Getting paid is one of the most critical functions in any business, and digital invoices are becoming standard practice. With this in mind, web application developers are often tasked with generating and sending PDF invoices programmatically.
Whether you’re automating the invoice generation and notification process or building a GUI that allows your team to proactively remind clients about outstanding invoices, the first technical hurdle you’ll face is generating a PDF invoice. While you could write a custom PDF generation script, that’s a huge undertaking. Web-based services are convenient, but if you have confidentiality agreements with your clients, sending data to a third-party service over the internet might be problematic.
Fortunately, Foxit’s PDF tools allow you to quickly and securely generate PDF files. Using their HTML to PDF converter, you can make any HTML document - including invoices - into a PDF file that you can attach to an email or allow clients to download from your web application.
In this tutorial, you’ll see how to create a NodeJS application that uses the Foxit PDF SDK to generate PDF invoices from HTML invoices in a web app. Once created, you’ll use Nodemailer to send the invoice via SMTP to the client’s email address. You can follow each step below or [download the finished codebase on GitHub).
Visit the Foxit PDF SDK Web Demo and see for yourself, by exploring the configurations and features.
Building a Web Application to Create and Send PDF Invoices
In this tutorial, you’ll create an internal tool to help your billing department follow up on unpaid invoices. You’ll create a page that lists all the outstanding invoices and a page to preview each of them. Users will be able to click a link to send an email reminder to each client with the invoice attached.
You’ll use the Express web framework, Pure CSS for styling, and Nodemailer to send emails.
Prerequisites
Creating a New Express App
To create a new boilerplate Express web application, use the app generator:
npx express-generator --git --view=hbs
This will create a web app with a .gitignore file and Handlebars template files.
Next, add the Nodemailer npm package and install Express’ dependencies:
npm i nodemailer && npm i
The default application generated by Express comes with two route files: /routes/index.js and /routes/users.js. Remove the users.js route and create a new route file called invoices.js. Add this new route to your app.js file and remove the usersRoute:
...
var indexRouter = require('./routes/index');
var invoicesRouter = require('./routes/invoices');
var app = express();
...
app.use('/', indexRouter);
app.use('/invoices', invoicesRouter);
...
The invoices router is where you’ll do the bulk of the work in this application.
Before you create the route, you’ll need some data. In a real application, you’ll likely connect to a database, but for demonstration purposes, you will add your invoice data to a JSON file.
Create a new file at /data/invoices.json and add the following:
[
{
"id": "47427759-9362-4f8e-bfe4-2d3733534e83",
"customer": "Bins and Sons",
"contact_name": "Verne McKim",
"contact_email": "vmckim0@example.com",
"address": "3 Burning Wood Street",
"city_state": "Memphis, TN 38118",
"plan_id": "41595-5514",
"plan_name": "Starter",
"subtotal": 499.99,
"fee": 50.00,
"total": 549.99
},
{
"id": "1afdd2fa-6353-437c-a923-e43baac506f4",
"customer": "Koepp Group",
"contact_name": "Junia Pretious",
"contact_email": "jpretious1@example.com",
"address": "7170 Fairfield Hill",
"city_state": "Los Angeles, CA 90026",
"plan_id": "43419-355",
"plan_name": "Professional",
"amount": 999.99,
"fee": 50.00,
"total": 1049.99
},
{
"id": "59c216f8-7471-4ec2-a527-ab3641dc49aa",
"customer": "Lynch-Bednar",
"contact_name": "Evelin Stollenberg",
"contact_email": "estollenberg2@example.com",
"address": "9951 Erie Place",
"city_state": "Chicago, IL 60605",
"plan_id": "63323-714",
"plan_name": "Starter",
"amount": 499.99,
"fee": 50.00,
"total": 549.99
}
]
These three invoices contain customer, plan, and billing data that will help you generate an invoice in the next section.
Creating the Invoices Routes
The routes/invoices.js file will create three new routes in your application:
- /invoices - A list of all the invoices from the flat data file above.
- /invoices/:id - An invoice preview so users can see what the invoice will look like before sending it to the client.
