Introduction
In the last article I talked about creating Source and Destination connection and
passing all the data from source table to destination table using C# and SSIS library.
You can find more information for it here
In this write-up, I will demonstrate data transfer between two tables on same server
based on some condition (Will demonstrate use of Conditional Split using C#), creating
package entirely through coding in step by step process.
Though it very easy to create SSIS package through GUI (you just need to set few
properties and your package is ready to execute), here I am demonstrating coding
way to create SSIS package.
You Going to Learn (Index)
You have already learned about creation of source and destination connection, DATA
Flow Task in previous article. So I just give overview of them here.
- Create two table in Database (Source and Destination)
- Initial Tasks
- Create ConditionalSplit transformation, assign source output
- Assign filter condition
- Create destination data source and assign destination connection manager
- Create Path between filtered output and destination
- Input Map filtered output column to destination input column
- Save package and execute actual code
- Screenshots
- Bonus: Get leftout data and insert in into different table!
- Screenshots
In brief, we are going to create source connection, based on table data, we will
filter records based on condition using Conditional Split transformation (i.e. we
will get all the records where person age is less than 30) and the filtered output
will be inserted into destination table.
Step by Step ;
1. Create two table in Database (Source and Destination)
Create two dummy table by name
SourceTable and
DestinationTable1,
with same fields like this:-
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[SourceTable](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [varchar](20) NULL,
[Age] [int] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
SET ANSI_PADDING OFF
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[DestinationTable1](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [varchar](20) NULL,
[Age] [int] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
Also I have filled some dummy data into the source table
| ID
| Name
| Age
|
| 1
| Alok
| 30
|
| 2
| Ashish
| 30
|
| 3
| Jasdeep
| 30
|
| 4
| Ritesh
| 35
|
| 5
| Kamlesh
| 32
|
| 6
| Hariharan
| 36
|
2. Initial Tasks
- Createte
C# window form based project. Nothing fancy - Add button on the form and include
OnClick event handler, we will do
all the programming in the event handler - Now include supporting SSIS DotNet Assemblies into the project, for that right click
on the References in Solution Explorer Browse to %Program Files%\Microsoft SQL Server\100\SDK\Assemblies
Include following files
- Microsoft.SQLServer.DTSPipelineWrap
- Microsoft.SqlServer.DTSRuntimeWrap
- Microsoft.SqlServer.ManagedDTS
- Close add assemblies dialog and save the solution.
Following code will create will create the package object
Package objPackage = new Package();
objPackage.Name = "SSISExample";
objPackage.PackageType = DTSPackageType.DTSDesigner100;
objPackage.VersionBuild = 1;
Above, we have created SSIS Package object and given its name
“SSISExample”
and defined package type as
DTSPackageType.DTSDesigner100, there are
lot of other option too,Have a look here (here we meant to say we are creating Designer
oriented package) Before we move forward, its good to have over connection
manager up and running, here I am creating two Oledb connections to same database,
this connection will be used byOleDB Source and OleDB Destination.
var connectingString =
@"Data Source=localhost;Integrated Security=SSPI;Initial Catalog=TestDB;Provider=SQLNCLI10.1;Persist Security Info=True;";
ConnectionManager oleDBConnSrc = objPackage.Connections.Add("OLEDB");
oleDBConnSrc.ConnectionString = connectingString;
oleDBConnSrc.Name = "SourceConnection";
ConnectionManager oleDBDestination = objPackage.Connections.Add("OLEDB");
oleDBDestination.ConnectionString = connectingString;
oleDBDestination.Name = "DestinationConnection";
Here I have provided connectingString contain the connection string of SQL Database
I am connecting to. One thing you should take care, the user from which you are
loggingTo Database should have write access right on it.
oleDBConnSrc
and
oleDBDestination are two ConnectionManager object. Now we come
to most important part of the package, the actual battleground where all the import/export
is done. Though it backend name is Pipeline, how on designer screen it known by
name
“Data Flow Task”, all the coding of our source and destination will
done inside this Data Flow Task, and it’s pretty simple to create.
TaskHost dataFlowTaskHost = (TaskHost)objPackage.Executables.Add("SSIS.Pipeline.2");
dataFlowTaskHost.Name = @"SSISPipeline";
dataFlowTaskHost.FailPackageOnFailure = true;
dataFlowTaskHost.FailParentOnFailure = true;
dataFlowTaskHost.DelayValidation = false;
dataFlowTaskHost.Description = @"Data Flow Task";
MainPipe dataFlowTask = dataFlowTaskHost.InnerObject as MainPipe;
From our package object we will add Pipeline object using
objPackage.Executables.Add()
method and passing
"SSIS.Pipeline.2" as object name to create,'
and provide default properties to task object. Now we get
MainPipe
of created dataFlowTaskHost, and rest of the component is attached to this
MainPipe
(dataFlowTask).
