In this article, you will see a desktop application which creates many objects and searches for text in them.
Recently, I was looking for a storage system for my program. This is a desktop application that creates many objects and searches for text in them. So I thought: "Why don't I try something new." Instead of an SQL database, I could use some kind of document database. But I didn't want to have a separate server, I wanted this database to work with a simple file. Searching the Internet for this kind of databases for .NET applications quickly led me to LiteDB. And here I want to share my experience with this database.
Inheritance
My program works as follows. I want to store objects like this:
internal class Item
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public List<Field> Fields { get; set; } = new List<Field>();
}
But the Field class is abstract. And it has many descendants:
internal abstract class Field
{
}
internal sealed class TextField : Field
{
public string Text { get; set; }
}
internal sealed class PasswordField : Field
{
public string Password { get; set; }
}
internal sealed class DescriptionField : Field
{
public string Description { get; set; }
}
...
When working with SQL databases, I had to configure the storage of various descendants of the Field class. I thought that with LiteDB, I would have to write my own BSON serialization mechanism, LiteDB provides such an opportunity. But I was pleasantly surprised. Nothing is required of me. Serialization and deserialization of various types are already implemented. You just create the necessary objects:
var items = new Item[]
{
new Item
{
Title = "item1",
Description = "description1",
Fields =
{
new TextField
{
Text = "text1"
},
new PasswordField
{
Password = "123"
}
}
},
new Item
{
Title = "item2",
Description = "description2",
Fields =
{
new TextField
{
Text = "text2"
},
new DescriptionField
{
Description = "description2"
}
}
}
};
... and insert them into the database:
using (var db = new LiteDatabase(connectionString))
{
var collection = db.GetCollection<Item>();
collection.InsertBulk(items);
}
That's all. LiteDB has LiteDB.Studio utility that allows you to view the contents of your database. Let's see how our objects are stored:
{
"_id": {"$oid": "62bf12ce12a00b0f966e9afa"},
"Title": "item1",
"Description": "description1",
"Fields":
[
{
"_type": "LiteDBSearching.TextField, LiteDBSearching",
"Text": "text1"
},
{
"_type": "LiteDBSearching.PasswordField, LiteDBSearching",
"Password": "123"
}
]
}
It looks like each object has a _type property that allows correct deserialization from the database.
Well, we have saved our objects. Let's move on to reading.
Search of Text
As I said before, I need to search for Item objects in which the Title and Description properties and the properties of their fields (the Fields property) contain some text.
There is nothing complicated in searching inside the Title and Description properties. The documentation is pretty clear:
var items = collection.Query()
.Where(i => i.Title.Contains("1") || i.Description.Contains("1"))
.ToArray();
But there is a problem with searching by fields. You see, the abstract class Field does not contain any properties. That's why I can't refer to them. Fortunately, LiteDB allows you to use string query syntax:
var items = collection.Query()
.Where("$.Title LIKE '%1%' OR $.Description LIKE '%1%'")
.ToArray();
So, how can we search inside fields using this syntax? The documentation gives a hint that the query should look something like this:
$.Title LIKE '%1%' OR $.Description LIKE '%1%' OR $.Fields[@.Text]
LIKE '%1%' OR $.Fields[@.Description] LIKE '%1%' OR $.Fields[@.Password] LIKE '%1%'
But this leads to an error:
Left expression `$.Fields[@.Text]` returns more than one result.
Try use ANY or ALL before operant.
And yes, using ANY function solves the problem:
$.Title LIKE '%1%' OR $.Description LIKE '%1%' OR ANY($.Fields[@.Text LIKE '%1%'])
OR ANY($.Fields[@.Description LIKE '%1%']) OR ANY($.Fields[@.Password LIKE '%1%'])
But I want to make a couple of comments about this expression. First of all, it may seem that we can use expressions like this:
ANY($.Fields[@.Text LIKE '%1%'])
But this is not the case. If you try to query elements using this expression, you will get the following error:
Expression 'ANY($.Fields[@.Text LIKE "%1%"])' are not supported as predicate expression.
Strange, isn't it? It turns out that you should write like this:
ANY($.Fields[@.Text LIKE '%1%']) = true
I immediately recall 1 and 0 in SQL Server predicates. I don't know why they implemented it this way.