- /invoices/:id/email - An endpoint that generates and sends the PDF invoice to the contact email on file.
The last route will be addressed later, but you can start by adding the first two routes. Open the invoices.js file and add the following:
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const invoices = require('../data/invoices.json');
const { exec } = require('child_process');
const nodemailer = require('nodemailer');
router.get('/', function(req, res) {
res.render('invoice-list', {
invoices: invoices,
success: req.query['success'],
error: req.query['error'],
});
});
router.get('/:id', function(req, res) {
const invoice = invoices.find(invoice => invoice.id === req.params['id']);
if (!invoice) {
res.redirect('/invoices');
}
const date = new Date().toLocaleDateString("en", {
year:"numeric",
day:"2-digit",
month:"2-digit",
});
res.render('invoice-single', { invoice, date });
});
router.get('/:id/email', function(req, res) {
});
module.exports = router;
Your application is almost ready to test, but first, you need to create the two view files.
Adding Views and Styles
Express separates logic and presentation into routes/ and views/. Add two new files to the views/ directory: invoice-list.js and invoice-single.js.
Add the following to your invoice-list.js file:
<h1><a href="/invoices">Unpaid Invoices</a></h1>
{{#if success}}
<p class="success"><strong>Success!</strong> The invoice has been sent to the client.</p>
{{/if}}
{{#if error}}
<p class="error"><strong>Whoops!</strong> Something went wrong and your invoice could not be sent.</p>
{{/if}}
{{#each invoices}}
<h3>{{this.customer}}</h3>
<p>ID: {{this.id}} <br/>
<a href="/invoices/{{this.id}}">View</a> | <a href="/invoices/{{this.id}}/email">Email Reminder</a>
</p>
{{/each}}
Open the invoice-single.js file and add this:
<div class="pure-g">
<div class="pure-u-1-2">
<h1>Invoice</h1>
</div>
<div class="pure-u-1-2" style="text-align: right;">
<p class="muted">Issued on {{ date }}</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="pure-g">
<div class="pure-u-1-2">
<h3>Provider</h3>
<p>
<strong>Tiller, Inc.</strong><br/>
1255 S. Clark<br/>
Chicago, IL 60608
</p>
</div>
<div class="pure-u-1-2" style="text-align: right;">
<h3>Billed to</h3>
<p>
<strong>{{invoice.customer}}</strong><br/>
{{invoice.contact_name}}<br/>
{{invoice.address}}<br/>
{{invoice.city_state}}
</p>
</div>
</div>
<table class="pure-table pure-table-horizontal">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Plan Name</th>
<th class="text-right">Amount</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>{{invoice.plan_id}}</td>
<td>{{invoice.plan_name}}</td>
<td class="text-right">${{invoice.subtotal}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td class="text-right">Subtotal:</td>
<td class="text-right">${{invoice.subtotal}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td class="text-right">Taxes and Fees:</td>
<td class="text-right">${{invoice.fee}}</td>
</tr>
<tr class="bold">
<td></td>
<td class="text-right">Total:</td>
<td class="text-right">${{invoice.total}}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="footer">
<p>Please make checks payable to <strong>Tiller, Inc</strong>. Invoices are due 30 days after date issued.</p>
<p>Thank you for your business!</p>
</div>
Next, you’ll need to add styles to your app’s stylesheet and load the Pure CSS module to make it look nice. Open the views/layout.hbs file and replace it with the following to import Pure and create a single column grid layout:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>{{title}}</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://unpkg.com/purecss@2.0.3/build/pure-min.css" integrity="sha384-cg6SkqEOCV1NbJoCu11+bm0NvBRc8IYLRGXkmNrqUBfTjmMYwNKPWBTIKyw9mHNJ" crossorigin="anonymous">
<link rel='stylesheet' href='/stylesheets/style.css' />
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="pure-g">
<div class="pure-u-1">
{{{body}}}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Open your application’s public/style.css file and add the following:
body {
background-color: #f7f7f7;
color: #333333;
}
a {
color: #156d6a;
}
h1 a,
h2 a,
h3 a {
text-decoration: none;
}
table {
width: 100%;
}
.container {
background-color: #ffffff;
max-width: 700px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 30px;
}
.muted {
color: #999999;
}
.bold {
font-weight: bold;
}
.text-right {
text-align: right;
}
.footer p {
margin-top: 30px;
}
.success {
background-color: #c0f5f3;
color: #0d928d;
padding: 10px;
}
.error {
background-color: #f5c0c0;
color: #792525;
padding: 10px;
}
While you don’t have to add styles, it will make your invoices look more professional as Foxit captures all the styling in your HTML document when it generates PDFs.
