Background
"Tour of Heroes" is the official tutorial app of Angular 2+. The app contains some functional features and technical features which are common when building a real-world business application:
- A few screens presenting tables and nested data
- Data binding
- Navigation
- CRUD operations over a backend, and optionally through a generated client API
- Unit testing and integration testing
In this series of articles, I will demonstrate the programmer experiences of various frontend development platforms when building the same functional features: "Tour of Heroes", a fat client talking to a backend.
The frontend apps on Angular, Aurelia, React, Vue, Xamarin and MAUI are talking to the same ASP.NET (Core) backend through generated client APIs. To find the other articles in the same series, please search "Tour of Heroes" in my articles. And at the end of the series, some technical factors of programmer experiences will be discussed:
- Computing science
- Software engineering
- Learning curve
- Build size
- Runtime performance
- Debugging
Choosing a development platform involves a lot of non-technical factors which won't be discussed in this series.
References
Introduction
This article is focused on MAUI.
Development platforms:
- ASP.NET Core 8
- .NET Multi-platform App UI
Demo Repository
Checkout DemoCoreWeb in GitHub, and focus on the following areas:
ASP.NET Core Web API csproj provides only Web APIs.
This folder contains a MAUI application (Fonlow.Heroes.Maui.csproj) that reassembles the functionality of "Tour of Heroes".
Fonlow.Heroes.MauiFonlow.Heroes.ViewModelsFonlow.Heroes.ViewCoreWebApi.ClientApi
Remarks
DemoCoreWeb was established for testing NuGet packages of WebApiClientGen for .NET, and demonstrating how to use the libraries in real world projects.
Using the Code
Prerequisites
- Core3WebApi.csproj has NuGet package
Fonlow.WebApiClientGenCore imported. - Add CodeGenController.cs to Core3WebApi.csproj.
- Core3WebApi.csproj includes CodeGen.json. This is optional, just for the convenience of running some PowerShell script to generate client APIs.
- CreateWebApiClientApi3.ps1. This is optional. This script will launch the Web API on IIS Express and post the data in CodeGen.json.
Remarks
Depending on your CI/CD process, you may adjust item 3 and 4 above. For more details, please check:
Generate Client API
Run CreateWebApiClientApi3.ps1, the generated codes will be written to CoreWebApi.ClientApi.
Data Models and API Functions
namespace DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client
{
public class Hero : object
{
public long Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
Most data models used in the MAUI client app from the generated client API library.
public partial class Heroes
{
private System.Net.Http.HttpClient client;
private JsonSerializerSettings jsonSerializerSettings;
public Heroes(System.Net.Http.HttpClient client,
JsonSerializerSettings jsonSerializerSettings=null)
{
if (client == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("Null HttpClient.", "client");
if (client.BaseAddress == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException
("HttpClient has no BaseAddress", "client");
this.client = client;
this.jsonSerializerSettings = jsonSerializerSettings;
}
public async Task DeleteAsync(long id)
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes/"+id;
using (var httpRequestMessage =
new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Delete, requestUri))
{
var responseMessage = await client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage);
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
public async Task<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero[]> GetAsync()
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes";
using (var httpRequestMessage =
new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, requestUri))
{
var responseMessage = await client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage);
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
var stream = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync();
using (JsonReader jsonReader =
new JsonTextReader(new System.IO.StreamReader(stream)))
{
var serializer = new JsonSerializer();
return serializer.Deserialize<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero[]>
(jsonReader);
}
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
public async Task<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero> GetAsync(long id)
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes/"+id;
using (var httpRequestMessage = new HttpRequestMessage
(HttpMethod.Get, requestUri))
{
var responseMessage = await client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage);
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
var stream = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync();
