The SQL DATEDIFF function calculates and returns the difference between two date values. The value returned is an integer. You can use DATEDIFF to calculate a wide variety of calendar calculation by varying the datepart parameter.
Description
Use SQL DATEDIFF to return the difference between the two dates based on a specified date part. The DATDIFF function returns this difference as an integer value.
The DATEDIFF function returnes the number years, months, weeks, or days between two dates.
The general form for the DATEDIFF is
DATEDIFF(date part, start value, end value)
Where date part corresponds to a list of predefined date parts such as year, month, weeks, and days.
The difference is calculated between start value and end value.
This function may seem a bit complicated, but it is really worth understanding as it has many practical uses in SQL.
You can use it to calculate the number of days a bill is past due, or the number of days or weeks between two dates.
Consider this example:
The HR Vice President wants to award all employees with a years of service award. She would like you to product a report of all employees with more than ten years of service.
To do this we’ll use the DATEDIFF report to both display number of years of service and to also to filter out those with less than ten years of service.
Here is the SQL
SELECT NationalIDNumber,
HireDate,
DATEDIFF(year, HireDate, GETDATE()) YearsOfService
FROM HumanResources.Employee
WHERE DATEDIFF(year, HireDate, GETDATE()) >= 10
ORDER BY YearsOfService DESC
Whose results are
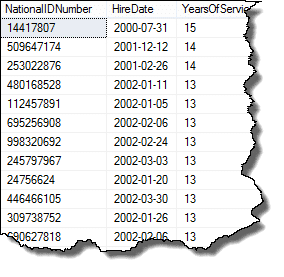
DATEDIFF Results
Syntax
DATADIFF ( datepart, startdate, enddate ).
SQL DATEDIFF Usage Notes
- The datepart as the first argument indicates the value type the SQL
DATEDIFF function returns as a difference between the start date and the end date. The list of valid values for the date part argument includes a year, month, day, etc. These values can also be an abbreviation like yy for a year and mm for a month. - Start date and end date as the final two arguments can be of date, datetime, datetimeoffset, datetime2, samlldatetime, and time data type.
- The return type of the
DATEDIFF function is an int and indicates the difference between the start date and end date. - If the date part is a date, then the SQL
DATEDIFF function sets the time part of the date to 00:00:00. When specified as a time, then the DATEDIFF function sets the missing date part to 1900-01-01. - If any of the start date and end date has more time parts than the other,
DATADIFF sets the missing parts of smaller value to zero. - The SQL
DATADIFF function does not support the YDM format when date values are passed as strings because it casts the literal strings to the datetime2 data type. Therefore, date values must be first converted to datetime or smalldatetime data types instead of passing as string values.
SQL DATEDIFF Examples
We will use the Adventureworks2019 database for the following queries.
SELECT DATEDIFF(MINUTE, '2021/05/01 06:00', '2021/05/01 11:14') AS DateDiffResult;
The following example is a simple SQL DATEDIFF query to calculate the difference between two date values in terms of minutes.
In the next example, we calculate the days left in the order delivery by applying the SQL DATEDIFF function to the OrderDate and DueDate columns of the SalesOrderHeader table.
SELECT SalesOrderID, OrderDate, DueDate, DATEDIFF(day, OrderDate, DueDate) DaysLeft
FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader
Next, let’s apply the SQL DATEDIFF function with an aggregate function. For every job title, the query calculates the maximum number of years an employee has worked.
SELECT JobTitle, DATEDIFF(year, MAX(HireDate), SYSDATETIME()) AS YearsEmployed
FROM HumanResources.Employee
GROUP BY JobTitle
The above query displays the job title and the maximum number of years an employee has worked under this job title. MAX function selects the maximum date value against each job title as indicated by the Group By clause. SYSDATETIME returns the current time. Here, SQL DATEDIFF calculates the difference between the hired date and the current time.
