Introduction
Shell Thumbnail Handlers (or as they're sometimes known, Shell Thumbnail Providers) are COM servers that you can write to customize the appearance of the thumbnail icons in the Windows Shell. We're familiar with many of these - for example, we expect to see a thumbnail of a jpeg file, but it turns out that making your own is quite straightforward, especially with a little help from the library SharpShell.
In this article, I'll show you how to write a Shell Thumbnail Handler for a Text File. This is a great starting point if you want to create your own shell thumbnail providers.
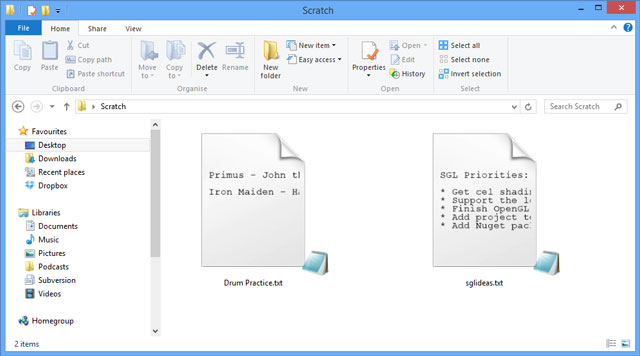
Above: A screenshot of an example Thumbnail Handler for text files. This thumbnail handler renders the first few lines of text.
The Series
This article is part of the series '.NET Shell Extensions', which includes:
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Context Menus
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Icon Handlers
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Info Tip Handlers
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Drop Handlers
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Preview Handlers
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Icon Overlay Handlers
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Thumbnail Handlers
- .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Property Sheets
Getting Started
Typically, writing Shell Extension handlers involves creating a class that implements a well defined set of COM interfaces. Now, as these COM interfaces are often not included in the .NET Framework, we have to implement them ourselves. However, the SharpShell library has all of these interfaces included - it also provides base classes for extensions, making it very straightforward to implement them. Let's get started with our text file thumbnail handler now.
Our Goal
We're going to build the extension step-by-step shortly, but first let's just see the end result, because I think it highlights very well how easy SharpShell makes it to implement these handlers. Below is the entire code for the extension - as you can see, it is very simple and straightforward! Don't worry about the details too much now, because we'll build the extension from the ground up next.
[ComVisible(true)]
[COMServerAssociation(AssociationType.FileExtension, ".txt")]
public class TxtThumbnailHandler : SharpThumbnailHandler
{
public TxtThumbnailHandler()
{
lazyThumbnailFont = new Lazy<Font>(() => new Font("Courier New", 12f));
lazyThumbnailTextBrush = new Lazy<Brush>(() => new SolidBrush(Color.Black));
}
protected override Bitmap GetThumbnailImage(uint width)
{
try
{
using(var reader = new StreamReader(SelectedItemStream))
{
var previewLines = new List<string>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
var line = reader.ReadLine();
if (line == null)
break;
previewLines.Add(line);
}
return CreateThumbnailForText(previewLines, width);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
LogError("An exception occurred opening the text file.", exception);
return null;
}
}
private Bitmap CreateThumbnailForText(IEnumerable<string> previewLines, uint width)
{
var thumbnailSize = new Size((int) width, (int) width);
var bitmap = new Bitmap(thumbnailSize.Width,
thumbnailSize.Height, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
using (var graphics = Graphics.FromImage(bitmap))
{
graphics.TextRenderingHint = TextRenderingHint.AntiAlias;
graphics.DrawImage(Properties.Resources.Page, 0, 0,
thumbnailSize.Width, thumbnailSize.Height);
var xOffset = width * 0.2f;
var yOffset = width * 0.3f ;
var yLimit = width - yOffset;
graphics.Clip = new Region(new RectangleF(xOffset, yOffset,
thumbnailSize.Width - (xOffset * 2), thumbnailSize.Height - width*.1f));
foreach (var line in previewLines)
{
graphics.DrawString(line, lazyThumbnailFont.Value,
lazyThumbnailTextBrush.Value, xOffset, yOffset);
yOffset += 14f;
if (yOffset + 14f > yLimit)
break;
}
}
return bitmap;
}
private readonly Lazy<Font> lazyThumbnailFont;
private readonly Lazy<Brush> lazyThumbnailTextBrush;
}
This is not very much work to get a working shell extension! Now let's go into the details.