IDTSComponentMetaData100 sourceOleDB = dataFlowTask.ComponentMetaDataCollection.New();
sourceOleDB.ComponentClassID = "DTSAdapter.OLEDBSource.2";
CManagedComponentWrapper srcDesignTime = sourceOleDB.Instantiate();
srcDesignTime.ProvideComponentProperties();
sourceOleDB.Name = "TestDB DATA Source";
Here, we create object in the dataFlowTask object, and assign
ComponentClassID
= "DTSAdapter.OLEDBSource.2", to tell package that we are adding
OLEDBSource adapter.After that we instantiate it design time component, and get’s
it properties which we will assign subsequently
sourceOleDB.RuntimeConnectionCollection[0].ConnectionManagerID = oleDBConnSrc.ID;
sourceOleDB.RuntimeConnectionCollection[0].ConnectionManager =
DtsConvert.GetExtendedInterface(oleDBConnSrc);
Now assign Source DB adapter with source connection manager, above code do that
bit, now we will set property for table to open in read mode
srcDesignTime.SetComponentProperty("AccessMode", 0);
srcDesignTime.SetComponentProperty("OpenRowset", "[dbo].[SourceTable]");
srcDesignTime.AcquireConnections(null);
srcDesignTime.ReinitializeMetaData();
srcDesignTime.ReleaseConnections();
Here
AccessMode=0 denote we are opening database in view mode and
OpenRowSet
property denote the table we want to open.Till now, all the
instruction are blindly copied from previous article,From Step 3 we start with actual
article.
3. Create ConditionalSplit transformation, assign source output
Now we already have source output column, now it time to create
ConditionalSplit
transformation.
IDTSComponentMetaData100 conditionalSplit = dataFlowTask.ComponentMetaDataCollection.New();
conditionalSplit.Name = "conditionalSplit1";
conditionalSplit.ComponentClassID = "DTSTransform.ConditionalSplit.2";
CManagedComponentWrapper conditionalSplitDesignTime = conditionalSplit.Instantiate();
conditionalSplitDesignTime.ProvideComponentProperties();
conditionalSplit.InputCollection[0].ExternalMetadataColumnCollection.IsUsed = false;
conditionalSplit.InputCollection[0].HasSideEffects = false;
conditionalSplitDesignTime.AcquireConnections(null);
conditionalSplitDesignTime.ReinitializeMetaData();
conditionalSplitDesignTime.ReleaseConnections();
In above code, we are creating transformation of type
“DTSTransform.ConditionalSplit.2”,
which will instruct
SSIS to create
ConditionalSplit transformation and using
CManagedComponentWrapper
class we will instantiate its design property Now we will connect the path of Source
output column with
ConditionalSplit input column and setup the usage of each column.
IDTSPath100 pathSourceconditionalSplit = dataFlowTask.PathCollection.New();
pathSourceconditionalSplit.AttachPathAndPropagateNotifications(sourceOleDB.OutputCollection[0],conditionalSplit.InputCollection[0]);
var vInput1 = conditionalSplit.InputCollection[0].GetVirtualInput();
foreach (IDTSVirtualInputColumn100 vColumn in vInput1.VirtualInputColumnCollection)
{
conditionalSplitDesignTime.SetUsageType(conditionalSplit.InputCollection[0].ID,
vInput1, vColumn.LineageID, DTSUsageType.UT_READONLY);
}
4. Assign filter condition
Now we already have
ConditionSplit object from step3, now we will create new output collection, so that we can assign out filter condition there. We will create output collection by name “
ConditionalSplitFilerCondtion” and assign the inputcollection id to it, so that it can perform filter on incoming data
var newOutputCollection = conditionalSplit.OutputCollection.New();
newOutputCollection.Name = "ConditionalSplitFilerCondtion";
newOutputCollection.HasSideEffects = false;
newOutputCollection.ExclusionGroup = 1;
newOutputCollection.ExternalMetadataColumnCollection.IsUsed = false;
newOutputCollection.ErrorRowDisposition = DTSRowDisposition.RD_FailComponent;
newOutputCollection.TruncationRowDisposition = DTSRowDisposition.RD_FailComponent;
newOutputCollection.ErrorOrTruncationOperation = "Computation";
newOutputCollection.SynchronousInputID = conditionalSplit.InputCollection[0].ID;
Once we have output collection object, we will create custom property for “
Expression”,
“
FriendlyExpression” and “
EvalutionOrder” and assign our filter condition there
([Age] <31).
