platz.ObjectBuilder NuGet package and follow instructions from the readm.txt file.
To use SchoolContext, we need to add a project reference to the DemoSqlForms.Database project and add the connection string to “appsettings.json” file.
Now let’s modify Index.razor page.
@page "/"
@using Platz.ObjectBuilder
<QueryComponent DbContextType="typeof(DemoSqlForms.Database.Model.SchoolContext)"
StoreDataPath="StoreData" DataService="MyDataService" Namespace="Default" />
Right-click on the “DemoSqlForms.ObjectBuilder.App” project and select “Debug” then “Start New Instance”.
You will see the application that allows us to build queries visually.
Select the Enrollment entity, then select the Course entity. You will see that two objects were added to the “From” panel. Now in the “Select” panel, enter “@p1” to “Filter” for “e.StudentID” column. You should see a query window like so:

Now click “…” on the Settings panel and enter “EnrollmentDetails” to “Query Return Type name” control and click “Save”, and close the application.
We created query definitions which saved as a json file in the folder “DemoSqlForms.ObjectBuilder.App\StoreData”. We can use the t4 template to generate code from this json definition.
4.1 Code Generation
Let’s return to “DemoSqlForms.App” project. If you open the project folder “Platz.Config.Link” you will see “CopyMe.PlatzDataService.tt.txt” file. Double click on this file, select all code (<ctrl+a>) and copy it to clipboard (<ctrl+c>).
Now in the “Forms” folder, create a subfolder “DataServices”.
In the “DataServices” folder, create a file called “SchoolDataService.tt” and paste content from the clipboard (<ctrl+v>).
You need to change line 12 to point to “StoreData” folder inside “DemoSqlForms.ObjectBuilder.App” project where we saved our query:
<# var JsonStorePath = @"DemoSqlForms.ObjectBuilder.App\StoreData"; #>
Now when you save the file, Visual Studio will generate code for you and place it in “SchoolDataService.cs”.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Linq;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
namespace Default
{
#region Interface
public partial interface IMyDataService
{
List<EnrollmentDetails> GetEnrollmentDetailsList(params object[] parameters);
}
#endregion
#region Data Service
public partial class MyDataService : DataServiceBase<SchoolContext>, IMyDataService
{
public List<EnrollmentDetails> GetEnrollmentDetailsList(params object[] parameters)
{
var p1 = (Int32)parameters[0];
using (var db = GetDbContext())
{
var query =
from c in db.Course
join e in db.Enrollment on c.CourseID equals e.CourseID
where e.StudentID == p1
select new EnrollmentDetails
{
EnrollmentID = e.EnrollmentID,
CourseID = e.CourseID,
Grade = e.Grade,
StudentID = e.StudentID,
Credits = c.Credits,
Title = c.Title,
};
var result = query.ToList();
return result;
}
}
}
#endregion
#region Entities
public partial class EnrollmentDetails
{
public Int32 EnrollmentID { get; set; }
public Int32 CourseID { get; set; }
public Grade? Grade { get; set; }
public Int32 StudentID { get; set; }
public Int32 Credits { get; set; }
public String Title { get; set; }
}
#endregion
}
The generated file contains EnrollmentDetails business object class and MyDataService:: GetEnrollmentDetailsList method that returns joined data for Enrollment and Course entities. It also accepts parameter p1 and data will be filtered by the StudentID field.
4.2 EnrollmentListForm and EnrollmentList.razor Page
Now we add EnrollmentListForm code:
using Default;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App.Forms
{
public class EnrollmentListForm : MyDataService
{
protected override void Define(DataServiceFormBuilder builder)
{
builder.Entity<EnrollmentDetails>(e =>
{
e.ExcludeAll();
e.Property(p => p.EnrollmentID).IsPrimaryKey();
e.Property(p => p.StudentID).IsFilter().IsReadOnly();
e.Property(p => p.CourseID);
e.Property(p => p.Grade);
e.Property(p => p.Title);
e.Property(p => p.Credits);
e.ContextButton("Edit", "EnrollmentEdit/{0}/{1}").ContextButton
("Delete", "EnrollmentDelete/{0}/{1}");
e.DialogButton("StudentList", ButtonActionTypes.Custom, "Back");
e.DialogButton("EnrollmentEdit/0/{1}", ButtonActionTypes.Add);
});
builder.SetListMethod(GetEnrollmentDetailsList);
}
}
}
We inherit class EnrollmentListForm from the generated MyDataService and use SetListMethod to specify the generated GetEnrollmentDetailsList.