Secondly, I was confused by the phrase Try use ANY or ALL before operant. For me, this does not correspond to a function call. It turns out that LiteDB supports the following syntax:
$.Fields[*].Text ANY LIKE '%1%'
Unfortunately, this is not described in the documentation. I came across this in the source code of tests for LiteDB on Github. This syntax works fine as a predicate without any comparison with true.
Finally, we can rewrite your query expression as follows:
$.Title LIKE '%1%' OR $.Description LIKE '%1%' OR ($.Fields[*].Text ANY LIKE '%1%')
OR ($.Fields[*].Description ANY LIKE '%1%') OR ($.Fields[*].Password ANY LIKE '%1%')
There are a couple more things that bother me here. Firstly, for each new field type, I will have to rewrite this expression if I use a new property name. Is there anything we can do about it? Well, we can.
LiteDB supports the BsonField attribute, which specifies the name of the database field in which this property is stored. It is used as follows:
internal sealed class TextField : Field
{
[BsonField("TextField")]
public string Text { get; set; }
}
internal sealed class PasswordField : Field
{
[BsonField("TextField")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
internal sealed class DescriptionField : Field
{
[BsonField("TextField")]
public string Description { get; set; }
}
Now we can write one query expression for any Field objects:
$.Title LIKE '%1%' OR $.Description LIKE '%1%' OR $.Fields[*].TextField ANY LIKE '%1%'
When I add a new descendant of the Field class, I can simply mark its property with the [BsonField("TextField")] attribute. Then I won't need to change the expression of my query.
Unfortunately, this method doesn't quite solve all our problems. The fact is that the descendant of the Field can have an arbitrary number of properties in which I need to search for text. This means that I may not be able to save them all in the existing database fields.
That's why I will still use the following form of the expression:
$.Title LIKE '%1%' OR $.Description LIKE '%1%' OR ($.Fields[*].Text ANY LIKE '%1%')
OR ($.Fields[*].Description ANY LIKE '%1%') OR ($.Fields[*].Password ANY LIKE '%1%')
We have another problem. I have used my search string %1% several times in the expression. There is also an SQL injection attack (although I'm not sure I can use the word SQL here). In short, I'm talking about using parameters in my queries. And the LiteDB API allows us to use them:
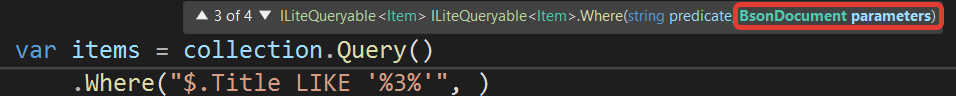
But what exactly should we do? Unfortunately, the documentation failed me again. I had to go to the source code of the LiteDB tests and look there how I should use the parameters:
var items = collection.Query()
.Where("$.Title LIKE @0 OR $.Description LIKE @0 OR ($.Fields[*].Text ANY LIKE @0)
OR ($.Fields[*].Description ANY LIKE @0) OR ($.Fields[*].Password ANY LIKE @0)", "%1%")
.ToArray();
Well, the search is done. But how fast is it?
Indexes
LiteDB supports indexes. Of course, my application doesn't store a really large amount of data, so it's not critically important. However, it would be great to use indexes and execute queries as fast as possible.
First of all, we need to understand whether this query uses some kind of index or not. For this purpose, LiteDB has the EXPLAIN command. In LiteDB.Studio, I execute my query this way:
EXPLAIN
SELECT $ FROM Item
WHERE $.Title LIKE '%1%'
OR $.Description LIKE '%1%'
OR ($.Fields[*].Text ANY LIKE '%1%')
OR ($.Fields[*].Description ANY LIKE '%1%')
OR ($.Fields[*].Password ANY LIKE '%1%')
The result contains information about the index that was used:
"index":
{
"name": "_id",
"expr": "$._id",
"order": 1,
"mode": "FULL INDEX SCAN(_id)",
"cost": 100
},
As you can see, we have to go through all the data now. I would like to achieve a better result.