Try our SDK for Web Demo in your browser, no download or login required.
At this point, you are ready to test your application. From the command line, run npm start and open your web browser to localhost:3000/invoices. You should see a list of invoices like this:
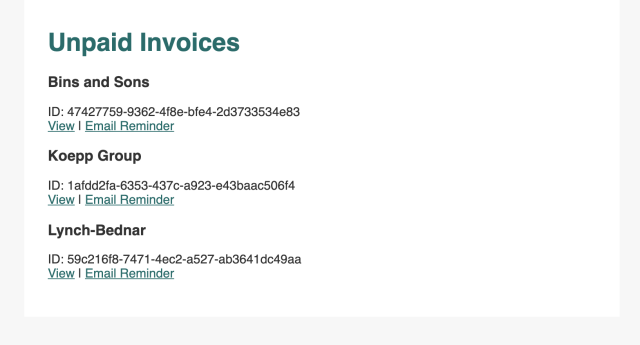
Click "View" to preview each invoice:
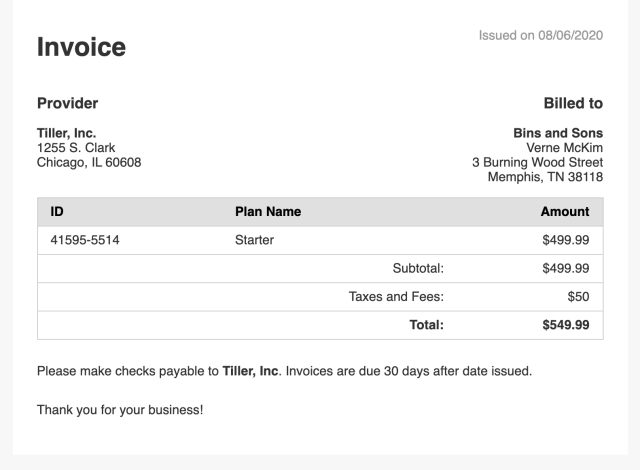
In the last two steps, you’ll use the Foxit HTML to PDF tool to generate PDF invoices before you send attach them to an email using Nodemailer.
Generating PDFs with Foxit
You can use Foxit’s SDK for a wide variety of PDF creation and manipulation operations, but one common use case is generating a PDF file from an HTML document or URL. The process of downloading and compiling the HTML to PDF executable is documented here. Once you’ve successfully run the demo from your command line, you can proceed.
Node’s child_process library includes a function called exec() that allows you to execute a command-line function. This is a convenient method for running Foxit executables written in C++. To run the HTML to PDF executable, update your /:id/email route by replacing it with the following:
...
router.get('/:id/email', function(req, res) {
const htmlToPdfPath = '/path/to/foxit/html2pdf';
const outputFolder = __dirname + '/../invoices/';
const invoice = invoices.find(invoice => invoice.id === req.params['id']);
if (!invoice) {
res.redirect('/invoices?error=1');
}
exec(
${htmlToPdfPath} -h localhost:3000/invoices/${req.params['id']} -o ${outputFolder}${req.params['id']}.pdf,
(err, stdout, stderr) => {
if (err || stderr) {
console.error(err, stderr);
res.redirect('/invoices?error=1');
} else {
console.log(PDF generated and saved to ${outputFolder}${req.params['id']}.pdf);
res.redirect('/invoices?success=1');
}
});
});
Before you run this code, be sure to update the htmlToPdfPath to point to your htmltopdf executable.
Go back to your list of invoices and click "Email Reminder" on any of the invoices, the Node app will call the htmltopdf executable. The executable will, in turn, convert your invoice from the HTML document served by Express to a PDF file. You can find the PDF file in your web application’s invoices/ directory.