We defined properties as usual but navigation links have two placeholders now: “EnrollmentEdit/{0}/{1}” and “EnrollmentDelete/{0}/{1}”.
The reason is that EnrollmentListForm is a dependant form of StudentListForm. When we select a student and click the “Enrollments” context menu button, we need to supply the StudentID primary key to EnrollmentListForm and this StudentID will be propagated to the EnrollmentEditForm as “{1}” placeholder, but “{0}” is reserved for EnrollmentEditForm primary key – EnrollmentID.
EnrollmentList.razor page will look like this:
@page "/EnrollmentList/{StudentId:int}"
<h1>Student Enrollments</h1>
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="StudentHeaderForm" Id="@StudentId" />
<FormDataServiceListComponent TForm="EnrollmentListForm"
ServiceParameters="@(new object[] { StudentId })"/>
@code {
[Parameter]
public int StudentId { get; set; }
}
Page route now accepts StudentId parameter and we use ServiceParameters to supply StudentId to FormDataServiceListComponent. The engine will use ServiceParameters to generate navigation links to populate placeholder beginning “{1}” and above.
We also added FormDynamicEditComponent that shows StudentHeaderForm which has all fields set as read-only.
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App.Forms
{
public class StudentHeaderForm : DynamicEditFormBase<SchoolContext>
{
protected override void Define(DynamicFormBuilder builder)
{
builder.Entity<Student>(e =>
{
e.ExcludeAll();
e.Property(p => p.ID).IsReadOnly();
e.Property(p => p.FirstMidName).IsReadOnly();
e.Property(p => p.LastName).IsReadOnly();
});
}
}
}
If we run the application now and in Student List, choose a student and click on the “Enrollments” context menu button, we will see:

You can see student read-only details in the header and enrollments table below.
If we click on the “Back” button, we will return back to the Student List page.
4.3 Enrollment Edit and Delete
The last step is to create a EnrollmentEditForm definition as simple as we’ve done it previously.
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App.Forms
{
public class EnrollmentEditForm : DynamicEditFormBase<SchoolContext>
{
protected override void Define(DynamicFormBuilder builder)
{
builder.Entity<Enrollment>(e =>
{
e.Property(p => p.EnrollmentID).IsPrimaryKey().IsReadOnly();
e.Property(p => p.StudentID).IsFilter().IsHidden();
e.Property(p => p.CourseID).IsRequired().Dropdown<Course>().Set
(c => c.CourseID, c => c.Title);
e.Property(p => p.Grade).IsRequired().Rule
(DefaultGrade, FormRuleTriggers.Create).Dropdown<Grade>().Set(g => g, g => g);
e.DialogButton(ButtonActionTypes.Cancel).DialogButton
(ButtonActionTypes.Submit);
e.DialogButtonNavigation("EnrollmentList/{1}",
ButtonActionTypes.Cancel, ButtonActionTypes.Delete, ButtonActionTypes.Submit);
});
}
public FormRuleResult DefaultGrade(Enrollment model)
{
model.Grade = Grade.A;
return null;
}
}
}
Here, we used Dropdown definitions. For the CourseID property, we use the Course entity and specify that [value] will be Course.CourseID and [name] will be Course.Title. For the “Grade” property, we specify the “Grade” enum and dropdown [value] and [name] will have “Grade” enum items (A, B, C, etc.)
Then we need to add razor pages for Edit.
@page "/EnrollmentEdit/{EnrollmentId:int}/{StudentId:int}"
<h1>Student Enrollment Edit</h1>
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="StudentHeaderForm" Id="@StudentId" ReadOnly="true" />
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="EnrollmentEditForm" Id="@EnrollmentId"
ServiceParameters="new object[] { StudentId }" />
@code {
[Parameter]
public int EnrollmentId { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public int StudentId { get; set; }
}
And for Delete.