using (JsonReader jsonReader = new JsonTextReader
(new System.IO.StreamReader(stream)))
{
var serializer = new JsonSerializer();
return serializer.Deserialize<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero>
(jsonReader);
}
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
public async Task<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero> PostAsync(string name)
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes?name="+
(name == null ? "" : Uri.EscapeDataString(name));
using (var httpRequestMessage =
new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Post, requestUri))
{
var responseMessage = await client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage);
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
var stream = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync();
using (JsonReader jsonReader = new JsonTextReader
(new System.IO.StreamReader(stream)))
{
var serializer = new JsonSerializer();
return serializer.Deserialize<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero>
(jsonReader);
}
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
public async Task<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero>
PostWithQueryAsync(string name)
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes/q?name="+
(name == null ? "" : Uri.EscapeDataString(name));
using (var httpRequestMessage = new HttpRequestMessage
(HttpMethod.Post, requestUri))
{
var responseMessage = await client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage);
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
var stream = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync();
using (JsonReader jsonReader = new JsonTextReader
(new System.IO.StreamReader(stream)))
{
var serializer = new JsonSerializer();
return serializer.Deserialize<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero>
(jsonReader);
}
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
public async Task<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero> PutAsync
(DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero hero)
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes";
using (var httpRequestMessage = new HttpRequestMessage
(HttpMethod.Put, requestUri))
{
using (var requestWriter = new System.IO.StringWriter())
{
var requestSerializer = JsonSerializer.Create(jsonSerializerSettings);
requestSerializer.Serialize(requestWriter, hero);
var content = new StringContent
(requestWriter.ToString(), System.Text.Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
httpRequestMessage.Content = content;
var responseMessage = await client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage);
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
var stream = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync();
using (JsonReader jsonReader =
new JsonTextReader(new System.IO.StreamReader(stream)))
{
var serializer = new JsonSerializer();
return serializer.Deserialize<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero>
(jsonReader);
}
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
}
public async Task<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero[]> SearchAsync(string name)
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes/search?name="+
(name == null ? "" : Uri.EscapeDataString(name));
using (var httpRequestMessage =
new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, requestUri))
{
var responseMessage = await client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage);
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
var stream = await responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync();
using (JsonReader jsonReader =
new JsonTextReader(new System.IO.StreamReader(stream)))
{
var serializer = new JsonSerializer();
return serializer.Deserialize<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero[]>
(jsonReader);
}
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
public DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero[] Search(string name)
{
var requestUri = "api/Heroes/search?name="+
(name == null ? "" : Uri.EscapeDataString(name));
using (var httpRequestMessage =
new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, requestUri))
{
var responseMessage = client.SendAsync(httpRequestMessage).Result;
try
{
responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCodeEx();
var stream = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStreamAsync().Result;
using (JsonReader jsonReader =
new JsonTextReader(new System.IO.StreamReader(stream)))
{
var serializer = new JsonSerializer();
return serializer.Deserialize<DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero[]>
(jsonReader);
}
}
finally
{
responseMessage.Dispose();
}
}
}
}
View Models
View Models are contained in Fonlow.Heroes.ViewModels.csproj.
Fonlow.HeroesVM.HeroesVM will be utilized by multiple views.