Step 1: Creating the Project
First, create a new C# Class Library project.
Tip: You can use Visual Basic rather than C# - in this article, the source code is C# but the method for creating a Visual Basic Shell Extension is just the same.
In this example, we'll call the project 'TxtThumbnailHandler'. Rename the 'Class1.cs' file to 'TxtThumbnailHandler.cs'.
Now add the following references:
System.Windows.FormsSystem.Drawing
These references contain various useful bits and pieces that other parts of the SharpShell library will need, such as icons and context menus.
Tip: If you use Nuget to install SharpShell (see 'Step 2') you don't need to add these references - they'll be added automatically.
Step 2: Referencing SharpShell
We now need to add a reference to the core SharpShell library. You can do that in a few different ways:
Add Reference
Download the 'SharpShell Core Library' zip file at the top of the article and add a reference to the SharpShell.dll file.
Tip: The download on this article is correct at the time of writing - if you need the latest version, use Nuget (as described below) or get the library from sharpshell.codeplex.com.
Use Nuget
If you have Nuget installed, just do a quick search for SharpShell and install it directly - or get the package details at https://www.nuget.org/packages/SharpShell.

IMPORTANT: SharpShell is being updated regularly, I get feature requests often and implement them quickly, so I strongly recommend using the Nuget package to reference SharpShell - it's easier to automatically keep it up-to-date.
Step 3: Deriving from SharpThumbnailHandler
Now that we've set up the project, we can derive the TxtThumbnailHandler class from SharpThumbnailHandler, which is the base class for Thumbnail Handler Shell Extensions.
public class TxtThumbnailHandler : SharpThumbnailHandler
{
}
For a thumbnail handler, there is one abstract function in the base class that we must implement in the derived class.
GetThumbnailImage
protected abstract Bitmap GetThumbnailImage(uint width);
This function will be called to get the bitmap for your thumbnail. It's really important to understand the following points:
- Thumbnail handlers are initialized via streams - not file paths. This means you don't know the path of the file you are previewing, you only have its stream.
- The file stream is stored in the
SelectedItemStream property. You can use this to read the file and build the thumbnail. - Try and respect the
width variable, its the width the system wants. However, worst comes to the worst, it will scale your image if needed. - Typically, you set the
height of the bitmap to the same as the width, but it can be less, the system will respect this. However, the thumbnail cannot be higher than it is wide.
Now let's see how we'd implement this function in our example.
protected override Bitmap GetThumbnailImage(uint width)
{
try
{
using(var reader = new StreamReader(SelectedItemStream))
{
var previewLines = new List<string>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
var line = reader.ReadLine();
if (line == null)
break;
previewLines.Add(line);
}
return CreateThumbnailForText(previewLines, width);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
LogError("An exception occurred opening the text file.", exception);
return null;
}
}
Well, the first thing we do is make sure that we use an exception handler around the bulk of the logic.
Tip: SharpShell wraps all calls to abstract functions in exception handlers and logs exceptions to the windows event log if the server is compiled in debug mode. But it's a good practice to deal with exceptions ourselves if we expect them. Don't forget, you can call 'Log' or 'LogError' to write to the SharpShell Windows Application event log.
Next, we create a stream reader for the SelectedItemStream (which is the stream of the shell item we're previewing). From this, we read a few lines of text, and pass onto the function CreateThumbnailForText.