@page "/EnrollmentDelete/{EnrollmentId:int}/{StudentId:int}"
<h1>Student Enrollment Delete</h1>
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="StudentHeaderForm" Id="@StudentId" />
<FormDynamicEditComponent TForm="EnrollmentEditForm" Id="@EnrollmentId"
ServiceParameters="new object[] { StudentId }" ForDelete="true" />
@code {
[Parameter]
public int EnrollmentId { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public int StudentId { get; set; }
}
In both pages, we show StudentHeaderForm as a header and we supply StudentId in ServiceParameters.
Now the application is ready for testing, clicking on the Student Enrollments “Edit” action, you will see:

If we click the “Delete” action, this page will be shown:

All the database operations for Insert, Update, and Delete will be performed by the SqlForms engine using the form definitions we provided.
5. Summary
In this article, we have demonstrated an approach to building a Blazor UI application using type-safe definitions in C#. This technique can save lots of time for a developer working on a prototype or a low-budget application using Platz.SqlForms.
This approach has several advantages:
- Middle or Junior developer can easily use it, and no front-end experience required
- Code will be structured very well and business logic only allowed in business rules
- Business logic can be easily unit tested
- The resulting codebase is much smaller and doesn’t require expensive maintenance
- Complex queries and business objects can be generated in a visual tool
However, there are some disadvantages:
- SqlForms dynamic components have limitations and cannot generate any UI you want
- Composite Primary Keys are not supported
- Only one bootstrap presentation currently available
We also considered Platz.ObjectBuilder tool that can save lots of time for defining business objects and mapping them to LINQ query results. Although the Object Builder doesn’t support complex queries at the moment, we demonstrated a concept on how visual tool output can be consumed by the t4 template to produce code that doesn’t require maintenance: any time you need to change something you simply modify the query and regenerate code.
Project Platz.SqlForms is open-source and it is being developed by the Pro Coders team.
You can find all the detailed information on Github.
To submit a bug or feature request, use this link:
Issues · ProCodersPtyLtd/MasterDetailsDataEntry (github.com)
5.1 What’s Next
My next article will be about embedded database designer:
Microsoft Blazor Open-source Platz.SqlForms - using Schema Builder to design and maintain SQL Server database
Appendix
Setup Demo Database
You can read how to setup the Entity Framework model first database in detail here:
Tutorial: Get started with EF Core in an ASP.NET MVC web app | Microsoft Docs.
SchoolContext
We create a folder “Model” in “DemoSqlForms.Database” project and add the SchoolContext.cs file.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
using System.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.Database.Model
{
public class SchoolContext : DbContext
{
public SchoolContext()
{
}
public SchoolContext(DbContextOptions<SchoolContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
if (!optionsBuilder.IsConfigured)
{
IConfigurationRoot configuration =
new ConfigurationBuilder().AddJsonFile
("appsettings.json", optional: false).Build();
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer
(configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"));
}
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Enrollment>(entity =>
{
entity.HasOne(d => d.Course)
.WithMany(p => p.Enrollments)
.HasForeignKey(d => d.CourseID)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Restrict)
.HasConstraintName("FK_Enrollment_Course");
entity.HasOne(d => d.Student)
.WithMany(p => p.Enrollments)
.HasForeignKey(d => d.StudentID)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Restrict)
.HasConstraintName("FK_Enrollment_Student");
});
}
public DbSet<Course> Course { get; set; }
public DbSet<Enrollment> Enrollment { get; set; }
public DbSet<Student> Student { get; set; }
}
public class Course
{
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.None)]
public int CourseID { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public int Credits { get; set; }
public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; }
}
public enum Grade
{
A, B, C, D, F
}
public class Enrollment
{
public int EnrollmentID { get; set; }
public int CourseID { get; set; }
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public Grade? Grade { get; set; }
public Course Course { get; set; }
public Student Student { get; set; }
}
public class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string FirstMidName { get; set; }
public DateTime EnrollmentDate { get; set; }
public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; }
}
}
I will briefly mention that this file contains Entity Framework DbContext and Entities of our demo database. SchoolContext reads the connection string from “appsettings.json” which we will add to the “DemoSqlForms.App” project.