namespace Fonlow.Heroes.VM
{
public class HeroesVM : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public HeroesVM()
{
DeleteCommand = new Command<long>(DeleteHero);
SearchCommand = new Command<string>(Search);
}
public void Load(IEnumerable<Hero> items)
{
Items = new ObservableCollection<Hero>(items);
NotifyPropertyChanged("Items");
NotifyPropertyChanged("Count");
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
public ObservableCollection<Hero> Items { get; private set; }
public IEnumerable<Hero> Top4
{
get
{
if (Items == null)
{
return null;
}
return Items.Take(4);
}
}
Hero selected;
public Hero Selected
{
get { return selected; }
set
{
selected = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged("Selected");
NotifyPropertyChanged("AllowEdit");
}
}
public int Count
{
get
{
if (Items == null)
{
return 0;
}
return Items.Count;
}
}
public void NotifyPropertyChanged
([System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CallerMemberName] string propertyName = "")
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
public ICommand DeleteCommand { get; private set; }
public ICommand SearchCommand { get; private set; }
async void DeleteHero(long id)
{
var first = Items.FirstOrDefault(d => d.Id == id);
if (first != null)
{
if (first.Id == Selected?.Id)
{
Selected = null;
}
await HeroesFunctions.DeleteAsync(id);
Items.Remove(first);
NotifyPropertyChanged("Items");
NotifyPropertyChanged("Count");
}
}
public bool AllowEdit
{
get
{
return Selected != null;
}
}
async void Search(string keyword)
{
var r = await HeroesFunctions.SearchAsync(keyword);
Items = new ObservableCollection<Hero>(r);
NotifyPropertyChanged("Items");
NotifyPropertyChanged("Count");
}
}
}
Views
Editing
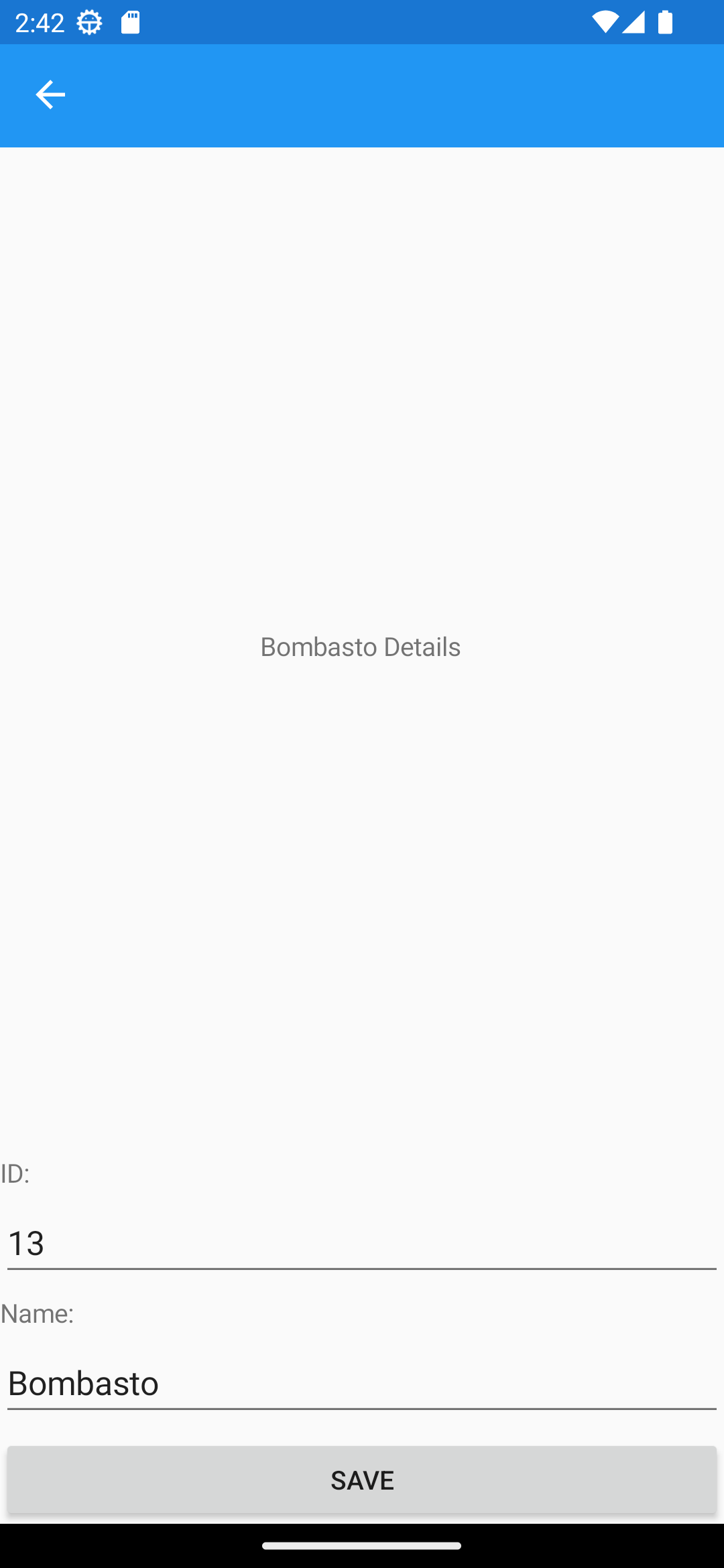
HeroDetailPage.xaml
="1.0"="utf-8"