- Here
Expression and FriendlyExpression are almost same,however we have assign value
to both. Also, it contain the ID (column), we have assign ContainID=true - For
EvalutionOrder, we can have multiple conditions and each condition result in
different output. So it’s like assigning priority.
IDTSCustomProperty100 myPropCS = newOutputCollection.CustomPropertyCollection.New();
myPropCS.ContainsID = true;
myPropCS.Name = "Expression";
myPropCS.Value = "[Age] < 31";
myPropCS.ExpressionType = DTSCustomPropertyExpressionType.CPET_NOTIFY;
myPropCS = newOutputCollection.CustomPropertyCollection.New();
myPropCS.ContainsID = true;
myPropCS.Name = "FriendlyExpression";
myPropCS.Value = "[Age] < 31";
myPropCS.ExpressionType = DTSCustomPropertyExpressionType.CPET_NOTIFY;
myPropCS = newOutputCollection.CustomPropertyCollection.New();
myPropCS.Name = "EvaluationOrder";
myPropCS.Value = "0";
myPropCS.ExpressionType = DTSCustomPropertyExpressionType.CPET_NOTIFY;
5. Create Destination Data source and assign Destination Connection Manager
Code is similar to that’s of Source Adapter, except we will pass
ComponentClassID
as
"DTSAdapter.OleDbDestination",
AccessMode
= 3 and
OpenRowSet Propertly contain the Destination Table.
IDTSComponentMetaData100 destinationOleDb =
dataFlowTask.ComponentMetaDataCollection.New();
destinationOleDb.ComponentClassID = "DTSAdapter.OleDbDestination";
CManagedComponentWrapper destDesignTime = destinationOleDb.Instantiate();
destDesignTime.ProvideComponentProperties();
destinationOleDb.RuntimeConnectionCollection[0].ConnectionManagerID = oleDBDestination.ID;
destinationOleDb.RuntimeConnectionCollection[0].ConnectionManager =
DtsConvert.GetExtendedInterface(oleDBDestination);
destDesignTime.SetComponentProperty("AccessMode", 3);
destDesignTime.SetComponentProperty("OpenRowset",
"[dbo].[DestinationTable1]");
destDesignTime.AcquireConnections(null);
destDesignTime.ReinitializeMetaData();
destDesignTime.ReleaseConnections();
6. Create Path between Filtered output and Destination
Now our source and destination adapter are ready. Also Filtered output column is
ready, now we connect filtered output column with destination input column, so that
destination become aware what comings its way. For that we will add path between
them
IDTSPath100 pathDestination = dataFlowTask.PathCollection.New();
pathDestination.AttachPathAndPropagateNotifications(conditionalSplit.OutputCollection["ConditionalSplitFilerCondtion"],
destinationOleDb.InputCollection[0]);
Here
AttachPathAndPropagateNotifications method of initialize destination
input from ConditionSplit filtered output, since we know the name of incoming collection
we can used named output collection.
7. Map source output column to destination input column
IDTSInput100 destinationinput = destinationOleDb.InputCollection[0];
IDTSVirtualInput100 vdestinationinput = destinationinput.GetVirtualInput();
foreach (IDTSVirtualInputColumn100 vColumn in
vdestinationinput.VirtualInputColumnCollection)
{
IDTSInputColumn100 vCol = destDesignTime.SetUsageType(destinationinput.ID, vdestinationinput, vColumn.LineageID, DTSUsageType.UT_READWRITE);
string cinputColumnName = vColumn.Name;
var columnExist = (from item in destinationinput.ExternalMetadataColumnCollection.Cast<IDTSExternalMetadataColumn100>()
where item.Name == cinputColumnName
select item).Count();
if (columnExist > 0)
destDesignTime.MapInputColumn(destinationinput.ID, vCol.ID,
destinationinput.ExternalMetadataColumnCollection[vColumn.Name].ID);
}
Here we get destination input column, mark them available in design view, then search
for matching column name is destination table, if we found match, we map the column
using MapInputColumn method
8. Save package and Execute Package
SSIS file is actually XML file, if you rename the dtsx file to xml, you can view
all the property set by us, we will save it, and view it in the Business Intelligence
studio
Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime.Application app = new Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime.Application();
app.SaveToXml(string.Format(@"c:\workSamplePackage\SamplePackage{0}.dtsx",
DateTime.Now.ToString("hhmmss")),
objPackage, null);
objPackage.Execute();
objPackage.Dispose();
app = null;
9. ScreenShot
If we open the above created package file in Business Intelligence studio, it would
look like this :-
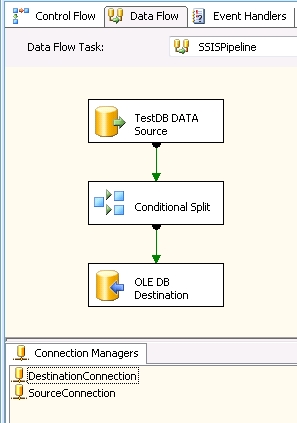
You could clearly see the two Connection manager and ConditionalSplit, which we
have added. Also source and Destination connection we have created.if you open conditional
split it will look something like this:-

now if you run this, its show something like this :-

It say 6 rows has been transferred from source database to ConditionalSplit and
OnFiltering 3 rows is transferred from ConditionalSplit to Destination Table, here
have look at the destination table

10.Bonus: Get leftout data and insert in into different table!