The entities will look like:

DbInitializer
To initialize our database with test data, we add DbInitializer.cs file.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.Database.Model
{
public static class DbInitializer
{
public static void Initialize(SchoolContext context)
{
context.Database.EnsureCreated();
if (context.Student.Any())
{
return;
}
var students = new Student[]
{
new Student{FirstMidName="Carson",LastName="Alexander",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2005-09-01")},
new Student{FirstMidName="Meredith",LastName="Alonso",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")},
new Student{FirstMidName="Arturo",LastName="Anand",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2003-09-01")},
new Student{FirstMidName="Gytis",LastName="Barzdukas",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")},
new Student{FirstMidName="Yan",LastName="Li",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")},
new Student{FirstMidName="Peggy",LastName="Justice",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2001-09-01")},
new Student{FirstMidName="Laura",LastName="Norman",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2003-09-01")},
new Student{FirstMidName="Nino",LastName="Olivetto",
EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2005-09-01")}
};
foreach (Student s in students)
{
context.Student.Add(s);
}
context.SaveChanges();
var courses = new Course[]
{
new Course{CourseID=1050,Title="Chemistry",Credits=3},
new Course{CourseID=4022,Title="Microeconomics",Credits=3},
new Course{CourseID=4041,Title="Macroeconomics",Credits=3},
new Course{CourseID=1045,Title="Calculus",Credits=4},
new Course{CourseID=3141,Title="Trigonometry",Credits=4},
new Course{CourseID=2021,Title="Composition",Credits=3},
new Course{CourseID=2042,Title="Literature",Credits=4}
};
foreach (Course c in courses)
{
context.Course.Add(c);
}
context.SaveChanges();
var enrollments = new Enrollment[]
{
new Enrollment{StudentID=1,CourseID=1050,Grade=Grade.A},
new Enrollment{StudentID=1,CourseID=4022,Grade=Grade.C},
new Enrollment{StudentID=1,CourseID=4041,Grade=Grade.B},
new Enrollment{StudentID=2,CourseID=1045,Grade=Grade.B},
new Enrollment{StudentID=2,CourseID=3141,Grade=Grade.F},
new Enrollment{StudentID=2,CourseID=2021,Grade=Grade.F},
new Enrollment{StudentID=3,CourseID=1050},
new Enrollment{StudentID=4,CourseID=1050},
new Enrollment{StudentID=4,CourseID=4022,Grade=Grade.F},
new Enrollment{StudentID=5,CourseID=4041,Grade=Grade.C},
new Enrollment{StudentID=6,CourseID=1045},
new Enrollment{StudentID=7,CourseID=3141,Grade=Grade.A},
};
foreach (Enrollment e in enrollments)
{
context.Enrollment.Add(e);
}
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
Now we need to make changes to the “DemoSqlForms.App” project.
Connection String
Add the connection string to “appsettings.json”, the file will look like this:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;
Database=DemoSqlForms1;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
The connection string specifies the SQL Server LocalDB. LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express Database Engine and is intended for app development, not production use. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB creates .mdf DB files in the C:/Users/<user> directory.
Program.cs
In the file Program.cs, we remove the line:
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
and add create database logic, the code will look like:
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = CreateHostBuilder(args).Build();
CreateDbIfNotExists(host);
host.Run();
}
private static void CreateDbIfNotExists(IHost host)
{
using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
try
{
var context = services.GetRequiredService<SchoolContext>();
DbInitializer.Initialize(context);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
var logger = services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>();
logger.LogError(ex, "An error occurred creating the DB.");
}
}
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});
}
}
Method CreateDbIfNotExists simply executes DbInitializer that will create the database on the first run and populate test data.
Startup.cs
Here in the ConfigureServices method, we need to add DbContext initialization logic:
services.AddDbContext<SchoolContext>
(options => options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
services.AddDatabaseDeveloperPageExceptionFilter();
we also added Platz.SqlForms initialization logic already:
services.AddPlatzSqlForms();
The code will look like this:
using DemoSqlForms.Database.Model;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.HttpsPolicy;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Platz.SqlForms;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoSqlForms.App
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
services.AddServerSideBlazor();
services.AddDbContext<SchoolContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer
(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
services.AddDatabaseDeveloperPageExceptionFilter();
services.AddPlatzSqlForms();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapBlazorHub();
endpoints.MapFallbackToPage("/_Host");
});
}
}
}
History
- 11th January, 2021: Initial version