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="Fonlow.Heroes.Views.HeroDetailPage">
<ContentPage.Content>
<StackLayout>
<Label Text="{Binding Name, StringFormat='{0} Details'}"
VerticalOptions="CenterAndExpand"
HorizontalOptions="CenterAndExpand" />
<Label Text="ID:"></Label>
<Entry Text="{Binding Id}" Placeholder="ID"></Entry>
<Label Text="Name:"></Label>
<Entry Text="{Binding Name}" Placeholder="Name"></Entry>
<Button Text="Save" Clicked="Save_Clicked"/>
</StackLayout>
</ContentPage.Content>
</ContentPage>
HeroDetailPage.xaml.cs (Codes Behind)
namespace Fonlow.Heroes.Views
{
[XamlCompilation(XamlCompilationOptions.Compile)]
public partial class HeroDetailPage : ContentPage
{
public HeroDetailPage(long heroId)
{
InitializeComponent();
BindingContext = VM.HeroesFunctions.LoadHero(heroId);
}
Hero Model
{
get
{
return BindingContext as Hero;
}
}
private async void Save_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
await VM.HeroesFunctions.SaveAsync(Model);
}
}
}
Heroes List
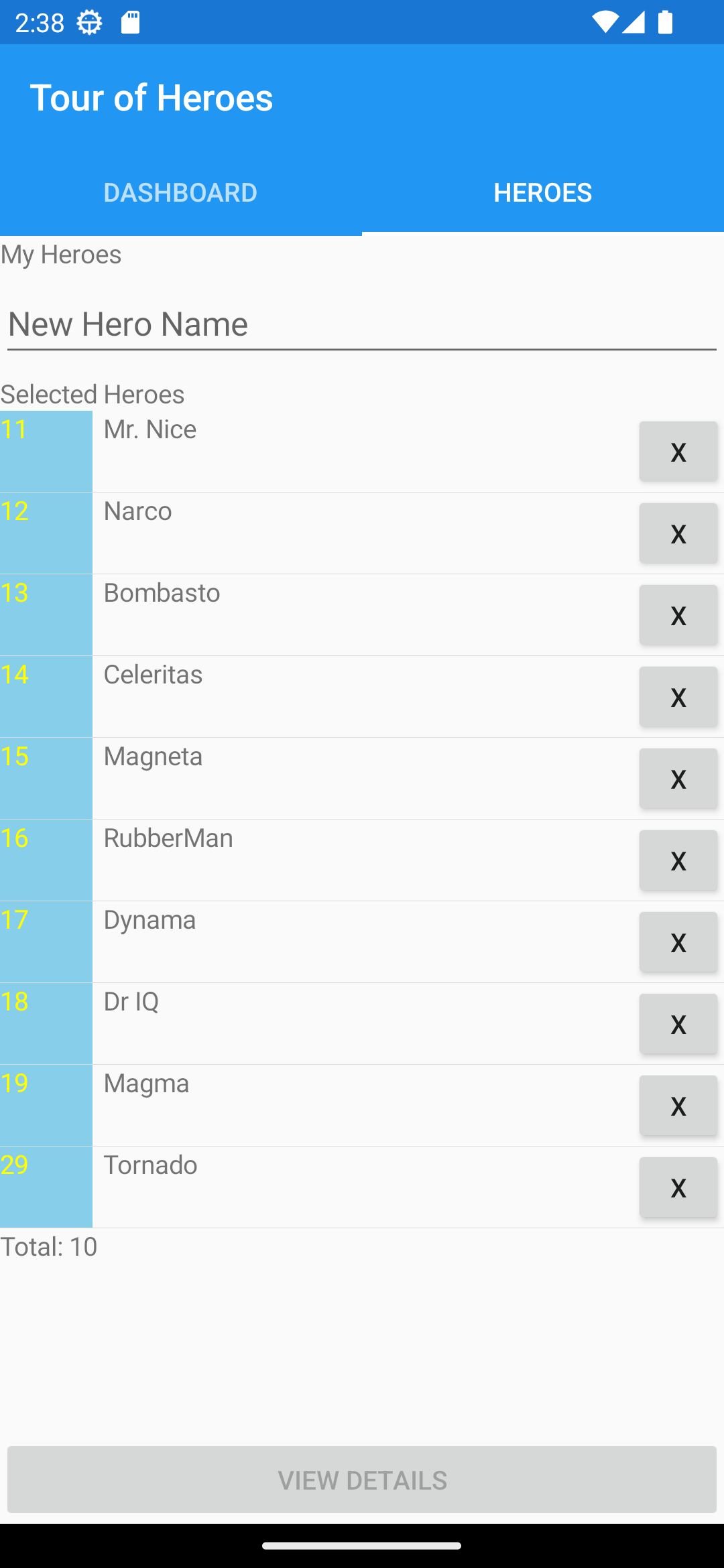
HeroesView.xaml
="1.0"="UTF-8"
<ContentView xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="Fonlow.Heroes.Views.HeroesView"
xmlns:vmNS="clr-namespace:Fonlow.Heroes.VM;
assembly=Fonlow.Heroes.ViewModels"
x:Name="heroesView"
>
<ContentView.BindingContext>
<vmNS:HeroesVM/>
</ContentView.BindingContext>
<ContentView.Content>
<StackLayout>
<Label Text="My Heroes"/>
<Entry Placeholder="New Hero Name" Completed="Entry_Completed"/>
<ListView x:Name="HeroesListView" ItemsSource="{Binding Items}"
Header="Selected Heroes" Footer="{Binding Count, StringFormat='Total: {0}'}"
SelectedItem="{Binding Selected}"
ItemSelected="HeroesListView_ItemSelected"
>
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<ViewCell>