The documentation explicitly says that it is possible to create an index based on an array type property. In this case, I can search for any elements in this array. For example, I can create an index to search inside the Text properties of my fields:
collection.EnsureIndex("TextIndex", "$.Fields[*].Text");
Now we can use this index in our queries:
var items = collection.Query()
.Where("$.Fields[*].Text ANY LIKE @0", "%1%")
.ToArray();
The EXPLAIN command in LiteDB.Studio shows that this query really uses the index we created:
"index":
{
"name": "TextIndex",
"expr": "MAP($.Fields[*]=>@.Text)",
"order": 1,
"mode": "FULL INDEX SCAN(TextIndex LIKE \"%1%\")",
"cost": 100
},
But how can we combine all our properties in one index? Here, we can use the CONCAT command. It combines several values into one array. Here's what creating a full index looks like:
collection.EnsureIndex("ItemsIndex", @"CONCAT($.Title,
CONCAT($.Description,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Text,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Password,
$.Fields[*].Description
)
)
)
)");
To use it, we have to rewrite the expression of our query:
var items = collection.Query()
.Where(
@"CONCAT($.Title,
CONCAT($.Description,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Text,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Password,
$.Fields[*].Description
)
)
)
) ANY LIKE @0",
"%1%")
.ToArray();
Now our search really uses the index:
"index":
{
"name": "ItemsIndex",
"expr": "CONCAT($.Title,CONCAT($.Description,CONCAT(MAP($.Fields[*]=>@.Text),
CONCAT(MAP($.Fields[*]=>@.Password),MAP($.Fields[*]=>@.Description)))))",
"order": 1,
"mode": "FULL INDEX SCAN(ItemsIndex LIKE \"%3%\")",
"cost": 100
},
Unfortunately, the LIKE operator still results in a FULL INDEX SCAN. We can only hope that the index gives some advantage. But wait. Why should we only hope when we can measure it? After all, we have BenchmarkDotNet.
I wrote the following code for performance testing:
[SimpleJob(RuntimeMoniker.Net60)]
public class LiteDBSearchComparison
{
private LiteDatabase _database;
private ILiteCollection<Item> _collection;
[GlobalSetup]
public void Setup()
{
if (File.Exists("compare.dat"))
File.Delete("compare.dat");
_database = new LiteDatabase("Filename=compare.dat");
_collection = _database.GetCollection<Item>();
_collection.EnsureIndex("ItemIndex", @"CONCAT($.Title,
CONCAT($.Description,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Text,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Password,
$.Fields[*].Description
)
)
)
)");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
var item = new Item
{
Title = "t",
Description = "d",
Fields =
{
new TextField { Text = "te" },
new PasswordField { Password = "p" },
new DescriptionField { Description = "de" }
}
};
_collection.Insert(item);
}
}
[GlobalCleanup]
public void Cleanup()
{
_database.Dispose();
}
[Benchmark(Baseline = true)]
public void WithoutIndex()
{
_ = _collection.Query()
.Where("$.Title LIKE @0 OR $.Description LIKE @0 OR
($.Fields[*].Text ANY LIKE @0) OR ($.Fields[*].Description
ANY LIKE @0) OR ($.Fields[*].Password ANY LIKE @0)",
"%1%")
.ToArray();
}
[Benchmark]
public void WithIndex()
{
_ = _collection.Query()
.Where(@"CONCAT($.Title,
CONCAT($.Description,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Text,
CONCAT($.Fields[*].Password,
$.Fields[*].Description
)
)
)
) ANY LIKE @0",
"%1%")
.ToArray();
}
}
Here are the results:
| Method | Mean | Error | StdDev | Ratio |
WithoutIndex | 752.7 us | 14.71 us | 21.56 us | 1.00 |
WithIndex | 277.5 us | 4.30 us | 4.02 us | 0.37 |
As you can see, the index does provide a significant performance advantage.
Conclusion
That's all I wanted to say. Overall, I have a pretty good impression of LiteDB. I am ready to use it as a document storage for small projects. Unfortunately, the documentation, in my opinion, is not at the best level.
I hope this information will be useful to you. Good luck!
P.S. If you like this article, you can read more on my blog.
History
- 14th July, 2022: Initial version