So, we also need to create the CreateThumbnailForText function:
private Bitmap CreateThumbnailForText(IEnumerable<string> previewLines, uint width)
{
var thumbnailSize = new Size((int) width, (int) width);
var bitmap = new Bitmap(thumbnailSize.Width, thumbnailSize.Height,
PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
using (var graphics = Graphics.FromImage(bitmap))
{
graphics.TextRenderingHint = TextRenderingHint.AntiAlias;
graphics.DrawImage(Properties.Resources.Page, 0, 0, thumbnailSize.Width,
thumbnailSize.Height);
var xOffset = width * 0.2f;
var yOffset = width * 0.3f ;
var yLimit = width - yOffset;
graphics.Clip = new Region(new RectangleF(xOffset, yOffset,
thumbnailSize.Width - (xOffset * 2), thumbnailSize.Height - width*.1f));
foreach (var line in previewLines)
{
graphics.DrawString(line, lazyThumbnailFont.Value,
lazyThumbnailTextBrush.Value, xOffset, yOffset);
yOffset += 14f;
if (yOffset + 14f > yLimit)
break;
}
}
return bitmap;
}
Again, we're dealing with some fairly straightforward logic here. We create a bitmap of the requested size, making sure that we use 32 bit ARGB mode (i.e., we make sure we have an alpha-channel). Then we create a graphics object to draw onto it.
Following that, we render a *.png resource file onto the bitmap (the resource file is in the sample project, it's an image of a page). Now we just render some of the text on top of the page image (making sure we keep within the bounds of the image we just drew).
That's it - we can return the bitmap and we're done! Well, actually, there are two member variables used in this function, here's their declaration:
public TxtThumbnailHandler()
{
lazyThumbnailFont = new Lazy<Font>(() => new Font("Courier New", 12f));
lazyThumbnailTextBrush = new Lazy<Brush>(() => new SolidBrush(Color.Black));
}
private readonly Lazy<Font> lazyThumbnailFont;
private readonly Lazy<Brush> lazyThumbnailTextBrush;
Step 4: Handling the COM Registration
There are just a few things left to do. First, we must add the ComVisible attribute to our class. This because our class is a COM server and must be visible to other code trying to use it.
[ComVisible(true)]
public class TxtThumbnailHandler : SharpThumbnailHandler
Next, we must give the assembly a strong name. There are ways around this requirement, but generally this is the best approach to take. To do this, right click on the project and choose 'Properties'. Then go to 'Signing'. Choose 'Sign the Assembly', specify 'New' for the key and choose a key name. You can password project the key if you want to, but it is not required:

Finally, we need to associate our extension with some of the types of shell items we want to use it for. We can do that with the COMServerAssociation attribute:
[ComVisible(true)]
[COMServerAssociation(AssociationType.FileExtension, ".txt")]
public class TxtThumbnailHandler : SharpThumbnailHandler
So what have we done here? We've told SharpShell that when registering the server, we want it to be associated with *.txt files.
You can associate with files, folders, classes, drives and more - full documentation on using the association attribute is available on the CodePlex site at COM Server Associations.
Tip: Many SharpShell servers support the 'AssociationType.ClassOfExtension' association. With this, you provide something like *.txt and the server is registered for all text files (which might be txt, text, txtfile, dat, etc.). Please be aware that Thumbnail handlers do not support the ClassOfExtension association type!
We're done! Building the project creates the TxtThumbnailHandler assembly, which can be registered as a COM server to add the extension to the system, allowing you to quickly have a preview of the contents of text files.
Debugging the Shell Extension
If you have seen any of my other articles on .NET Shell Extensions, you may recognize the 'Server Manager' tool. This is a tool in the SharpShell source code that can be used to help debug Shell Extensions.
Tip: If you want the latest version of the tools, they're available pre-built from the CodePlex site.
Open the Sever Manager tool and use File > Load Server to load the TxtThumbnailHandler.dll file. You can also drag the server into the main window. Selecting the server will show you some details on it. Select the server.

Now you can choose 'text server in test shell'. All files associated with the server are highlighted in bold, select the file and the thumbnail tab on the right - your thumbnail handler will be used to generate a thumbnail preview.

Installing and Registering the Shell Extension
You can check the 'Installing and Registering the Shell Extension' section of the .NET Shell Extensions - Shell Context Menus for details on how to install and register these extensions - the process is the same.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting shell extensions is very hard, so I've got a page I'm keeping up to date with some tips, it's on the CodePlex site at:
History
- 17th March, 2013: Initial version
