Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Analytic function optimization module in GPdotNET
- Examples of function optimizations
- C# Implementation behind GPdotNET Optimization module
Introduction

GPdotNET is an artificial intelligence tool for applying Genetic Programming and Genetic Algorithm in modeling and optimization of various engineering problems. It is .NET (Mono) application written in C# programming language which can run on both Windows and Linux based OS, or any OS which can run Mono framework. On the other hand, GPdotNET is very easy to use. Even if you have no deep knowledge of GP and GA, you can apply those methods in finding solution. The project can be used in modeling any kind of engineering process, which can be described with discrete data. It is also to be used in education while teaching students about evolutionary methods, mainly GP and GA. GPdotNET is an open source project hosted at http://gpdotnet.codeplex.com.
With the release of GPdotNET v2, it is also possible to find optimum for any analytic function regardless of independent variables. For example, you can find optimum value for an analytically defined function with 2, 5, 10 or 100 independent variables. By using classic methods, function optimization of 3 or more independent variables is very difficult and sometimes impossible. It is also very hard to find optimum value for functions which are relatively complex regardless of number of independent variables.
Because GPdotNET is based on Genetic Algorithm, we can find approximated optimum value of any function regardless of the limitation of number of independent variables, or complex definition. This blog post is going to give you a detailed and full description how to use GPdotNET to optimize function. Blog post will also cover C# implementation behind optimization process by showing representation of Chromosome with real number, as well as Fitness calculation which is based on Genetic Programming tree expression. In this blog post, several real world problem of optimization will be presented which will be solved with GPdotNET.
Analytic Function Optimization Module in GPdotNET
When GPdotNET is opened, you can choose several predefined and calculated models from various domain problems, as well as creating New model among other options. By choosing New model, new dialog box appears like picture below:
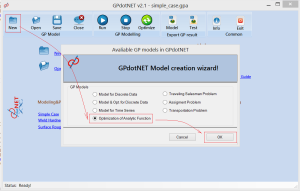
By choosing Optimization of Analytic Function (see picture above), and pressing OK button, GPdotNET prepares model for optimization and opens 3 tab pages:
- Analytic function
- Settings and
- Optimize Model
Analytic Function
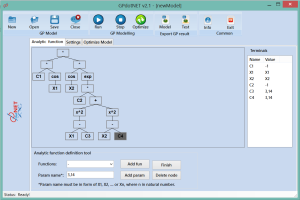
With “Analytic function” tab, you can define expression of a function. More information about how to define mathematics expression of analytic function can be found on my previous blog post.
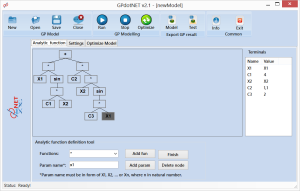
By using “Analytic definition tool” at the bottom of the page, it is possible to define analytic expression. Expression tree builder generates function in Genetic Programming Expression tree, because GPdotNET fully implements both methods. Sharing features of Genetic programming in Optimization based Genetic Algorithm is unique and it is implement only in GPdotNET.
When the process of defining function is finished, press Finish button in order to proceed with further actions. Finish button action apply all changes to Optimization Model Tab. So if you have made some changes in function definition, by pressing Finish button, changes would be send to optimization tab.
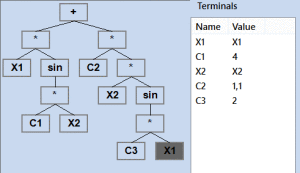
Defining expression of function is relatively simple, but it is still not a natural way for defining function, and will be changed in the future. For example in picture 2, you can see Expression tree which represents:
 .
.
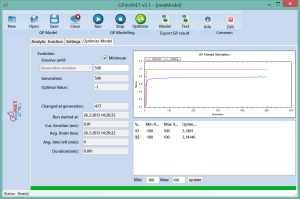
Setting GA Parameters
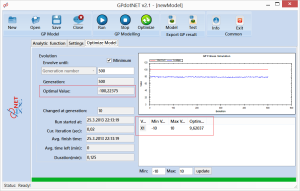
The second step in optimization is setting Genetic Algorithm parameter, which will be used in optimization process. Open the Setting tab and set the main GA parameters, like in the picture below:
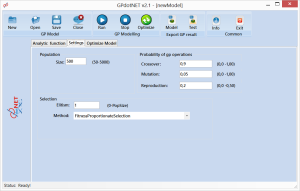
To successfully apply GA in the Optimization, it is necessary to define:
- Population size
- Probabilities of genetic operators and
- Selection methods
These parameters are general for all GA and GP models. You can find more information about parameters at http://bhrnjica.net/gpdotnet - the official site for GPdotNET.
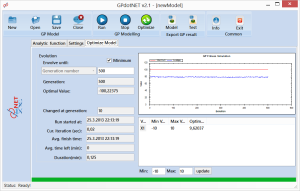
Optimize Model (Running Optimization)
When GA parameters are defined, we can start with optimization by selecting Optimization model tab. Before run, we have to define constrains for each independent variables. This is only limitation we have to define in order to start optimization. The picture below shows how to define constraints in 3 steps:
- Select row by left mouse click
- Enter min and max value in text boxes
- Press update button
Perform these 3 actions for each defined independent variable.
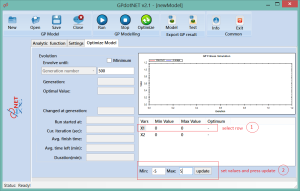
When the process of defining constraints is finished, it is time to run the calculation by pressing Optimize button, from the main toolbar (green button). During optimization process, GPdotNET is presenting a nice animation of fitness values, as well as showing current best optimal value. The picture below shows the result of optimization process. It can be seen that the optimal value for this sample is  .