Now that you can generate PDF invoices, the last step is to send these invoices to your customers.
Sending Emails with Nodemailer
Nodemailer provides a convenient interface to access many email transport layers. SMTP is one of the most prevalent, but you could also use Amazon SES or your server’s sendmail command.
To test Nodemailer, you can use the [stream transport’s JSON option, which lets you log the message to your console. To set up your message and send it with Nodemailer, add the following just below the "PDF generated and saved to…" console.log statement in your /invoices/:id/email route:
...
const message = {
from: 'accounting@example.com',
to: invoice.contact_email,
subject: 'Reminder: Your Invoice from Tiller, Inc. is Due',
html: <p>Hey ${invoice.contact_name},</p><p>I just wanted to remind you that your invoice for last month's services is now due. I've attached it here for your convenience.</p><p>Thanks for your business!</p>,
attachments: [
{
filename: 'invoice.pdf',
path: ${outputFolder}${req.params['id']}.pdf,
}
]
};
nodemailer
.createTransport({jsonTransport: true})
.sendMail(message, function (err, info) {
if (err) {
res.redirect('/invoices?error=1');
} else {
console.log(info.message);
res.redirect('/invoices?success=1');
}
});
...
Refresh your Node application and click "Email Reminder" on any of the invoices. This time, you’ll see the entire email data object as JSON in your console:
{
"from": {
"address": "accounting@example.com",
"name": ""
},
"to": [
{
"address": "jpretious1@example.com",
"name": ""
}
],
"subject": "Reminder: Your Invoice from Tiller, Inc. is Due",
"html": "<p>Hey Junia Pretious,</p><p>I just wanted to remind you that your invoice for last month's services is now due. I've attached it here for your convenience.</p><p>Thanks for your business!</p>",
"attachments": [
{
"content": "JVBERi0xLjMKJcTl8uXrp...",
"filename": "invoice.pdf",
"contentType": "application/pdf",
"encoding": "base64"
}
],
"headers": {},
"messageId": "<65ea9109-8d5a-295e-9295-8e98e1b2c667@example.com>"
}
The attachments.content string is your encoded PDF file, so I’ve truncated it above for brevity’s sake.
To test the email with a real SMTP server), you can use Mailtrap. Assuming you have an account, replace the createTransport({jsonTransport: true}) call with the following:
createTransport({
host: "smtp.mailtrap.io",
port: 2525,
auth: {
user: "<YOUR_MAILTRAP_USERID>",
pass: "<YOUR_MAILTRAP_PASS>"
}
})
Now, when you email the invoice, Mailtrap will capture the output and let you download the PDF attachment. In your Mailtrap account, you should see an email like the one below:
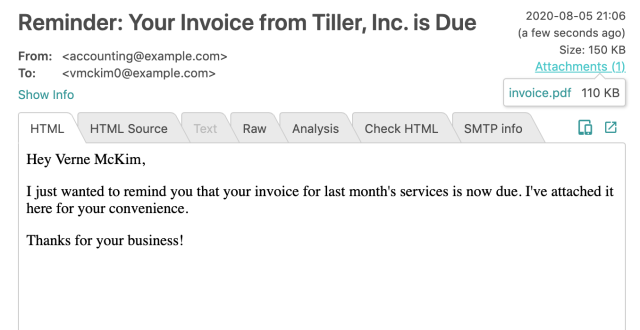
Once you’re ready to deploy your app to production, replace the Mailtrap SMTP credentials with a production mail server. Your web application can now generate and send PDF invoices to clients whenever your billing team wants to follow up.
Conclusion
If you need to present invoices online and send them as PDFs, the above application should give you a useful starting point. Foxit’s HTML to PDF tool is a convenient and performant way to generate PDFs, but it’s not the only solution they provide.
Try Foxit PDF SDK’s advanced technology on your chosen platform(s): Web, Windows, Android, iOS, Linux, UWP, or Mac. Sign up for a free thirty-day trial today.
Foxit is the clear option when you need to build PDF support into your web, mobile, or desktop applications.