Since we already have output connection from the ConditionalSplit for leftout data,
now we create another table DestinationTable2, where we put all the left out data.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[DestinationTable2](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [varchar](20) NULL,
[Age] [int] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
In brief, we will create one more OleDBDestination and attach output connection
from ConditionalSplit to its input collection. We will use same code for Mapping
of input columns and saving the Package.
IDTSComponentMetaData100 destinationOleDbLO =
dataFlowTask.ComponentMetaDataCollection.New();
destinationOleDbLO.ComponentClassID = "DTSAdapter.OleDbDestination";
CManagedComponentWrapper destDesignTimeLO = destinationOleDbLO.Instantiate();
destDesignTimeLO.ProvideComponentProperties();
destinationOleDbLO.Name = "LeftOutData Destination";
destinationOleDbLO.Description = "For Left out data";
destinationOleDbLO.RuntimeConnectionCollection[0].ConnectionManagerID = oleDBDestination.ID;
destinationOleDbLO.RuntimeConnectionCollection[0].ConnectionManager =
DtsConvert.GetExtendedInterface(oleDBDestination);
destDesignTimeLO.SetComponentProperty("AccessMode", 3);
destDesignTimeLO.SetComponentProperty("OpenRowset", "[dbo].[DestinationTable2]");
destDesignTimeLO.AcquireConnections(null);
destDesignTimeLO.ReinitializeMetaData();
destDesignTimeLO.ReleaseConnections();
Only thing different here is, that we have provided name of destination oledb, as
we have already have one destination oledb connection active. Second important thing
to note is that the name and description should be filled after we instantiate the
ManagedComponentWrapper and ProvideComponentProperties method is already called;
otherwise these changes would be reflected.
Here we have created the path between
default Conditional Split and Destination. Since default occupy first position,
so we can use 0 index to identify it.
IDTSPath100 pathDestinationLO = dataFlowTask.PathCollection.New();
pathDestinationLO.AttachPathAndPropagateNotifications(conditionalSplit.OutputCollection[0],
destinationOleDbLO.InputCollection[0]);
IDTSInput100 destinationinputLO = destinationOleDbLO.InputCollection[0];
IDTSVirtualInput100 vdestinationinputLO = destinationinputLO.GetVirtualInput();
foreach (IDTSVirtualInputColumn100 vColumn in
vdestinationinputLO.VirtualInputColumnCollection)
{
IDTSInputColumn100 vCol = destDesignTimeLO.SetUsageType(destinationinputLO.ID,
vdestinationinputLO, vColumn.LineageID,
DTSUsageType.UT_READWRITE);
string cinputColumnName = vColumn.Name;
var columnExist =
(from item in
destinationinputLO.ExternalMetadataColumnCollection.Cast<IDTSExternalMetadataColumn100>()
where item.Name == cinputColumnName
select item).Count();
if (columnExist > 0)
destDesignTimeLO.MapInputColumn(destinationinputLO.ID, vCol.ID,
destinationinputLO.ExternalMetadataColumnCollection[vColumn.Name].ID);
}
you can use code mentioned in step 8 to save the package
11. ScreenShot
Now above created package file would look like this :-

You could clearly see the two Connection manager and ConditionalSplit, which we
have added. Also source and two Destination connection we have created.
now if you run this, its show something like this :-

It say 6 rows has been transferred from source database to ConditionalSplit and
OnFiltering 3 rows is transferred from ConditionalSplit to Destination Table and 3 rows are transffered to Leftout table,
here have look at the destination table, i have truncated both DestinationTable1 and DestinationTable2 before executing the package

Point of Interest
Watch out for more article on series!