.
Examples of Function Optimization
In this topic, we are going to calculate optimal value for some known functions by using GPdotNET. To prove the optimal value is correct or very close to correct, we will calculate optimization with Wolfram Alpha.
Function: x sin(4x)+1.1 x sin(2y) ; 0≤x,y≤10
GP Expression tree looks like the following picture on the left size.
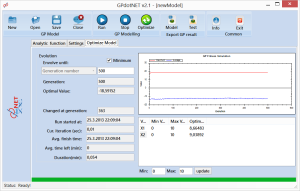
Optimal value is found (right above picture) for 0.054 min, at 363 generation of total of 500 generation. Optimal value is f(8.66,9.03)=-18.59.
Here is Wolfram Alpha calculation of the same function:
http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=min+x*sin%284*x%29%2B+1.1+*y*+sin%282+*y%29%2C+0%3Cx%3C10%2C0%3Cy%3C10
Function: (x^2+x)cos(x), -10≤x≤10
GP expression tree looks like the following picture (left size):
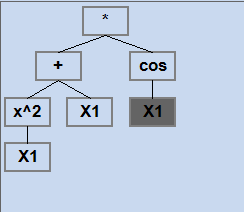
Optimal value is found for 0.125 min, at 10 generation of total of 500 generation. Optimal value is F(9.62)=-100.22.
Here is Wolfram Alpha calculation of the same function.
http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=minimum+%28x%5E2%2Bx%29*cos%28x%29+over+%5B-10%2C10%5D
Easom’s function fEaso(x1,x2)=-cos(x1)•cos(x2)•exp(-((x1-pi)^2+(x2-pi)^2)), -100<=x(i)<=100, i=1:2.
GP expression tree looks like the following picture (left size):
Optimal value is found for 0.061 min, at 477 generation of total of 500 generation. Optimal value is F(9.62)=-1, for x=y=3.14.
Function can be seen at this MatLab link.
C# Implementation behind GPdotNET Optimization Module
GPdotNET Optimization module is just a part which is incorporated in to GPdotNET Engine. Specific implementation for this module is Chromosome implementation, as well as Fitness function. Chromosome implementation is based on floating point value instead of classic binary representation. Such a Chromosome contains array of floating point values and each element array represent function independent variable. If the function contains two independent variables (x,y) chromosome implementation will contains array with two floating points. Constraints of chromosome values represent constraints we defined during settings of the optimization process. The following source code listing shows implementation of GANumChrosomome class in GPdotNET:
public class GANumChromosome: IChromosome
{
private double[] val = null;
private float fitness = float.MinValue;
}
When the chromosome is generated, array elements get values randomly between min and max value defined by function definition. Here is the source code of Generate method.
public void Generate(int param = 0)
{
if(val==null)
val = new double[functionSet.GetNumVariables()];
else if (val.Length != functionSet.GetNumVariables())
val = new double[functionSet.GetNumVariables()];
for (int i = 0; i < functionSet.GetNumVariables(); i++)
val[i] = Globals.radn.NextDouble(functionSet.GetTerminalMinValue(i),
functionSet.GetTerminalMaxValue(i));
}
Mutation is accomplished when randomly chosen array element, randomly changes its value. Here is a listing:
public void Mutate()
{
int crossoverPoint = Globals.radn.Next(functionSet.GetNumVariables());
val[crossoverPoint] = Globals.radn.NextDouble
(functionSet.GetTerminalMinValue(crossoverPoint), functionSet.GetTerminalMaxValue(crossoverPoint));
}
Crossover is little bit complicated. It is implemented based on the book Practical Genetic Algoritms see pages 56,57,48,59. Here is an implementation:
public void Crossover(IChromosome ch2)
{
GANumChromosome p = (GANumChromosome)ch2;
int crossoverPoint = Globals.radn.Next(functionSet.GetNumVariables());
double beta;
for (int i = crossoverPoint; i < functionSet.GetNumVariables(); i++)
{
beta = Globals.radn.NextDouble();
val[i] = val[i] - beta * (val[i] - p.val[i]);
p.val[i] = p.val[i] + beta * (val[i] - p.val[i]);
}
}
Fitness function for Optimization is straightforward, it evaluates each chromosome against tree expression. For minimum optimization problem, the better chromosome is lower value. For maximum, better chromosome is the chromosome with higher fitness value. Here is an implementation:
public float Evaluate(IChromosome chromosome, IFunctionSet functionSet)
{
GANumChromosome ch = chromosome as GANumChromosome;
if (ch == null)
return 0;
else
{
var term = Globals.gpterminals.SingleTrainingData;
for (int i = 0; i < ch.val.Length; i++)
term[i] = ch.val[i];
var y = functionSet.Evaluate(_funToOptimize, -1);
if (double.IsNaN(y) || double.IsInfinity(y))
y = float.NaN;
term[term.Length - 1] = y;
if (IsMinimize)
y *= -1;
return (float)y;
}
}
Summary
We have seen that Function optimization module within GPdotNET is a powerful optimization tool. It can find a pretty close solution for very complex functions regardless of the number of independent variables. Optimization module uses Genetic Algorithm method with floating point value chromosome representation described in several books about GA. It is fast, simple and can be used in education as well as in solving real problems. More information about GPdotNET can be found here.
Filed under: .NET, C#, CodeProject, GPdotNET
Tagged: AI, C#, CodeProject, Function optimization, Genetic Algorithm, Genetic Programming, GPdotNET, Optimization