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="50" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="50" />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Label Text="{Binding Id}" Grid.Column="0"
TextColor="Yellow" BackgroundColor="SkyBlue"/>
<Label Text="{Binding Name}" Grid.Column="1"/>
<Button x:Name="DeleteButton" Text="X" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding Source={x:Reference heroesView},
Path=BindingContext.DeleteCommand}"
CommandParameter="{Binding Id}"
/>
</Grid>
</ViewCell>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
<Label Text="{Binding Selected.Name, StringFormat='{0} is my hero'}"/>
<Button Text="View Details" Clicked="Edit_Clicked"
IsEnabled="{Binding AllowEdit}"></Button>
</StackLayout>
</ContentView.Content>
</ContentView>
The view is bound to view model Fonlow.Heroes.VM.HeroesVM, and the visual components have bindings to respective the data and the functions of the view model.
HeroesView.xaml.cs
namespace Fonlow.Heroes.Views
{
[XamlCompilation(XamlCompilationOptions.Compile)]
public partial class HeroesView : ContentView
{
public HeroesView()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
HeroesVM Model
{
get
{
return BindingContext as HeroesVM;
}
}
async void Edit_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
await Navigation.PushAsync(new HeroDetailPage(Model.Selected.Id));
}
private void HeroesListView_ItemSelected
(object sender, SelectedItemChangedEventArgs e)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(e.SelectedItem == null);
}
private async void Entry_Completed(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var text = ((Entry)sender).Text;
var hero= await HeroesFunctions.AddAsync(text);
Model.Items.Add(hero);
}
}
}
And the codes behind can access to the view model too.
