Introduction
In this article we will try to see how we can model tables having one to many and many to many
relationships using Entity Framework. We will try to see what Entity framework does for us behind the
scenes and how can we use Entity Framework to work efficiently with the tables having relationships.
Background
Whenever we try to modal our database as per the application requirements, we find that the tables
will have some relationship with each other. There could be scenarios where the data in one table is
related to a data in another table. In this article we will try to see such relationships between tables
and will see how we can use Entity framework in presence of such relationships and use it to work with the
database.
What is One to Many Relationship
Lets say that for a table A each row will have a relationship with
multiple rows in table B.(or it can be visualized as each row in table B will have one and only one
parent row in table A). This is achieved by having a foreign key in the table B which will refer to the
primary key of table A. This type of relationship is called as One to Many relationship.
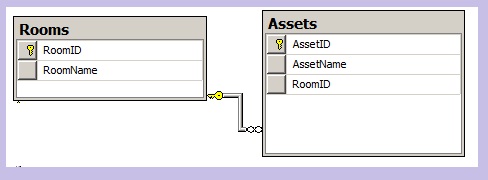
To illustrate this point lets have two simple tables in a sample database. The first table is for the
Rooms i.e. It will contain the information about various rooms in any office. The second table is for
Assets
i.e. it will contain information about the various assets of any organization. Now each asset will be kept in
a room so for each asset we need a way to associate it with a Room. This is done by creating a one to many
relationship between the tables with the Assets table containing a foreign key referring to a Room in the
Rooms table.
What is Many to Many Relationship
Now there could also be scenarios where the entities from one table refer to many entities of another table
and at the same time the entities in the other tables could also refer to many entities of the first table. This
scenario will call for having a many to many relationship between the tables. This is usually modeled by creating
another table that will have the foreign key relationship with both the tables and it will simply keep
track of the relationship between the original tables. This table itself will contain only the columns required
to model the relationship and these columns will make the composite key of this table.
Now to illustrate the above mentioned concept, Let say for the same sample database, we have multiple
projects data stored in the Project table. Now each project can choose any room from
a set of allowed rooms for their daily meetings. At the same time each Room can be requested by many projects.
To modal this relationship we need to create a table that will keep track of the Projects and Rooms. Let us
see how this can be done by adding the Projects and ProjectRooms(table which will facilitate this relationship)
to the database.

In the above table the Projects table contain the details of the projects and the ProjectRooms table keep
track of the Rooms that a project can book and vice-versa.
Using the code
Now we have the database with the relationships ready, the next thing we need to do is to see how we can
use Entity framework to use these relationships from our application. Let us start by adding an
ADO.NET entity
data model
to a website.

We will generate this model from our sample database and create the entities for it.

For now lets just proceed with these entities and we will try to understand how these entities are
generated in the following sections.
One to Many Relationship - Generating Entities
From the diagram above we can see that the entity framework was intelligent enough to understand that
there is a one to many relationship between Asset and Room. We can see that in the Navigation Properties
it has created the properties for the related entities i.e. the Room entity contain a property to get the
Assets(plural since there could be multiple Assets associated with it) and the Asset entity contain the
property to get the associated Room(singular since there could be only one Room for an Asset)
Now with these generated entities the important thing to note is that we can perform all the
(CRUD operations on the related entities even by using the properties associated with the original entity.
The following section will show how this can be done.
Performing CRUD Operations on Related tables
Now in the section let us try to perform all the CRUD operations on Asset entity by using the Room entity.
We will take the Room entity and use the Navigation property of Assets associated with it and try to perform
all the operations.
SELECT
Let us start by looking at how we can select all the Assets associated with any room. In this sample
application the Rooms data is shown in a Dropdown list so that user can select the Room for which he
want to see the Asset data. As soon as the user select any Room the associated Rooms will be fetched and shown
to the user.
using (SampleDbEntities entities = new SampleDbEntities())
{
string selectedValue = drpRooms.SelectedValue;
int roomIndex = Convert.ToInt32(selectedValue);
Room selectedRoom = entities.Rooms.SingleOrDefault<Room>(room => room.RoomID == roomIndex);
GridAssets.DataSource = selectedRoom.Assets;
GridAssets.DataBind();
}
The Assets associated with the selected Room will then be shown to the user.

Note:The above code snippet (and further coming code snippets) only shows the part
where the Assets data is fetched
using the Currently selected room. The other parts of the application that deals with showing the rooms
to the user is not shown here. So to get the complete understanding of the application please look at the
sample project.
INSERT
Now let us see how we can perform an insert operation to add an Asset using the selected Room.
using (SampleDbEntities entities = new SampleDbEntities())
{
string selectedValue = drpRooms.SelectedValue;
int roomIndex = Convert.ToInt32(selectedValue);
Room selectedRoom = entities.Rooms.SingleOrDefault<Room>(room => room.RoomID == roomIndex);
Asset asset = new Asset();
asset.AssetName = txtAddAsset.Text;
selectedRoom.Assets.Add(asset);
entities.SaveChanges();
}
The user can now simply select a Room and then add an Asset to that room.

