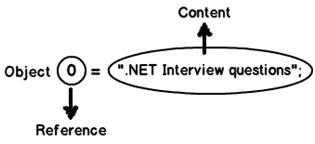
When we create any object, there are two parts to the object, one is the content and the other is reference to that content.
So for example, if you create an object as shown in the below code:
- “.NET interview questions” is the content.
- “
o” is the reference to that content.
object o = ".NET Interview questions";
“==” compares if the object references are the same while “.Equals()” compares if the contents are the same.
So if you run the below code, both “==” and “.Equals()” returns true because content as well as references are the same.

object o = ".NET Interview questions";
object o1 = o;
Console.WriteLine(o == o1);
Console.WriteLine(o.Equals(o1));
Console.ReadLine();
True
True
Now consider the below code where we have the same content but they point towards different instances. So if you run the below code, both “==” will return false and “.Equals()” will return true.

object o = ".NET Interview questions";
object o1 = new string(".NET Interview questions".ToCharArray());
Console.WriteLine(o == o1);
Console.WriteLine(o.Equals(o1));
Console.ReadLine();
False
True
When you are using string data type, it always does content comparison. In other words, you either use “.Equals()” or “==” it always does content comparison.
You can also watch the following video of the above explanation at C# interview questions and answers: Difference between "==" and ".Equals()"?

For further reading do watch the below interview preparation videos and step by step video series.