Navigation
Navigation is often called routing in JavaScript SPA libraries and frameworks.
[XamlCompilation(XamlCompilationOptions.Compile)]
public partial class HeroesView : ContentView
{
public HeroesView()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
async void Edit_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
await Navigation.PushAsync(new HeroDetailPage(Model.Selected.Id));
}
Navigations are generally implemented inside codes behind.
Integration Testing
Since the frontend of "Tour of Heroes" is a fat client, significant portion of the integration testing is against the backend.
using Fonlow.Testing;
using Xunit;
namespace IntegrationTests
{
public class HeroesFixture : DefaultHttpClient
{
public HeroesFixture()
{
Api = new DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Heroes(base.HttpClient);
}
public DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Heroes Api { get; private set; }
}
[Collection(TestConstants.IisExpressAndInit)]
public partial class HeroesApiIntegration : IClassFixture<HeroesFixture>
{
public HeroesApiIntegration(HeroesFixture fixture)
{
api = fixture.Api;
}
readonly DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Heroes api;
[Fact]
public async void TestGetAsyncHeroes()
{
var array = await api.GetAsync();
Assert.NotEmpty(array);
}
[Fact]
public void TestGetHeroes()
{
var array = api.Get();
Assert.NotEmpty(array);
}
[Fact]
public void TestGetHeroNotExists()
{
DemoWebApi.Controllers.Client.Hero h = api.Get(99999);
Assert.Null(h);
}
[Fact]
public void TestPost()
{
var hero = api.Post("Abc");
Assert.Equal("Abc", hero.Name);
}
[Fact]
public void TestPostWithQuery()
{
var hero = api.PostWithQuery("Xyz");
Assert.Equal("Xyz", hero.Name);
}
}
}
It is recommended the generated client API codes stay in its own csproj project, because of benefits:
- Convenient for crafting integration testing for different layers of the frontend codes.
- Convenient for versioning of the services and the client API codes.
- Exclude the generated codes from domain specific static code analysis.
- Isolated the generated codes from your hand-crafted codes, so you may have more accurate idea about the size and the complexity of your application codes.
Points of Interest
Through WebApiClientGen, the client data models are almost 100% one to one mapping from the service data models, thus you as an application programmer will enjoy rich data type constraints provided by .NET. For example, numeric types sbyte, byte, short, ushort, int, uint, long, ulong, nint and nuint are also mapped to client data types. This is a blessing to building enterprise applications, since .NET design time and runtime can guard you.
In .NET programming, WPF, Xamarin and MAUI provide decent programmer experience through built-in MVVM architecture. In Web frontend development, particularly with SPA, the closest programmer experience that you could get is through Angular and its Reactive Forms.
Xamarin vs MAUI
Xamarin support will end on May 1, 2024 for all Xamarin SDKs including Xamarin.Forms. Android API 34 and Xcode 15 SDKs (iOS and iPadOS 17, macOS 14) will be the final versions Xamarin will target from existing Xamarin SDKs (i.e., no new APIs are planned).
The example is created through migrating an Xamarin app to MAUI.
Differences
- On Xamarin, you need to create a platform specific application project for each platform: Android or iOS or Windows. On MAUI, generally you just need one application project.
- On
Xamarin.Forms, the default namespace of XAML is "http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms". On MAUI, "http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui". Nevertheless, the upgrade wizards should be able to do the replacement for you. - On Xamarin, platform neutral libraries should be built on .NET Standard. On MAUI, it is .NET (Core). However, if you have some 3rd party components still staying with .NET Standard, MAUI can link those libraries well.
History
- 9th December, 2023: Initial version