UPDATE
Similarly we can update an Asset details by first selecting a Room, fetching the associated Assets and
then updating any Asset.
using (SampleDbEntities entities = new SampleDbEntities())
{
GridViewRow row = GridAssets.SelectedRow;
int assetIndex = Convert.ToInt32(row.Cells[1].Text);
string selectedValue = drpRooms.SelectedValue;
int roomIndex = Convert.ToInt32(selectedValue);
Room selectedRoom = entities.Rooms.SingleOrDefault<Room>(room => room.RoomID == roomIndex);
Asset asset = selectedRoom.Assets.SingleOrDefault<Asset>(ast => ast.AssetID == assetIndex);
asset.AssetName = TextBox1.Text;
asset.RoomID = Convert.ToInt32(drpNewRoom.SelectedValue);
entities.SaveChanges();
}
The important thing to note here is that the associated Room itself can be changed for any asset
and the entity framework will take care of updating all the related tables.
DELETE
Deleting an Asset can also be done by simply fetching the selected Asset for a given Room and
deleting it from the Assets collection. The entity framework will take care of deleting it from
the respective tables and updating the relationships.
using (SampleDbEntities entities = new SampleDbEntities())
{
GridViewRow row = GridAssets.SelectedRow;
int assetIndex = Convert.ToInt32(row.Cells[1].Text);
string selectedValue = drpRooms.SelectedValue;
int roomIndex = Convert.ToInt32(selectedValue);
Room selectedRoom = entities.Rooms.SingleOrDefault<Room>(room => room.RoomID == roomIndex);
Asset asset = selectedRoom.Assets.SingleOrDefault<Asset>(ast => ast.AssetID == assetIndex);
entities.DeleteObject(asset);
entities.SaveChanges();
}
For all the operation above we used the selected Room entity and then performed all the
operation on the associated Assets. The entity framework took care of updating the respective tables.
Note:All the above code snippets only shows the part
where the actual relationship is being used in code. The other parts of the application that deals with showing the rooms
to the user is not shown here. So to get the complete understanding of the application please look at the
sample project.
Many to many relationship - Generating Entities
When we generated the entities from the database there was something missing. The
ProjectRoom
table has no corresponding entity generated. Why is that? If we look carefully at the entities we
can see that in fact the Entity framework did a very smart thing. It understood that the
ProjectRooms
table was created to model many to many relationship and thus it created the many to many relationship by
creating the Navigation properties in the respective entities and thus shielding the application code
to deal with the table that was created only to model relationship.
In simple words entity framework read the ProjectRooms table and created a Project property in the
Rooms
(plural since it will have many
Project associated) and a
Rooms property in the
Project entity(plural again
to reflect that many projects are associated with each room).
Now in the section let us try to some operations on these related entities by utilizing the
navigation properties created by the entity framework
Performing Operations on Related tables
Let us create a single page where the administrator can simply change the Rooms allocated to the Projects.

Selecting the Associated Rooms based on selected Project
using (SampleDbEntities entities = new SampleDbEntities())
{
string selectedValue = drpProjects.SelectedValue;
int projectIndex = Convert.ToInt32(selectedValue);
Project selectedProject = entities.Projects.SingleOrDefault<Project>(prj => prj.ProjectID == projectIndex);
GridRooms.DataSource = selectedProject.Rooms;
GridRooms.DataBind();
}
Adding a particular Room in the Selected Project
currentPrj.Rooms.Add(entities.Rooms.Where(room => room.RoomName == item.Text).First());
Removing a particular Room from the Selected Project
currentPrj.Rooms.Remove(entities.Rooms.Where(room => room.RoomName == item.Text).First());
For all the operation above we used the selected Project entity and then performed all the
operation on the associated Rooms. The entity framework took care of updating the respective tables.
Note:All the above code snippets only shows the part where the actual relationship is being used in code. The other parts of the application that deals with showing the rooms to the user is not shown here. So to get the complete understanding of the application please look at the sample project.
So we saw how can we use Entity framework to model and use one to many and many to many relationship.
before wrapping up there is one important thing to understand and that is Lazy loading. Entity framework
by default will not load all the associated entities. e.g. when we fetch the Room data there is a Navigation
property for Assets created but these Assets data will not be loaded unless they are requested i.e. Lazy Loading.
Same is the case with many to many relationship too.
Point of interest
In this small article, I tried to explain how we can use entity framework to model and use one to many and
many to many relationships. The project itself contained a lot of code so I tried to keep the code snippets in this
article small and relevant to the topic of discussion. To understand the things better I recommend looking
at the associated sample code files. This article is written from a beginner's perspective. I hope this has
been informative.
History
- 04 February 2013: First version.
